Customization Process
Prior to attempting to start and test the z/OS LSAM, various system, security, JES and LSAM configuration requirements must be fulfilled for your installation.
LSAM Options and JCL Procedures
Before continuing on, review the LSAM JCL Procedure in your system PROCLIB and the XPSPRMxx definition in INSTLIB. The following is a typical LSAM JCL procedure.
//OPCON01 PROC LOGEN='(-0)'
//*
//*******************************************************************
//* *
//* *
//*******************************************************************
//OPCONXPS EXEC PGM=XPSSUPV,REGION=0M,TIME=1440
//*STEPLIB DD DSN=OPCON.V210003.LINKLIB,DISP=SHR
//*
//*******************************************************************
//* XPSPARMS default is to use XPSMRM00
//* Optionally, specify an explicit XPSPARM member
//* If XPSPARMS is omitted, OpCon will use the system parmlib
//XPSPARMS DD DSN=OPCON.V210003.INSTLIB,DISP=SHR
//*******************************************************************
//*
//XPSJCL DD DSN=OPCON.V210003.INSTLIB,DISP=SHR <= FOR IVP
//TEMPJCL DD DSN=OPCON.V210003.TEMPJCL,DISP=SHR <= FOR IVP
//SYSEXEC DD DSN=OPCON.V210003.INSTLIB,DISP=SHR <= FOR IVP
//RECLOG DD DSN=OPCON.V210003.ZOS1.LSAMLOG&LOGEN,DISP=OLD
During Installation Verification Procedures (IVP), several DD statements are used to access IVP Jobs and REXX procedures. These DD statements are clearly marked ("IVP ONLY") and may be removed or modified when XPS390 is ready for production.
The XPSPARMS DD statement, if present, specifies the library containing the XPSPARM members. If it is not present, the agent will read the parms from the system PARMLIB. If the XPSPARMS DD statement includes a member name, that member will be used to initialize the agent configuration. If the statement or the member is not included, that agent will default to member XPSPRM00. (An agent started with a non-default XPSID will use member XPSPRM0x, where x is the XPSID.)
Next, you should review your Installation LSAM Run Time options in XPSPRM00.
The following is an example of a typical LSAM Parmlib XPSPRMxx member implementation:
If you are planning to use the step restart capability of SMA Opcon, you should change the RESTART parameter to RESTART=Y and review the defaults assigned to the parameters in the Restart section.
XPS021I - CURRENT STORED PARMS FOR ZOS1
MACHINEID=ZOS1 OPCON/XPS MACHINE NAME
PORT=3100 LSAM PORT
JORSPORT=+1 (3101) JORS PORT
PROCESS=30 PROCESS COUNT
USEJMR=NO JMR USER FIELD
INTV=00.00.20 WAKE UP INTERVAL
SPINOFF=Y Spin Log Each Night
JCLDD=XPSJCL DEFAULT JCL LIBRARY
OVERRIDE-DD=TEMPJCL DEFAULT OVERRIDE LIBRARY
JOBRC=MAXRC RC for failure check
QUEUED-IS-RUNNING=N Show queued jobs as running
FORCE-SYS-AFF=N Force System affinity
RESTART=Y Step restart active?
RESTORE-COND-CODES=Y Return codes for skipped steps
GDGOPT=A GDG option
DUPDSNACT=N Dup Dataset Action
RESDSNACT=S Dup Dataset Action on restart
XPRLIST=00 Dataset exclude list
AUTOSTEP=Y Automatic step selection
SYSPLEX=N LSAM on SYSPLEX?
TCPIP= TCP/IP Task Name
SMF15=K SMF Type 15 Disposition
SMF64=K SMF Type 64 Disposition
TRACLASS= Dynamic Tracking Classes
TRACLAS8= Dynamic Tracking Class Mask
TRACMASK= Dynamic Tracking Mask
TRACSCHD= Dynamic Tracking Schedule
USERID= Default USER
XPSDYNAM=IEESYSAS Dynamic task proc
MSGCLASS=A REXX SYSOUT CLASS
MLWTO=Y Multi-line WTO Triggers
SPFAUDIT=N Log ISPF User Chgs
LOG-UNIT= LSAMLOG allocation unit
LOG-VOLUME= LSAMLOG allocation volume
TRIGGER-RETPD=45 Trigger retention days
RECOVERY=PROMPT Recovery Option
SUBSYS=JES2 JES Subsystem
TRACE=N Trace Status
SETQUES=(JOB=120;MSG=3840;DSN=480;WTO=480;EVT=240)
All characters after the first space on the line and all lines that begin with an asterisk ('*') are considered comments. For backward compatibility, commas may be used for continuation, but, beginning with V4.01, they are optional between lines. As before, multiple parameters on a single line must be separated by commas.
Syntax
[@systemname ]parameter=[option]{,parameter=[option]}...
The optional @systemname prefix can be used to filter the input records. Any records beginning with an @systemname will be skipped, unless systemname matches the current system name, as defined in the static system symbol SYSNAME.
Run-time Parameters
| Parameter | Default | Details |
|---|---|---|
| ADOPT | Blank | Determines if the LSAM can become the primary LSAM authority during failover.
|
| EVENTPASS | 20 asterisks **** | Sets the event control password to be used for all external messages to the SAM, regardless of Userid. |
| Force-SYS-AFF | No | If Yes, the jobs will be submitted with affinity for submitting system.
|
| INTV | 00.00.20 | This value determines the maximum delay for external resource recognition (batch triggers, Pre-run Data Triggers, and so forth). A valid value must use the following syntax: hh.mm.ss. |
| JCLDD | XPSJCL | Sets the default DDNAME in the LSAM JCL Proc. It is used to locate JCL for any batch Job Start request from the SAM that does NOT have a DDNAME assigned. |
| LSAM | N | In a Sysplex environment, determines which LSAM is running as the primary LSAM.
|
| LOG-UNIT | Blank | Specifies a generic or esoteric name for a group of DASD devices for LSAMLOG allocation. 1 - 8 character name or blank. |
| LOG-VOLUME | Blank | Specifies a specific volume serial for LSAMLOG allocation. 1 - 6 character name or blank. |
| MACHINEID | * | Defines the name of the LSAM.
|
| MSGCLASS | A | Defines the MSGCLASS allocated to dynamic REXX tasks. The class is one character, A through Z or 0 through 9, and must be a valid output class specified at JES initialization. |
| MLWTO | YES | Determines if the LSAM should process minor lines of multi-line console messages. Valid values are YES and NO. |
| Override-DD | Blank | The name of a DD statement in the LSAM JCL to use as the default override DD, if one is not specified in the job definition. A blank value means that there will be no default. |
| XPSDYNAM | IEESYSAS | Identifies the cataloged procedure to use for dynamic tasks (Rexx and command). |
| PORT | 3100 | The port for the TCPIP HOST IP address. This value must be a valid TCP/IP port number and cannot be used by any other process. |
| JORSPORT | +1 | Port number for JORS, expressed as an offset from PORT or as an absolute port number. This is always stored as a relative offset, so it will change when PORT changes. JORSPORT=0 or +0 will disable the JORS server. |
| PROCESS | 030 | A number defining the maximum number of jobs the LSAM can simultaneously manage (1 – 512). This value is used during the LSAM's first initialization after an IPL to determine CSA usage. Refer to CSA Storage Allocation on CSA Storage Allocation to determine the impact of this parameter.After initialization, the maximum process count allowed will be limited by the initial allocation. PROCESS=0 can be used to prevent jobs from starting, similar to setting the machine to LIMITED. PROCESS=RESET will cause the LSAM to reset the process count to the value it had before PROCESS=0 was used. |
| RECOVERY | PROMPT | Determines the LSAM's behavior during recovery from a system failure. Upon reactivation, the LSAM searches the RECLOG for jobs that were executing at the time the system went down. If any are found, the operator may be prompted or the LSAM automatically sends termination messages to the SMANetCom. If prompted, the operator may select to ignore executing job terminations (for instance, if they were already terminated by the Scheduler and restarts are waiting). Valid values are PROMPT and AUTO. |
| RESTORE-COND-CODES | YES | The z/OS LSAM restores the return codes for skipped steps so that conditional processing in restarted jobs will proceed as if the full job was run. Setting this parameter to "NO" will leave the skipped steps in "not run" status. |
| SETQUES | Automatic calculations using PROCESS= | Overrides default queue limits. Refer to CSA Storage Allocation prior to setting these values. Extended CSA (ECSA) is consumed in proportion to these values. Valid queues include: (JOB=nnn [;MSG=nnn][;DSN=nnn] [;WTO=nnn][;EVT=nnn]) Note: These must be defined in the XPSPARMxx since they are not dynamic. Using the MODIFY command to change these values has no effect on the LSAM. |
| SPINOFF | Y | Determines if the LSAM automatically spins off a new LSAM LOG dataset each day at midnight. If set to N, a SPINLOG command (F lsamname,SPINLOG) should be scheduled each day to ensure the log does not exceed allocated space. If set to Y, the LSAM automatically manages the log. Valid values are Y (yes) and N (no). |
| SYSPLEX | N | Determines if the LSAM is running in a SYSPLEX environment. If Y, the XPSPLEX task is automatically started when the LSAM is started. Valid values are Y (yes) and N (no). |
| XPSPLEX | XPSPLEX | The name of the started task PROC for SYSPLEX communication. |
| SMF15 | K | Determines if the dataset trigger records are deleted or left in the SMF Data Sets. SMF must be recording record type 15 for JOB, STC and TSU SUBSYS for all dataset triggers. If D, the XPS390 SMF exit XPSU83 deletes the records after DSN trigger filtering. |
| SMF64 | K | Determines if the VSAM trigger records are deleted or left in the SMF Data Sets. SMF must be recording record type 64 for JOB, STC and TSU SUBSYS for all VSAM triggers. If D, the XPS390 SMF exit XPSU83 deletes the records after DSN trigger filtering. |
| SPFAUDIT | N | Determines if the LSAM issues XPS083I messages for ISPF Users that update or delete DSN Table entries. Valid values are Y (yes) and N (no). |
| TCPIP | Blank | Identifies the Host TCPIP application name on the z/OS machine. |
| TRACLASS | Blank | Defines an optional list of one to eight JES single character execution classes to monitor for external job tracking (e.g., TRACLASS=PR places all jobs in JES execution classes 'P' and 'R' in the current SAM schedule and will track them to completion). Note: The continuation character C, in column 72 of the job card, bypasses this option. |
| TRACLAS8 | Blank | When using 2-8 character job classes, this parameter will be used as a mask to match the class. The syntax is the same as used with TRACMASK. |
| TRACMASK | Blank | Defines a job name mask of eight characters (e.g., PROD****) for SMA Opcon external job tracking. Note: The continuation character C, in column 72 of the job card, bypasses this option. |
| TRACSCHD | AdHoc | Defines the default schedule name for external job tracking. |
| TRACE | N | Defines the trace level for the LSAM. Valid values include:
|
| TRIGGER_RETPD | 45 | Sets the number of days to retain unreferenced "passive" triggers.
|
| USEJMR | NO | Controls the use of the JMRUSEID field by the LSAM tracking exits. If YES, the LSAM uses the entire field. If NO, the LSAM does not use the field at all. A number from 0 – 63 can be used to specify the offset within the field that is used for a single bit flag. Note: USEJMR=NO is normally required to coexist with TWS. Enabling USEJMR may improve performance in some cases. |
| USERID | Blank | Defines the installation default RACF USER= to be used on any batch Job Start request from the SAM that does NOT already have an owning User assigned. This value is inserted in the USER= parameter of the JOB Card at submission. Specify NONE to disable |
| RUNMODE | Prod | When set to RUNMODE=TEST, batch jobs will be submitted with TYPRUN=SCAN and success or failure will be determined by the JCL scanner. |
| JOBRC | MAXRC | Determines how the job failure criteria are applied. Valid values are MAXRC, LASTRC, or JCL.
|
| QUEUED-IS-RUNNING | NO | By default, z/OS batch jobs show "Pre-run" status after submission to JES, then switch to "Running" when they start execution. Setting this parameter to "Yes" will make the job show that it is running as soon as it is submitted. This may effect automation triggers based on job status changes. |
| RESTART | NO | If YES, Restart support is active. If NO, the Restart support is not active. Note: If a user requests a Step restart when this support is disabled, the job status is set to 'Prerun failed' with message 'Restart not Active.' |
| GDGOPT | ABSOLUTE | Method used to reset the base generation for Generation Data Groups during a restart. Valid values include:
|
| DUPDSNACT | NONE | Action to take when a dataset to be created is already cataloged during a normal run. Valid values include:
|
| RESDSNACT | SCRATCH | Action to take when a dataset to be created is already cataloged during a restart. Valid values include:
|
| AUTOSTEP | YES | Automatic restart step assignment. Valid values include:
|
| XPRLIST | Blank | Two-character suffix for the XPRLSTxx member to load as the dataset cleanup filter table. Refer to Dataset Cleanup Filter Table for filter entry syntax, wildcard patterns, and operator commands. |
The XPSPRMxx member is used only at IPL time. Changes to Parameters after IPL should be done using the operator command [F lsamname,parm=option]. If the parameter change is to be permanent, it should also be made to XPSPRMxx so it is not rolled back at the next IPL. :::
Security Setup
Security for batch job submission and file permissions is provided through the Security Access Facility (SAF) that is used by all z/OS Security Packages. Every security package has the ability to "authorize" a submitter for a given job. Once you have set up your base installation security definitions for OPCON01 (STARTED CLASS), you must provide for job submission and OMVS communications or define the LSAM as a "Trusted User." In the figure below, standard RACF commands are used to define the lsamname LSAM as a surrogate submitter for Batch Jobs. This needs to be done FOR EACH SECURITY ID in production batch JCL. The OPCON LSAM inserts or replace an existing USER= in each JCL using the "Security ID" field of the SAM Schedule detail or the USERID= default in XPSPRMxx.
Example RACF Commands Allowing LSAM Submission of Batch Jobs
Define resource profiles in the SURROGAT class for each user who needs to allow others to be surrogate users.
RDEFINE SURROGAT execution-userid.SUBMIT UACC(NONE) OWNER(execution-userid)Specify that another user can act as a surrogate.
PE execution-userid.SUBMIT CLASS(SURROGAT) ID(OPCON01) ACCESS(READ)Validate that an execution-userid can be submitted by OPCON01.
RLIST SURROGAT execution-userid.SUBMIT AUTHUSERActivate the SURROGAT class.
SETROPTS RACLIST(SURROGAT) REFRESH
In addition to SURROGAT authority, your LSAM task also needs an OMVS Segment defined. This is a particular requirement of RACF that authorizes the LSAM to use the z/OS TCP/IP API. All that is needed is a unique UID value. No other OMVS options are required. The RACF Command is ALU OPCON01 OMVS(UID(nnnnnnnn)) where nnnnnnnn is any number from 0 to 2147483647.
OpCon Userid in the z/OS LSAM
The JCL editor in the z/OS Job Details allows the OpCon user to save JCL to the mainframe file system. To enforce z/OS security, the OpCon userid is mapped to a z/OS userid for access testing. There are two basic strategies for defining the userids depending on the versions of the z/OS LSAM and OpCon user interface.
Matching Userids
The matching userids strategy works with all versions of the LSAM and user interface. If the OpCon userid matches a z/OS userid exactly, then the mapping is trivial.
Partial Matching without Windows Domain
If the OpCon userid is longer than eight characters, the first eight characters will be used as the z/OS userid.
Partial Matching with Windows Domain
If the OpCon userid is in the form domain\user, as when Windows authentication is used, the results vary with releases:
LSAM versions below 15.07
In this case, the first eight characters of the userid, including the domain and separator, will be used, which will normally not be useful.
For example, if the OpCon user is "CORP\johndoe", the z/OS userid will be "CORP\JOH".
LSAM versions 15.07 and higher and UI versions below 16
In this case, only the characters following the separator will be used, but the UI only sends eight characters, so the result may not be correct.
For example, if the OpCon user is "CORP\johndoe", the z/OS userid will be "JOH".
LSAM versions 15.07 and higher and UI versions 16 or higher
In this case, only the first eight characters following the separator will be used.
For example, if the OpCon user is "CORP\johndoe", the z/OS userid will be "JOHNDOE".
Distributed Identity Mapping
Starting with version 16 of the z/OS LSAM, an attempt will be made to map the OpCon userid to a z/OS userid through distributed identity mapping, with registry name "OPCON", using a standard SAF call. If the identity mapping fails, then the z/OS userid will be obtained using the previous rules.
Distributed identity mapping is defined and enabled by the z/OS security administrator.
Defining Distributed Userids to the z/OS Security System
RACF
Distributed identity mapping in RACF is enabled by activating and RACLISTing the IDIDMAP class:
SETROPTS CLASSACT(IDIDMAP) RACLIST(IDIDMAP)
Ids are mapped with the RACMAP command:
RACMAP id(ZOSUSER) map userdidfilter(name('OpConUser')) registry(name('OPCON'))
RACMAP id(SYSPROG) map userdidfilter(name('ocadm')) registry(name('OPCON'))
Full Windows userids, with domain, are supported:
RACMAP id(ZOSUSER) map userdidfilter(name('Domain\OpConUser')) registry(name('OPCON'))
Wildcard mapping can be used to assign a default:
RACMAP id(ZOSUSER) map userdidfilter(name('*')) registry(name('OPCON'))
Changes to the identity mapping will become active when the IDIDMAP class is refreshed:
SETROPTS RACLIST(IDIDMAP) REFRESH
For more details, consult the Distributed Identity Filters section in the z/OS Security Server RACF Security Administrator's Guide.
CA-Top Secret and CA-ACF2
The CA-Top Secret and CA-ACF2 products also support distributed identity mapping.
Consult the appropriate product manuals for details.
CA-Top Secret Requirements
In the following figure, we use standard TOP SECRET commands to define the necessary permissions to OPCON datasets, and then add lsamname to the Started Task Class. We then define the lsamname LSAM as a surrogate submitter for Batch Jobs. We then give lsamname an OMVS segment descriptor allowing native IP communication.
Top Secret Definition Examples
TSS PER(lsamname) DSN(OPCON.) ACC(ALL)
TSS ADD(STC) PROC(lsamname) ACID(lsamname)
TSS ADD(OPER) SURROGAT(lsamname.SUBMIT)
TSS ADD(lsamname) UID(0) GROUP(OMVSGRP) DFLTGRP(OMVSGRP) -OMVSPGM(/bin/sh)
SMF Parameters
You must provide the following SMF environment for the z/OS LSAM.
- For dataset resource monitoring, ensure that the following SMF Types are being recorded:
- Type 14 & 15 Records for non-VSAM datasets.
- Type 64 records for VSAM datasets.
- Type 61 and 65 records to detect catalog actions.
- Exits IEFU83, IEFU84, IEFUSI, and IEFUJV must be active for the batch (default or JESx) and STC subsystems; and IEFU83 must be active for the TSO subsystem.
Batch jobs run in a JES subsystem. If the JES subsystem is separately defined in the SMF parameters, all of the batch exits must be active (IEFUJV, IEFUSI, IEFU83 and IEFU84).
SUBSYS(JES2,EXITS(IEFUJV,IEFUSI,IEFU83,IEFU84))
SMF Minimum Customization Requirements
ACTIVE /* ACTIVE SMF RECORDING */
DSNAME (SYS1.MAN1,
SYS1.MAN2,
SYS1.MAN3)
NOPROMPT /* DO NOT PROMPT OPERATOR */
REC (PERM) /* TYPE 17 PERM RECORDS ONLY */
MAXDORM (3000) /* WRITE IDLE BUFFER AFTER 30 MIN */
STATUS (010000) /* WRITE SMF STATS AFTER 1 HOUR */
JWT (0400) /* 522 AFTER 30 MINUTES */
SID (SYS1)
LISTDSN /* LIST DATA SET STATUS AT IPL */
SYS (NOTYPE (16:19,66:69) , EXITS (IEFU83, IEFU84, IEFUJV, IEFUSI),
NOINTERVAL, NODETAIL)
The above example shows type 61.64, 65, 30, 14 and 15 records being recorded. The type 14 and 15 SMF records can become voluminous and many shops do not wish to record them on a daily basis due to the impact on SMF Data Set (MAN1, MAN2, and so forth) capacities. Thus, you may request that XPS390 not allow the writing of these records to the SMF data sets. Use the SMF15= and SMF64= options in XPSPRMnn to control whether or not these SMF records are actually written to the SMF data sets.
The IKJTSOxx Parmlib member must be updated to reflect that the XPSPAUTH program is an Authorized TSO Command. Optionally, add the XPSCOMM program so it can be called as a TSO command.
TSO Parameters
AUTHCMD NAMES( +
… +
XPSPAUTH /* OPCON */ +
XPSCOMM /* OPCON */ +
…
A senior MVS Systems Programmer should have the authority to implement the IKJTSOxx Parmlib member changes using the TSO PARMLIB command.
The SMA Opcon ISPMLIB and ISPPLIB libraries are required in the TSO Logon Proc for each user of SMA Opcon that also has a TSO logon, or a CLIST or EXEC can be written using LIBDEF to provide access.
Library Authorization
Most all of the SMA Opcon LINKLIB library contents require APF authorization.
In the default configuration, the following members require LINKLST access:
- XPSASCRE
- XPSEVENT
If your installation standards do not allow the addition of libraries to APF list or LINKLST concatenations, you have to copy the contents of the SMA Opcon LINKLIB to defined libraries with the proper APF and LINKLST characteristics (e.g., SYS1.LINKLIB). However, your installation and maintenance procedures for XPS390 need to reflect the changes so subsequent maintenance releases applies properly. SMA supplies an IEBCOPY job in highlevel.midlevel.INSTLIB(LINKLST) to perform a link list copy.
With some customization, it is possible to run the z/OS agent without updating the link list. This can also be used to support multiple versions of the agent for testing.
- Modify all JCL that references agent programs with the appropriate JOBLIB or STEPLIB.
- On a SYSPLEX, set the XPSPLEX parm to use an XPSPLEX PROC with a STEPLIB matching the agent.
- Make a copy of the IEESYSAS system procedure, adding a STEPLIB for the agent library.
- Modify the XPSDYNAM entry in XPSPRMxx to identify the copy.
- Load XPSASCRE into LPA.
- SETPROG LPA,ADD,MODNAME=XPSASCRE,DSNAME=OPCON.V210004.LINKLIB
JCL and REXX Library
JCL for batch jobs and programs for dynamic REXX jobs must be located in libraries allocated to the LSAM. To add, remove, or change a library allocation: change the LSAM JCL, then stop and restart the LSAM using the RESET=C command or using a STOP and a START command. There are no restrictions on the DD names or library concatenations.
A library with a DD name beginning with 'TEMP' is eligible for temporary member processing, and must be writable by the LSAM task.
Sysplex Configuration
Configuration the z/OS LSAM and PSAM Environment
When scheduling more than one machine in a z/OS environment two options are available. Each option has its own unique benefits and uses.
- Scheduling Sysplex LSAMs or JES MAS from a master system. This option requires a Sysplex configuration. Only one machine that participates in scheduling is defined to SAM ("Machine ID") and the LSAM on that system manages the routing of all JCL, regardless of the Sysplex member on which it eventually executes. This is the recommended option for Clients utilizing a single Sysplex or JES2 Multi-Access Spool (MAS) configuration. In this configuration, one system is chosen as the master (Initiates an "LSAM" Gateway) and all others in the participating Sysplex are partition/Plex clients (Initiates a "PSAM" Monitor) whether or not they share spool or DASD volumes. The primary LSAM is defined in the SAM "Machine ID" option.
- Scheduling independent machines. This option requires that every machine that participates in scheduling be defined to SAM and the LSAM on each system submits all JCL for that system. This is the recommended option for Clients utilizing separate JES2 environments. In this configuration, every system is considered a master (Initiates an "LSAM") and the system on which JCL submission and execution occurs is defined in the SAM "Machine ID" option.
Both the above options can be used in the same Data Center. This is especially helpful in outsourcing or consolidated service environments. Dependencies among and between LSAMs and PSAMs in the data center aresupported by SMA Opcon SAM engine. Whether or not the LSAM main task runs as an LSAM or a Sysplex PSAM is controlled by runtime parameters on z/OS (LSAM=Y/N and SYSPLEX=Y/N). The default is to run as an LSAM master with Sysplex support turned off (SYSPLEX=N).
The "Machine ID" value is up to 8 characters, system name defined in the IEASYMxx member or any other suitable reference. Refer to the SAM installation procedure for details on adding the z/OS machine name to the HOST definition parameters on the SMA Opcon Scheduler platform.
Scheduling Independent Machines
When you are not running a Sysplex, the selection of a configuration for XPS390 is easy. It must be set up as individual machines with separate Machine IDs within SAM. Each LSAM has its own copy of JCL libraries, PROCLIBS, and so on. SAM handles all routing of work. You should not use NJE to send scheduled production jobs from one system to another in a local network -- use SMA Opcon to submit the job where it runs.
Configuration #1 - Independent LPAR Scheduling
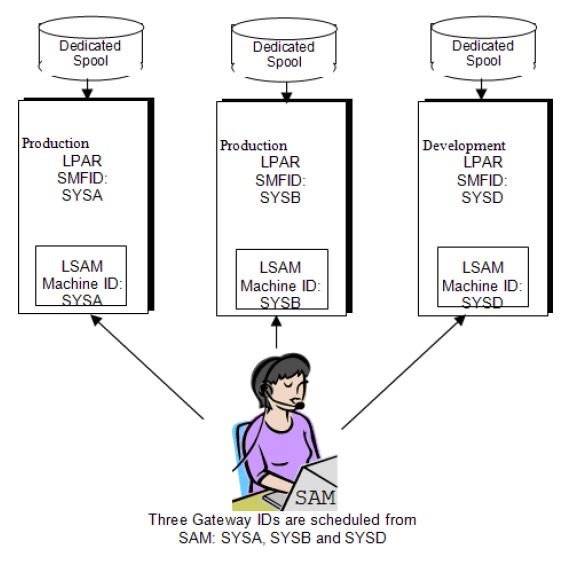
Each machine has all SMF Exits Installed, XPSPRMxx defined, etc. -- just as with a single machine installation. Each XPSPRMxx has the LSAM=Y and SYSPLEX=N options set. The SMA Opcon SAM HOST file, DNS, or SMA Opcon machine definitions contains the IP addresses for all three machines and their respective MACHINEIDs.
Scheduling a SYSPLEX
When configuring a Sysplex, the selection of a configuration for XPS390 depends upon your installation "Operational Profile".
Configuration #2 - Sysplex Scheduling
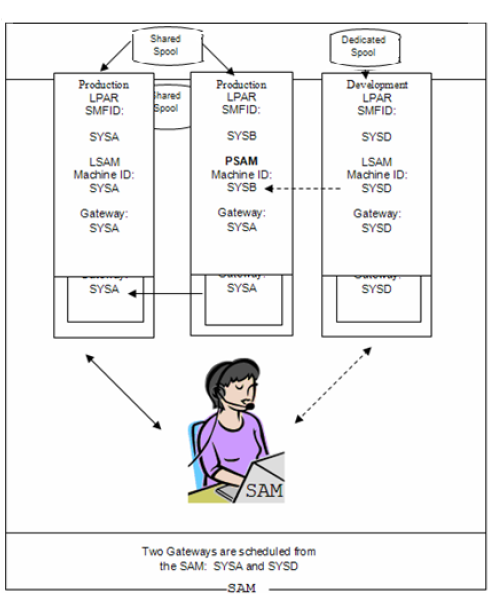
When Scheduling a Multi-Access Spool (MAS) environment, the machine that submits the batch JCL, the machine that converts the JCL (loads the Procs defined in the job), and the machine that runs the resulting job may all be different. JES2 MAS and JES3 Local processor support is only available in a Sysplex environment (any CF level). In the above example, we define the Primary LSAM as a "Gateway" for both SYSA and SYSB in the SAM Server. The Machine ID is the target system for the jobs within the MAS/Sysplex and the Gateway is always the Primary LSAM machine.
For this configuration option to function properly, the environment must employ a Sysplex (at any CF level). Workload Manager does not interfere with schedule operation when a Master Gateway is used. Also, you may use JES2 /*ROUTE XEQ records in JCL to route jobs to machines within the MAS and XPS390 tracks each job with no problem. However, we suggest using the Machine-id feature in SMA Opcon to route work to dedicated machines.
Within JES, the Converter/Interpreter routine is charged with Proc access and the resolution of symbolic variables. Since the JES2 Proc is most often located in SYS1.PROCLIB -- AND -- since some shops have a different SYS1.PROCLIB for each machine, the concatenation of PROC00 may not support JCL submission and conversion on every machine in the JES2 MAS. For this reason, we recommend one LSAM as the "Master" in a MAS environment. On JES3 all CI processing is done on the Global processor so the primary LSAM may be on any machine.
Each machine in the production Sysplex must have all the SMA Opcon Exits Installed, XPSPRMxx defined, etc. -- just as with a single machine installation. The Master Gateway's XPSPRMxx has the LSAM=Y option set. All other LSAMs in the Sysplex have the LSAM=N option set, or all machines may share the XPSPRMxx file, with LSAM=system identifying the primary system. The SMA Opcon Server HOST file, DNS, or SMA Opcon machine definition contains the IP addresses for the Primary LSAM gateway name only. Access to other systems in the Sysplex is handled entirely by the Gateway LSAM via XCF.
As illustrated in the figure under Scheduling a SYSPLEX, you may "mix-and-match" Gateways and independent LSAMs in the SAM configuration, as well as JES2 and JES3 systems. However, if all the LSAMs are members of the same Sysplex, then XPS390 can use the Sysplex message facility to route job submission from a single gateway, even across two or more JES2 MAS environments. In that case, all LSAMs, except the master gateway(s) must be running a PSAM environment.
OpCon Requirements for Sysplex Operation
Each LSAM in the SMA Opcon Sysplex must have unique OPCONxx Proc (where 'xx' is a unique suffix such as 01 -- 99) characteristics and matching XPSPRMxx member. There are several key elements to managing Sysplex scheduling via SMA Opcon.
- The OPCONxx Proc must be unique or must have unique overrides for each system. It is distributed as separate Procs, assuming a common Proclib. The RECLOG DD is a generation data set that requires a unique name on each machine. This can be done most easily with system symbols. The XPSPRMxx member should be unique for each system, or contain system specific overrides.
- Having only one Proc name (e.g., OPCONXPS) is a desirable feature for scalability. The RACF or SAF definitions only need to be done once (in a shared security DB).
- The primary LSAM Machine ID and IP address must be defined to the SAM HOSTS file, DNS, or SMA Opcon Machine definition. All other Machine-Ids in the Sysplex are defined through the Gateway machine id.
- The XPSPLEX started task must be running at all times on all machines that schedule production jobs. The XPSPLEX task cannot be shutdown while the OPCONxx task is running.
Operating Sysplex Sub-Groups
If your shop has one large Sysplex housing multiple logical production images, you need a Gateway primary LSAM for each production image (or group). Each group may contain any number of PSAMs. The primary LSAM and all PSAMs in each group must share a common XPSID, and each group must have a different XPSID.