SBMDBFCMD: Submit Database File Command
A symbolic command SBMDBFCMD can be used in an OpCon job master record to support extra long command lines in a SBMJOB command, up to the maximum of 20,000 characters supported by IBM i.
To run IBM i jobs that require command lines longer than the 2,000 characters currently supported by OpCon, store the command line text in an IBM i source file member (with a record length of 112). The OpCon User Interface for IBM i job master records can then be configured under the Call information tab to Call the command SBMDBFCMD. This pseudo-command name is followed by a quoted string that names the library, file and source member where the actual command text was stored (refer to examples below). When the job is scheduled to run, the IBM i LSAM job scheduler will replace the SBMDBFCMD with the text it finds in the source member as it submits the job.
When LSAM debug logging has been turned on, both the original SBMDBFCMD text and the subsequent, replaced CMD parameter of the SBMJOB command will appear in the log file LSALOGF30. Existing LSAM messages that appear in the OpCon job schedule status display are used to report any task failures, but additional extensions to some messages are provided to help diagnose specific errors that might occur when using the SBMDBFCMD command.
Configure OpCon Job Master in the EM
As shown in the following example, the new SBMDBFCMD is typed into the CALL field under the Call information tab of an IBM i job master record of the OpCon EM.
IBM i Job Master Details - SBMDBFCMD Example
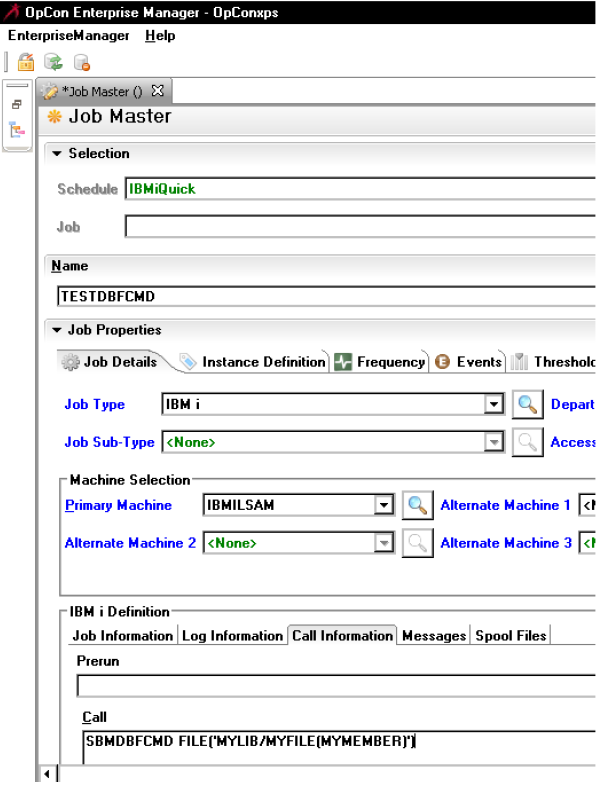
SBMDBFCMD syntax
There are various forms of the SBMDBFCMD that are acceptable. The basic requirements are that the command name appears first in the Call field and that it be followed by a string enclosed in single quotes that names the library/file (source_member) where the command line text will be found. This command is not case sensitive -- it will be translated to all upper case by the IBM i LSAM job scheduler, according to IBM i standards.
There is actually a SBMDBFCMD that has been added to the IBM i LSAM software, but it serves only as a token for controlling user authority to this feature and as a model of how the command syntax should appear in the OpCon User Interface Call field.
Following are some variations on the command syntax that are all acceptable:
SBMDBFCMD FILE('MYLIB/MYFILE(MYMEMBER)')
sbmdbfcmd file('mylib/myfile(mymember)')
SBMDBFCMD ('MYLIB/MYFILE(MYMEMBER)')
sbmdbfcmd 'mylib/myfile(mymember)'
It is possible to experiment with this command and its syntax from a command entry line within the LSAM menu system. A documentary version of an actual IBM i command exists for this purpose. Type in the command with a string and press <Enter>, or type just the command and press <F4> to enter the quoted string into a prompted FILE parameter field and then press <Enter>. An example of using the documentary command is offered below.
The string that names the library/file (source_member) MUST be enclosed in single quotes. The SBMDBFCMD substitution processing will fail if the quotes are missing. Double quotes are not supported.
The IBM i SBMDBFCMD Command
An actual IBM i command called SBMDBFCMD is included in the IBM i LSAM software. This command itself is not used by the IBM i LSAM job scheduler to perform the actual substitution of the command line text in the SBMJOB command prepared by the job scheduler. Its primary purpose is to control authorization of users to this new function.
However, the command itself is useful for the purpose of experimenting with the syntax of the SBMDBFCMD Call string, as noted above. Users authorized to the command can use it from the command line within the LSAM menu system. Type the same command syntax as documented above and then press <Enter> to help assure that the library/file (member) string is correctly formatted. It is also possible to prompt the command using <F4>, type in the quoted library/file (member) string, and then press <F3> to exit the prompt (or, press <Enter> to view the display and then quit the display). After using this command from command entry, the resulting command string that can be retrieved from command entry could be copied from the green screen workstation and pasted into the OpCon User Interface job master Call field.
When <Enter> is pressed after typing or prompting the SBMDBFCMD and its FILE string parameter, the following display is presented. This display panel is a simple form of documentation for the function.
SBMDBFCMD Pseudo-Command Display
Submit command from DB file (SBMDBFCMD)
Type choices, press Enter.
Source file name . . . . . . . . mylib/myfile(mymember)
Bottom
F3=Exit F4=Prompt F5=Refresh F12=Cancel F13=How to use this display
F24=More keys
Notice in the example above that the File string does not show the single quotes from this display panel. However, if the string is entered without using the single quotes, the command will fail to execute.
SBMDBFCMD Command Security
The actual IBM i command called SBMDBFCMD was created primarily as a way to control who has access to this new feature. Without careful security controls, the ability to run commands from an IBM i source file could create security loopholes.
There are at least two methods by which security should be controlled in order to prevent any security loopholes when using the SBMDBFCMD convention in OpCon jobs for IBM i:
- Secure the command object itself to prevent unauthorized users from access to this feature.
- Secure the IBM i source files where command line entries will be stored.
Both of these strategies depend on IBM i object authority. The first and most important line of defense is the authority to use the actual IBM i command object, SBMDBFCMD, which is stored in the LSAM's program object libraries. (The default names of those libraries. When subsequent LSAM release upgrades are installed, this command will be relocated to the base programs library, default name SMAPGM. Other library names may be used when multiple LSAM environments have been created.)
The IBM i LSAM job scheduler will perform an explicit inquiry to assure that the user named in the OpCon job master has EXECUTE authority (a subset of USE general authority, for program objects) to the command object. Even though the command object is not used during the preparation of the substitute command line, this authority check by the LSAM will prevent an unauthorized user from gaining access to this feature. Thus, unauthorized users cannot set up an OpCon job to execute any command line they wish from any source file member they choose. Only IBM i user profiles that have been authorized to *EXECUTE the command SBMDBFCMD will be allowed to run command lines that were stored in IBM i source files.
Coupled with the command object authority, carefully secure the IBM i source file where the command text for OpCon jobs will be stored. Only authorized users should be allowed to view and/or update the special source files created for this purpose. Do not use source files that are generally available to the public; otherwise the source members are exposed to potential changes that could be made by unauthorized users. In other words, if unauthorized users are allowed to update the source file, they could change the command line text of a scheduled job so that it runs some unauthorized process. The unauthorized process could be a malicious program.
SBMDBFCMD Command Source File
SMA recommends creating a unique and well-secured IBM i source physical file to store command line text. The source file must use a source file record length of 112, which will yield a source data field size of 100 bytes, in order to be compatible with the IBM i job scheduler process that reads source members to substitute the command line text.
To create an appropriate source file use the following IBM i command:
CRTSRCPF FILE(MYLIB/MYFILE) RCDLEN(112) AUT(\*EXCLUDE)
The AUT parameter in the example above is not a required value. However, SMA recommends revoking public authority to any source file that will be used to store command line text in order to help secure the system.
The command line source file for SBMDBFCMD can be located in any library. However, the library chosen may become part of a strategy for restricting access to this command line source file. Please review the discussion on command authority above.
Any meaningful source member name may be used. The source file member may be created and edited using any of the tools that IBM i will support, including Websphere development studio or the simple SEU source file editor from a green screen workstation. It is also possible to write a conversion program that would export long command lines from some software application and insert them automatically into command line source file members.
The potential for automating conversions makes the SBMDBFCMD command line strategy attractive for any job command lines that are very long. Even though OpCon will support up to 2,000 characters in the Call field of the job master, it might be helpful to use the SBMDBFCMD convention for command lines whenever long command lines are required instead of having to type hundreds of characters into the OpCon command line field.