ACS Webservices Operation
Once the sma.acs.ACSWebservices plugin has been registered with the OpCon system, it will be possible to perform agent and task definitions. All definitions can only be performed using Solution Manager.
Defining ACS Webservices Batch Users
The ACS Webservices task types BASICTOKEN and OPCONTOKEN uses opCon Batch users to define the user information for these task types. Before creating these task types, ensure that the appropriate Batch Users are created.
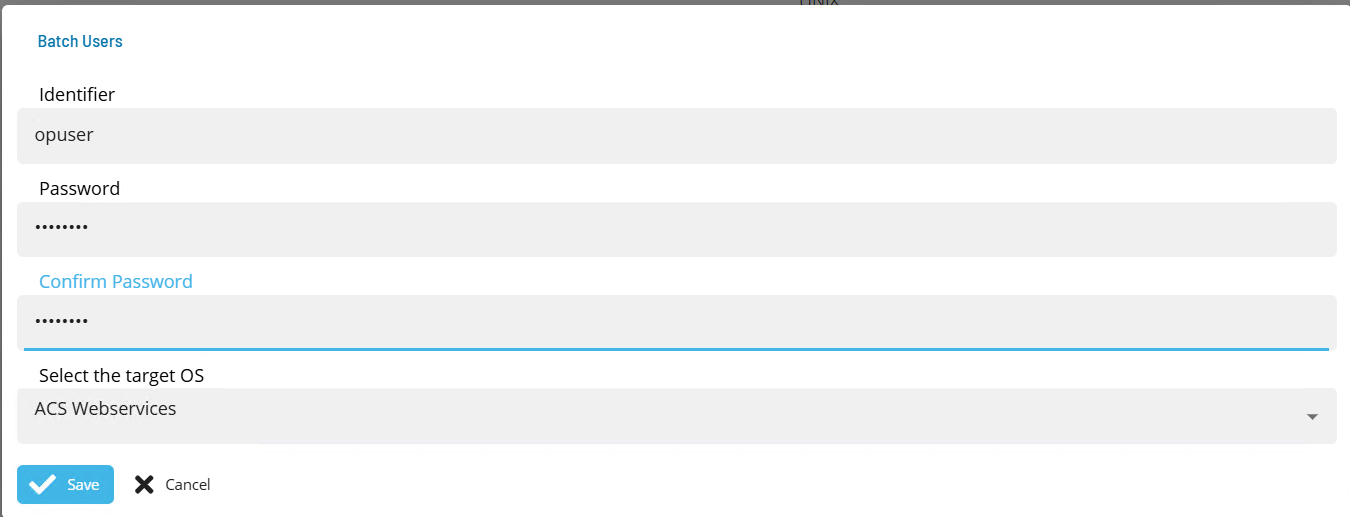
- Open Solution Manager.
- From the Home page select Library
- From the Security Menu select Batch Users.
- Select +Add to add a new Batch User.
- Select ACS Webservices from the Select the target OS drop-down list.
- Enter the User name that will be used to create the token in the Identifier field.
- Enter the password of the defined API User in the Password and Confirm fields.
- Select Save.
Defining ACS Webservices connection
The Agent definition is defined by adding a new ACSWebservices Agent definition using Solution Manager. Items defined in red are required values.
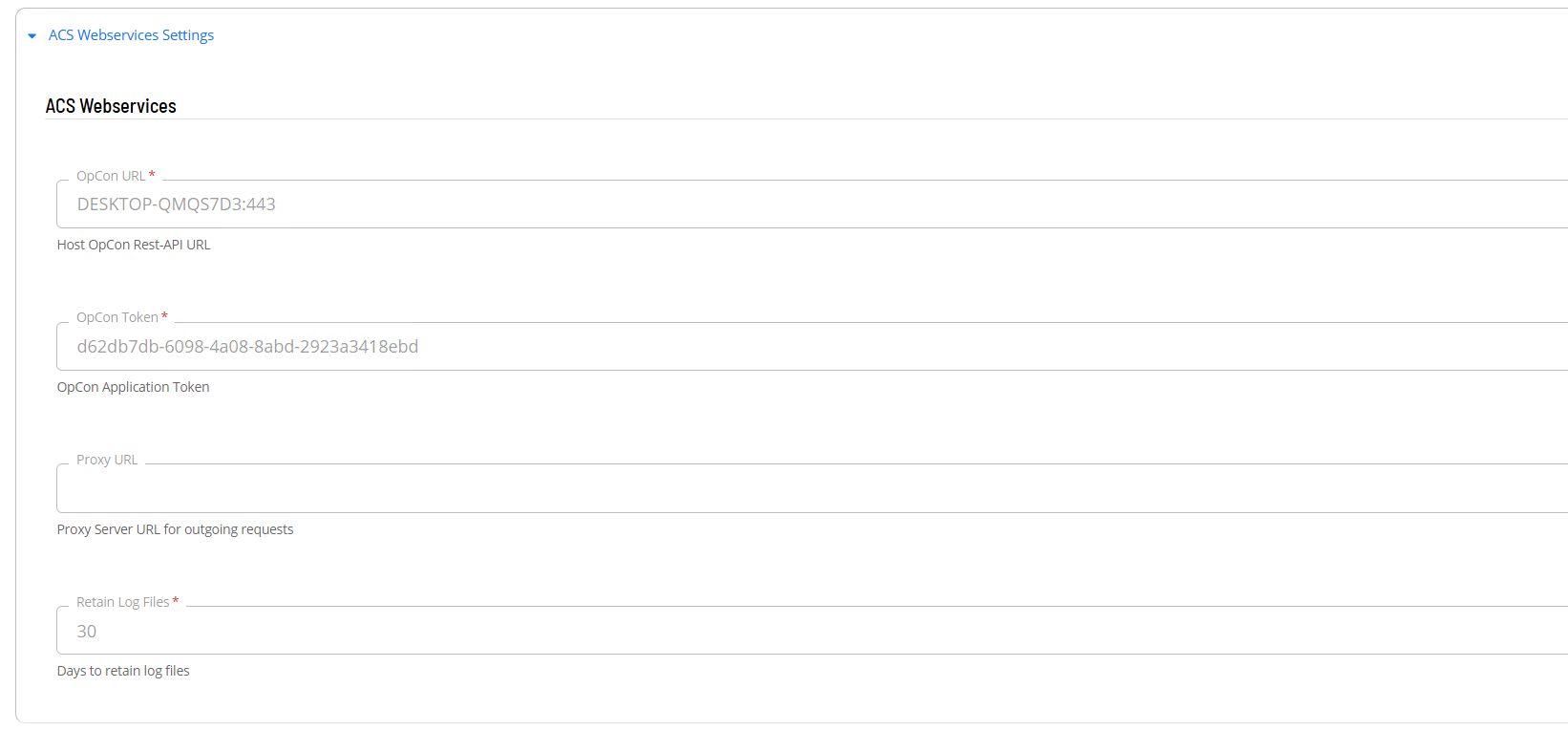
- Open Solution Manager.
- From the Home page select Library
- From the Administration Menu select Agents.
- Select +Add to add a new agent definition.
- Fill in the agent details
- Insert a unique name for the connection.
- Select ACS Webservices from the Type drop-down list.
- Select General Settings
- In the NetCom field enter \<Default> or a Netcom or Relay name.
- Select ACS Webservices Settings
- In the OpCon URL field enter the full url for the associated OpCon Rest-API server.
- In the OpCon Token field enter a valid OpCon application token that will be used to authenticate internal OpCon Rest-API requests.
- In the Proxy Url field enter the full url of the Proxy Server if required when submitting url requests outside the organization.
- Save the definition changes.
- Select Communications Settings
- ensure that Requires XML Escape Sequences:User-Defined field is set to True. Save the definition changes.
- Start the connection by selecting the Change Communication Status button and selecting Enable Full Comm..
Defining tasks
The ACS Webservices Connection supports the following task types:
| TaskType | Description |
|---|---|
| BASICTOKEN | Create a basic token. |
| OPCONTOKEN | Retrieve an OpCon token from an opCon system. |
| OAUTH2TOKEN | Retrieve an OAuth2 Token. |
| GET | Perform a GET HTTP request. |
| POST | Perform a POST HTTP request. |
| PUT | Perform a PUT HTTP request. |
| PATCH | Perform a PATCH HTTP request. |
| DELETE | Perform a DELETE HTTP request. |
Before defining a GET, POST, PUT, PATCH or DELETE task, the authentication method must be defined to create the authorization token required by these tasks.
The generated authentication tasks (BASICTOKEN, OPCONTOKEN or OAUTH2TOKEN) store the generated token as schedule instance properties of the schedule. These properties are then available for subsequent tasks in the schedule.
Data is passed between tasks using schedule instance properties. The ACS environment calls these properties 'scoped properties' and the list is automatically passed to each task. When using this mechanism, it is only required to define these values in the Response Variables field.
BASICTOKEN Task
The BASICTOKEN task is used to set a basic token as a schedule instance property so it can be used to provide authentication by subsequent tasks. The function allows the selection of a ACS Webservices Batch User to provide the base64 encoded authentication string.
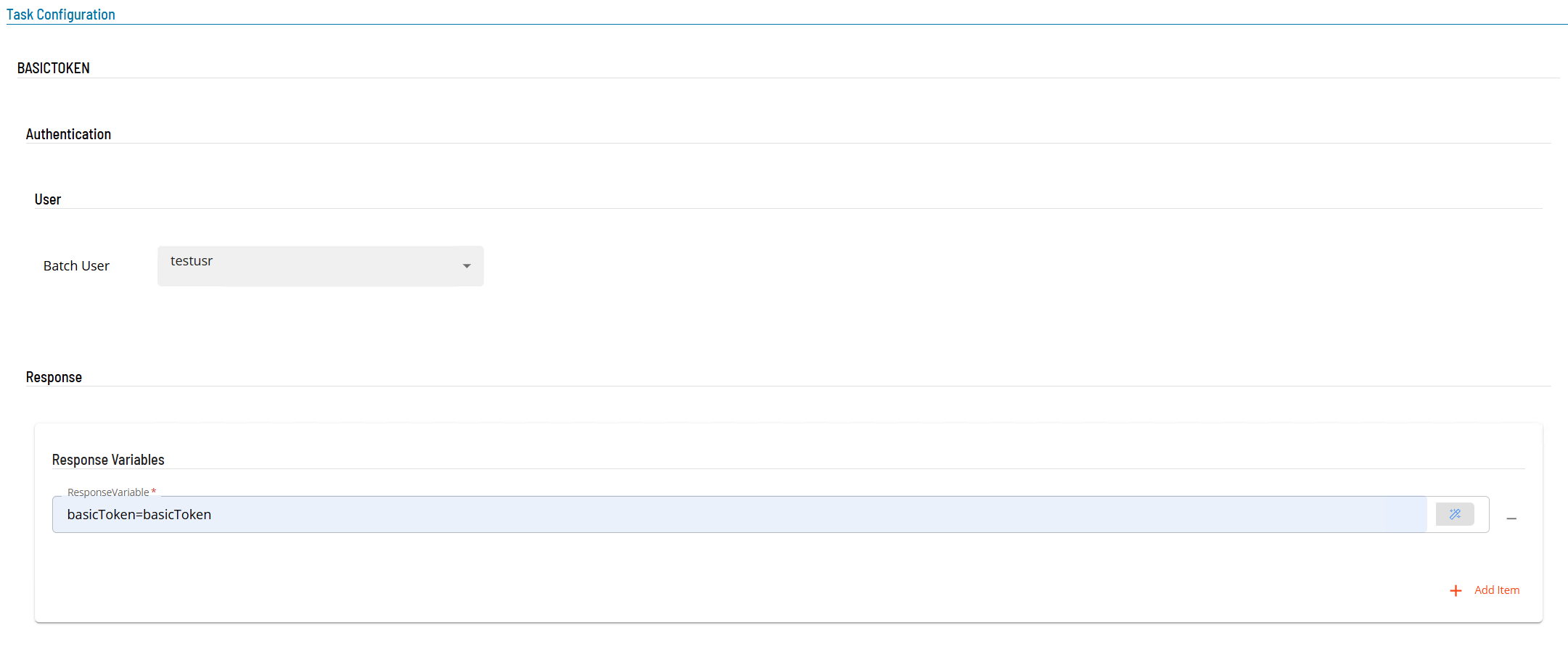
- Open Solution Manager.
- From the Home page select Library
- From the Administration Menu select Master Jobs.
- Select +Add to add a new master job definition.
- Fill in the task details.
- Select the Schedule name from the drop-down list.
- In the Name field enter a unique name for the task within the schedule.
- Select ACS Webservices from the Job Type drop-down list.
- Select BASICTOKEN from the Task Type drop-down list.
Enter details for Task Type BASICTOKEN.
- Select the Task Details button.
- In the Integration Selection section, select the primary integration which is an ACS Webservices connection previously defined.
- In the Authentication section
- select a Batch User from the drop-down list.
- In the Response Variable section
- define the variable that will contain the token. The format is name=value where the name part will be the schedule instance property name, the value part is ignored.
OPCONTOKEN Task
The OPCONTOKEN task is used to set an OpCon token as a schedule instance property so it can be used to provide authentication by subsequent tasks. The function allows the selection of a ACS Webservices Batch User to provide the OpCon encoded authentication string.
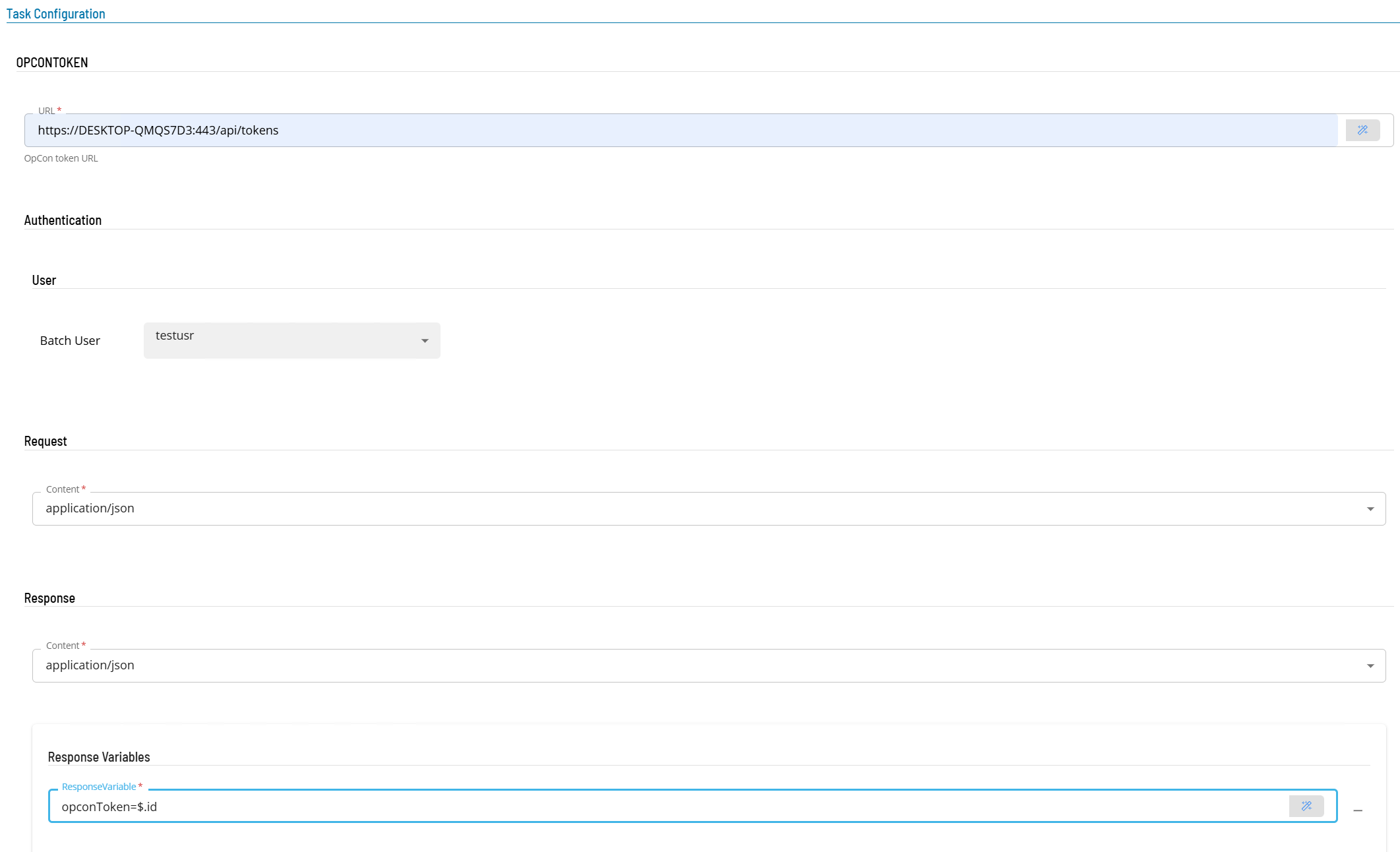
- Open Solution Manager.
- From the Home page select Library
- From the Administration Menu select Master Jobs.
- Select +Add to add a new master job definition.
- Fill in the task details.
- Select the Schedule name from the drop-down list.
- In the Name field enter a unique name for the task within the schedule.
- Select ACS Webservices from the Job Type drop-down list.
- Select OPCONTOKEN from the Task Type drop-down list.
Enter details for Task Type OPCONTOKEN.
- Select the Task Details button.
- In the Integration Selection section, select the primary integration which is an ACS Webservices connection previously defined.
- In the Authentication section
- In the URL field enter the full address of the end point (i.e. https://server:port/api/tokens).
- Select a Batch User from the drop-down list.
- In the Request section enter the following information
- Select the Content from the drop-down list (application/json).
- In the Response section
- Select the Content from the drop-down list (application/json).
- In Response Variables define a variable to contain data extracted from the returned JSON data. The extracted data will be stored as a schedule instance property in the schedule making the extracted information available to subsequent tasks. The format of the field definition is variable-name=jsonpath (i.e. opconToken=$.id) where
- variable-name is the name of the variable that will be created as a schedule instance property.
- jsonpath is the attribute value to extract from the returned JSON data using JPath notation - enter $.id
OAUTH2TOKEN Task
TheOAUTH2TOKEN task is used to set an OAuth2 token as a schedule instance property so it can be used to provide authentication by subsequent tasks.
- Open Solution Manager.
- From the Home page select Library
- From the Administration Menu select Master Jobs.
- Select +Add to add a new master job definition.
- Fill in the task details.
- Select the Schedule name from the drop-down list.
- In the Name field enter a unique name for the task within the schedule.
- Select ACS Webservices from the Job Type drop-down list.
- Select OAUTH2TOKEN from the Task Type drop-down list.
Enter details for Task Type OAUTH2TOKEN.
- Select the Task Details button.
- In the Integration Selection section, select the primary integration which is an ACS Webservices connection previously defined.
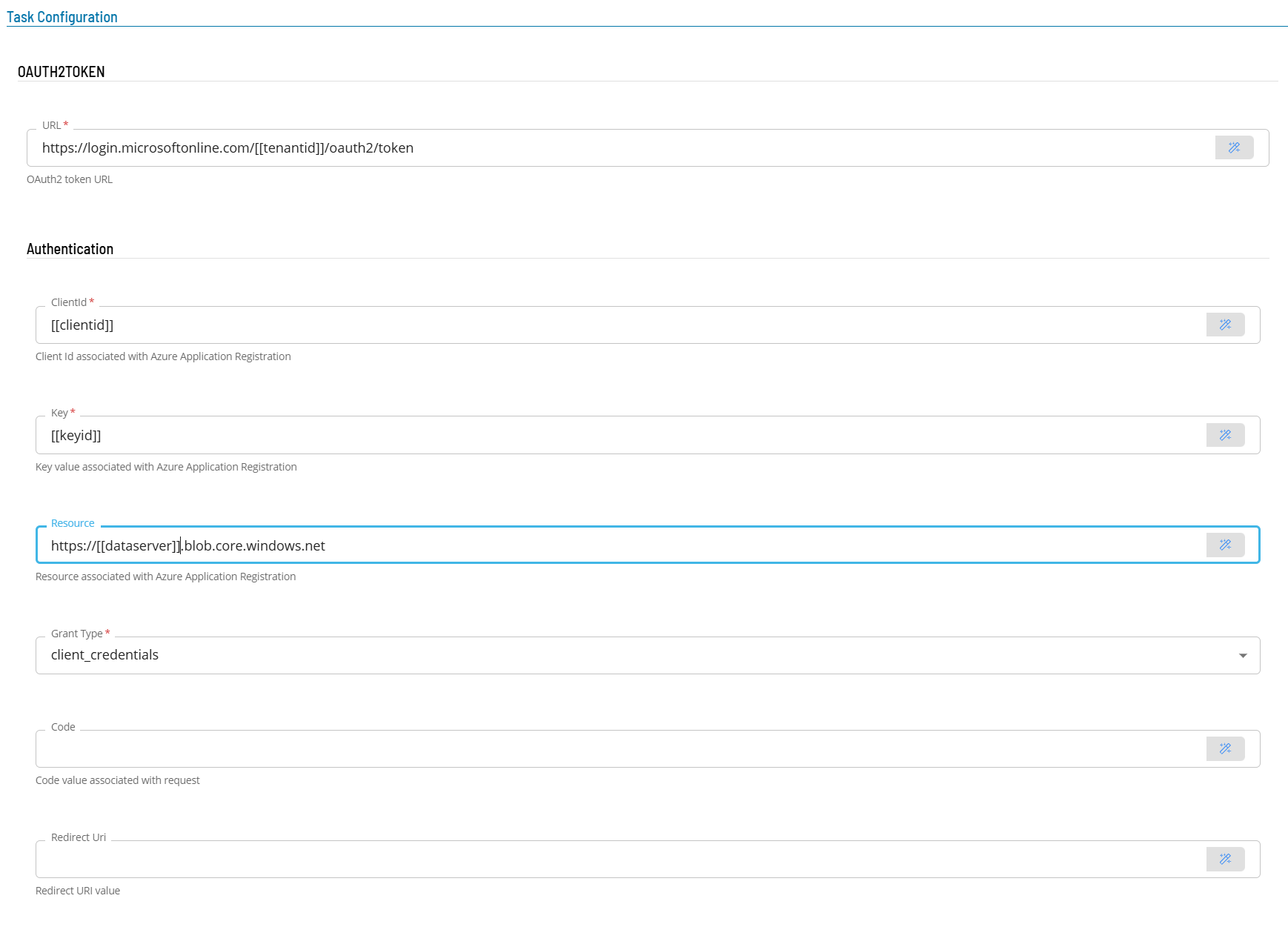
- In the URL field enter the full address of the end point using global properties (i.e. https://login.microsoftonline.com/[[tenantid]]/oauth2/token).
- In the Authentication section
- In the ClientId field enter the provided client id (use a global or an encrypted global property to safe guard the client id).
- In the KeyId field enter the provided key (use a global or an encrypted global property to safe guard the key).
- In the Resource field enter the resource the authentication request is for. The example shows an Azure Storage authentication request (https://[[dataserver]].blob.storage.net).
- In the Grant Type field select client_credentials from the drop-down list.
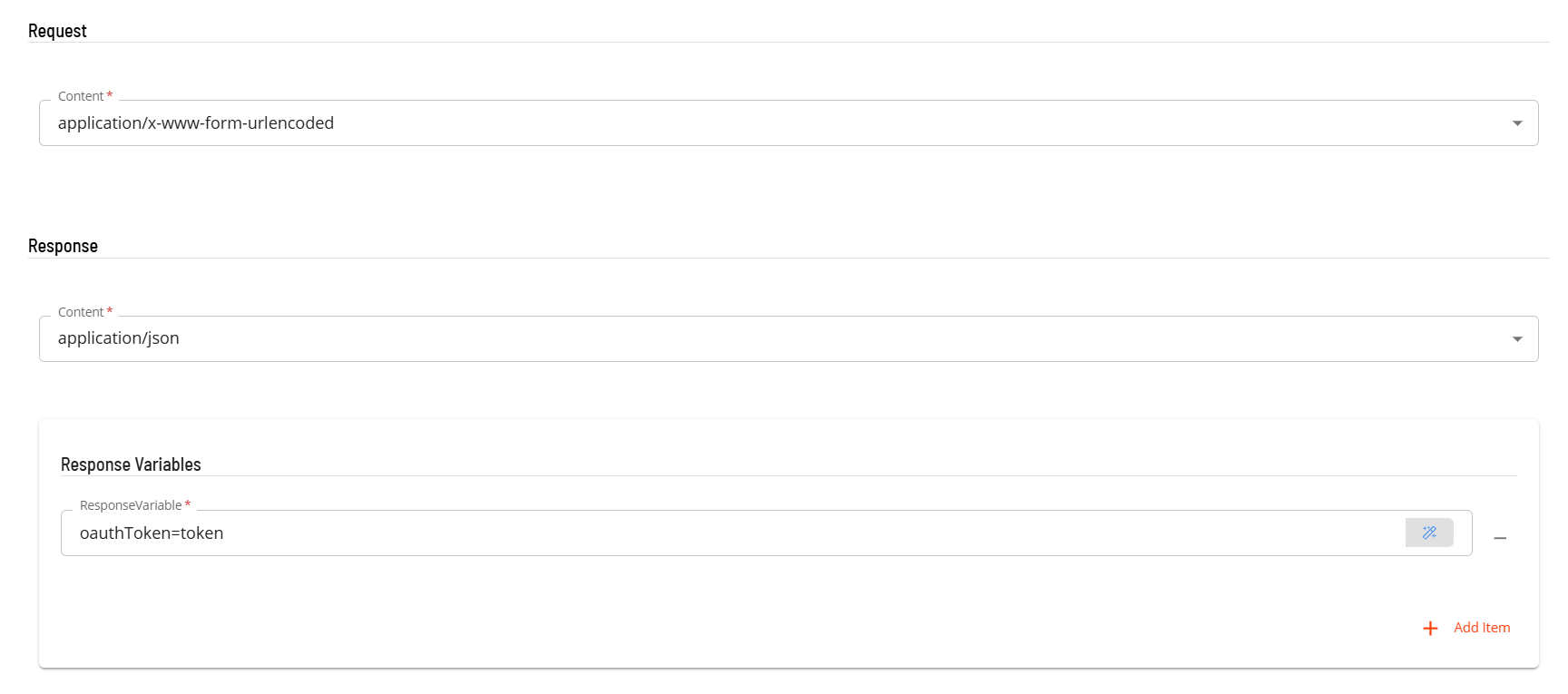
- In the Request section enter the following information
- Select the Content from the drop-down list (application/x-wwww-form-urlencoded).
- In the Response section
- Select the Content from the drop-down list (application/json).
- In Response Variables define a variable to contain data extracted from the returned JSON data. The extracted data will be stored as a schedule instance property in the schedule making the extracted information available to subsequent tasks. The format of the field definition is variable-name=jsonpath (i.e. oauthToken=$.id) where
- variable-name is the name of the variable that will be created as a schedule instance property.
- jsonpath is ignored as default value of access_token is used.
GET Task
The GET task is used to retrieve data from a remote Rest-API. Prior to executing a GET request if authentication is required, an authentication task (BASICTOKEN, OAUTH2TOKEN or OPCONTOKEN) must be executed successfully to store the required token as a schedule instance property of the schedule. The GET task should have a dependency set on the authentication task.
Variables can be used to define values that will be replaced in the Url and MsgBody fields. This allows 'place holders' to be defines and the values substituted during the execution of the task. Properties can also be used to provide dynamic or static values for variable substitution. An example would be to create a variable TestVar=ABC. The name of the variable TestVar which is defined in the Url or the MsgBody will be replaced with the value ABC.
- Open Solution Manager.
- From the Home page select Library
- From the Administration Menu select Master Jobs.
- Select +Add to add a new master job definition.
- Fill in the task details.
- Select the Schedule name from the drop-down list.
- In the Name field enter a unique name for the task within the schedule.
- Select ACS Webservices from the Job Type drop-down list.
- Select GET from the Task Type drop-down list.
Enter details for Task Type GET.
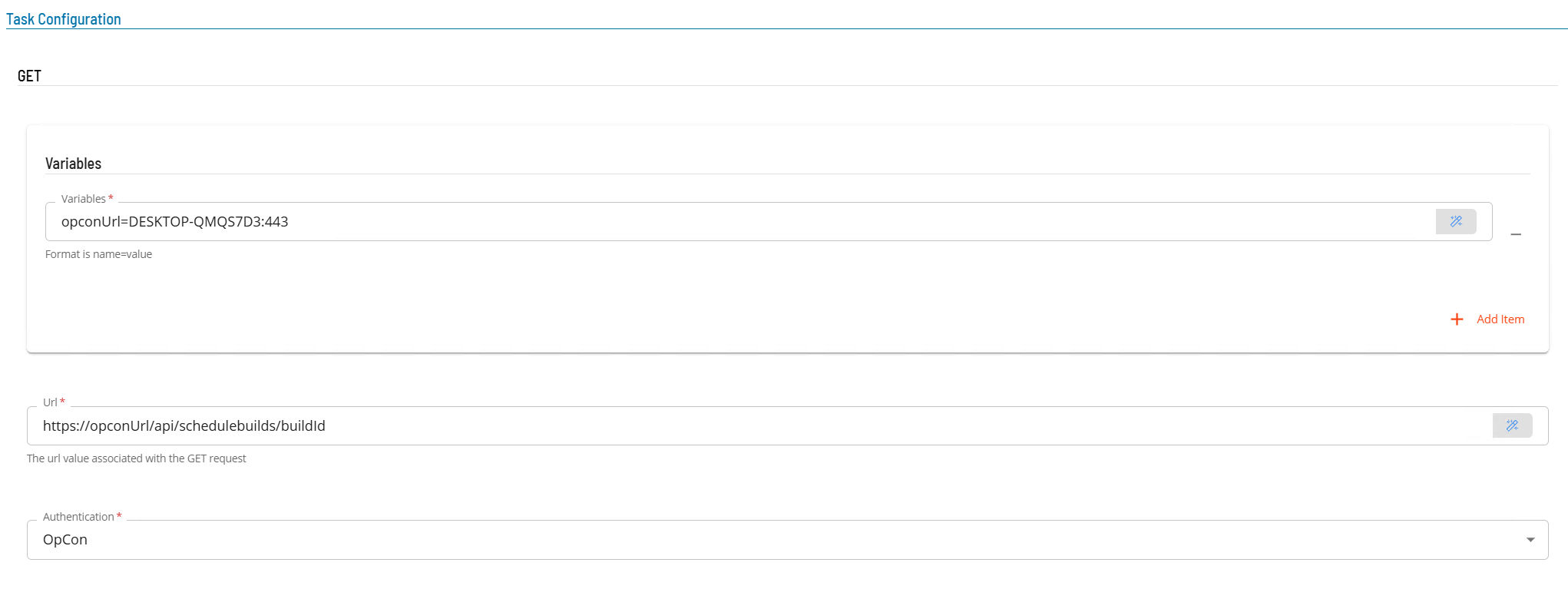
- Select the Task Details button.
- In the Integration Selection section, select the primary integration which is an ACS Webservices connection previously defined.
- In the Task Configuration section
- In Variables define name value pairs that can be used for substitution in url and message bodies.
- In the Url field enter the full address of the end point (i.e. https://server:port/api/tokens).
- From Authentication select an Authentication method for the task from the drop-down list (None, Basic, OAuth2, OpCon).
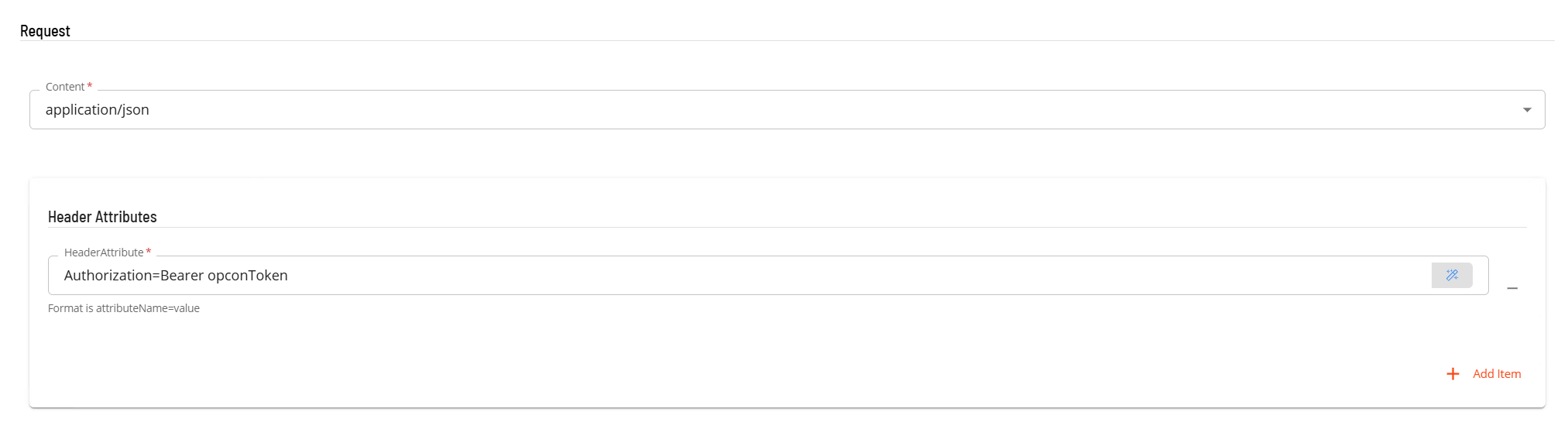
- In the Request section
- Select the Content from the drop-down list (application/json).
- In Header Attributes enter a reference to the authorization token previously created if an Authorization header is required. Enter a name value pair that contains the matching name of a schedule instance property (i.e. Authorization=Bearer schedule instance property name).
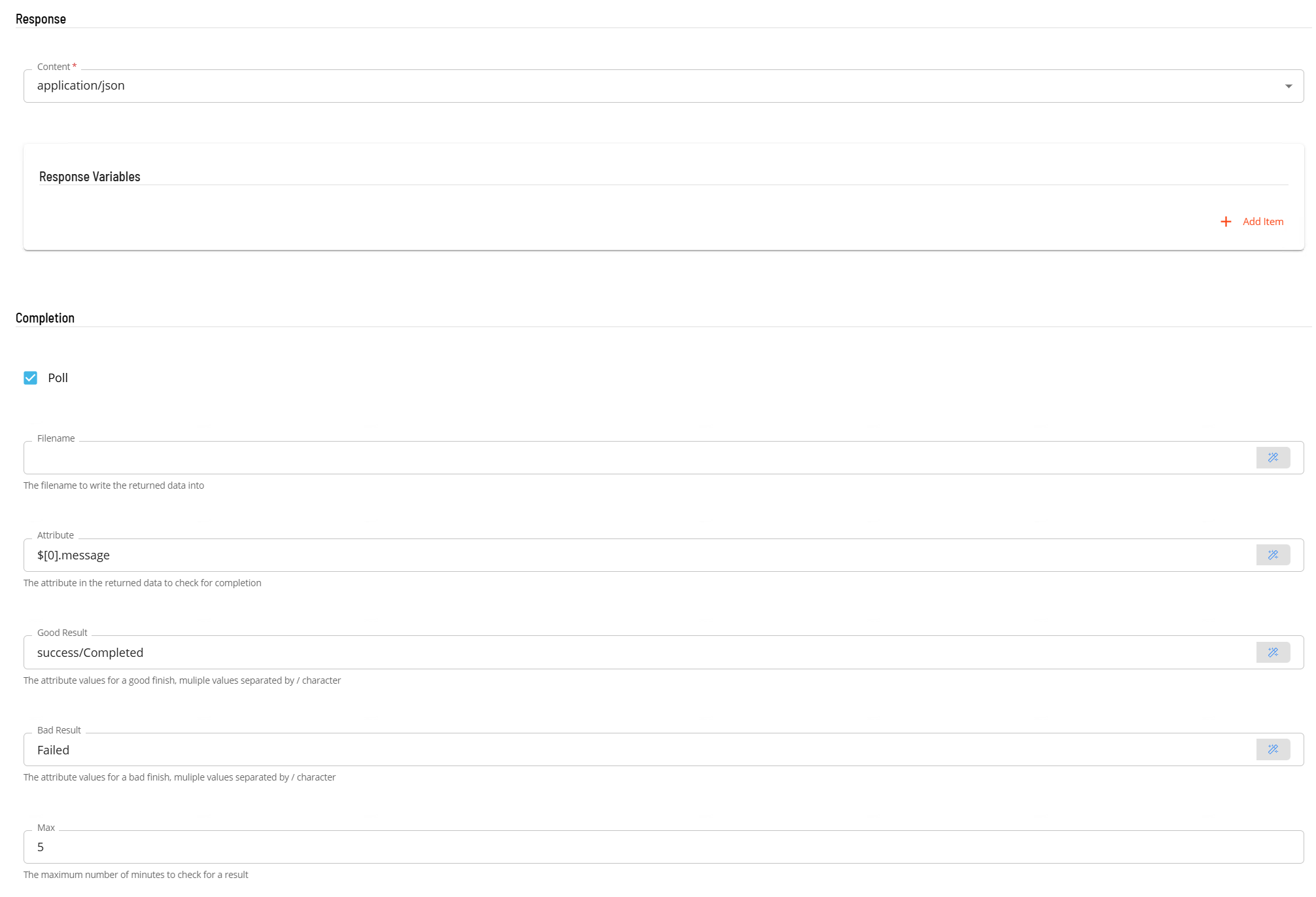
- In the Response section
- Select the Content from the drop-down list (application/json).
- In the Completion section is an optional section that can be used to examine the value of an attribute in the returned JSON to determine if the task completed successfully. It can also be used to 'poll' on a regular basis until the task is completed.
- Select the POll field to indicate that it should perform a poll as part of the completion process. If Poll is not selected a single check will be made on the defined Attribute using the Good and Bad Result values to determine the result.
- In the Attribute field, enter the attribute location in JPath format (i.e. $.result.message).
- In the Good Result field enter value(s) that define a good completion. Multiple values can be entered separated by a forward slash character (i.e. Success/Complete).
- In the Bad Result field enter value(s) that define a failed completion. Multiple values can be entered separated by a forward slash character (i.e. Error/Failed).
- In the Max field set the maximum time in minutes to poll checking the the defined Attribute using the Good and Bad Result values to determine the result. It is an optional value. If Polling is selected and no Max time is set, the polling will continue util a match is made.
POST Task
The POST task is used to submit data to a remote Rest-API. Prior to executing a POST request if authentication is required, an authentication task (BASICTOKEN, OAUTH2TOKEN or OPCONTOKEN) must be executed successfully to store the required token as a schedule instance property of the schedule. The POST task should have a dependency set on the authentication task.
Variables can be used to define values that will be replaced in the Url and MsgBody fields. This allows 'place holders' to be defines and the values substituted during the execution of the task. Properties can also be used to provide dynamic or static values for variable substitution. An example would be to create a variable TestVar=ABC. The name of the variable TestVar which is defined in the Url or the MsgBody will be replaced with the value ABC.
A special variable called JCorrelationId can be used to define a return point to the OpCon workflow after starting a task on a remote system. This approach prevents the need to 'poll' for task completion. The value of the variable consists of the ScheduleName, the JobName and the Date (format yyyy-mm-dd) of a task in the OpCon Daily tables. Before executing the POST request, the full jobId is retrieved through the OpCon Rest-API and this is then used as the substitution value. The message body of the POST request should then include a 'JCorrelationId' place holder. The defined OpCon task should be in a 'hold' state. The remote system would then include the capability to submit a Rest-API request to mark the task as 'Finished OK' or 'Failed' depending on the remote task completion.
- Open Solution Manager.
- From the Home page select Library
- From the Administration Menu select Master Jobs.
- Select +Add to add a new master job definition.
- Fill in the task details.
- Select the Schedule name from the drop-down list.
- In the Name field enter a unique name for the task within the schedule.
- Select ACS Webservices from the Job Type drop-down list.
- Select POST from the Task Type drop-down list.
Enter details for Task Type POST.
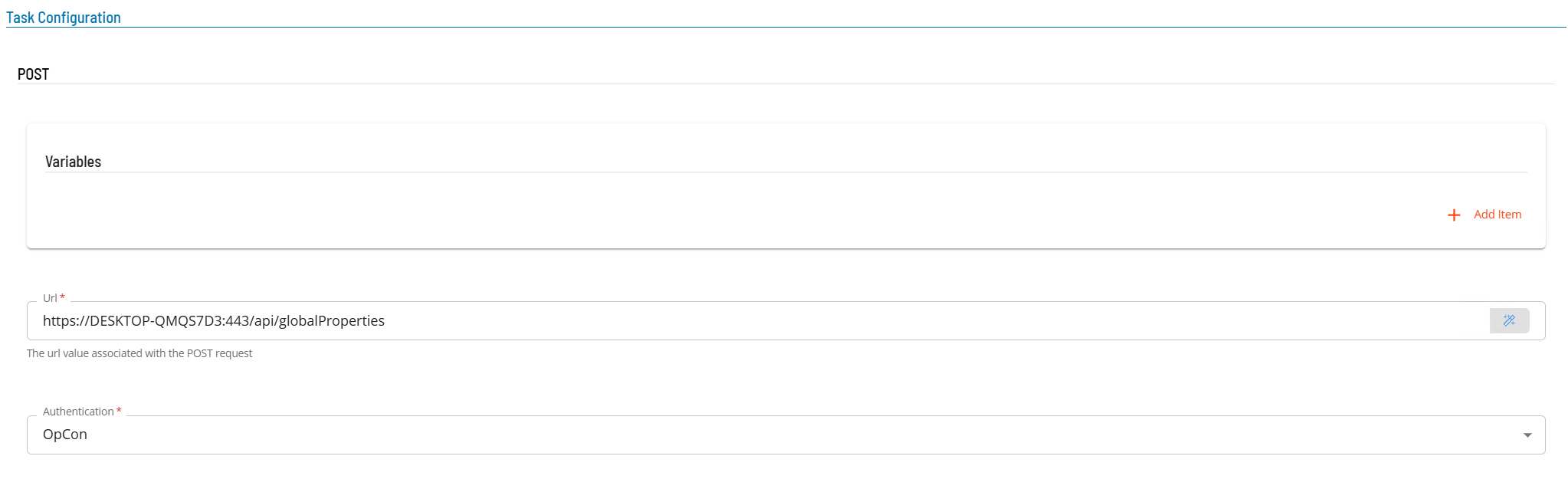
- Select the Task Details button.
- In the Integration Selection section, select the primary integration which is an ACS Webservices connection previously defined.
- In the Task Configuration section
- In Variables define name value pairs that can be used for substitution in url and message bodies.
- In the Url field enter the full address of the end point (i.e. https://server:port/api/tokens).
- From Authentication select an Authentication method for the task from the drop-down list (None, Basic, OAuth2, OpCon).
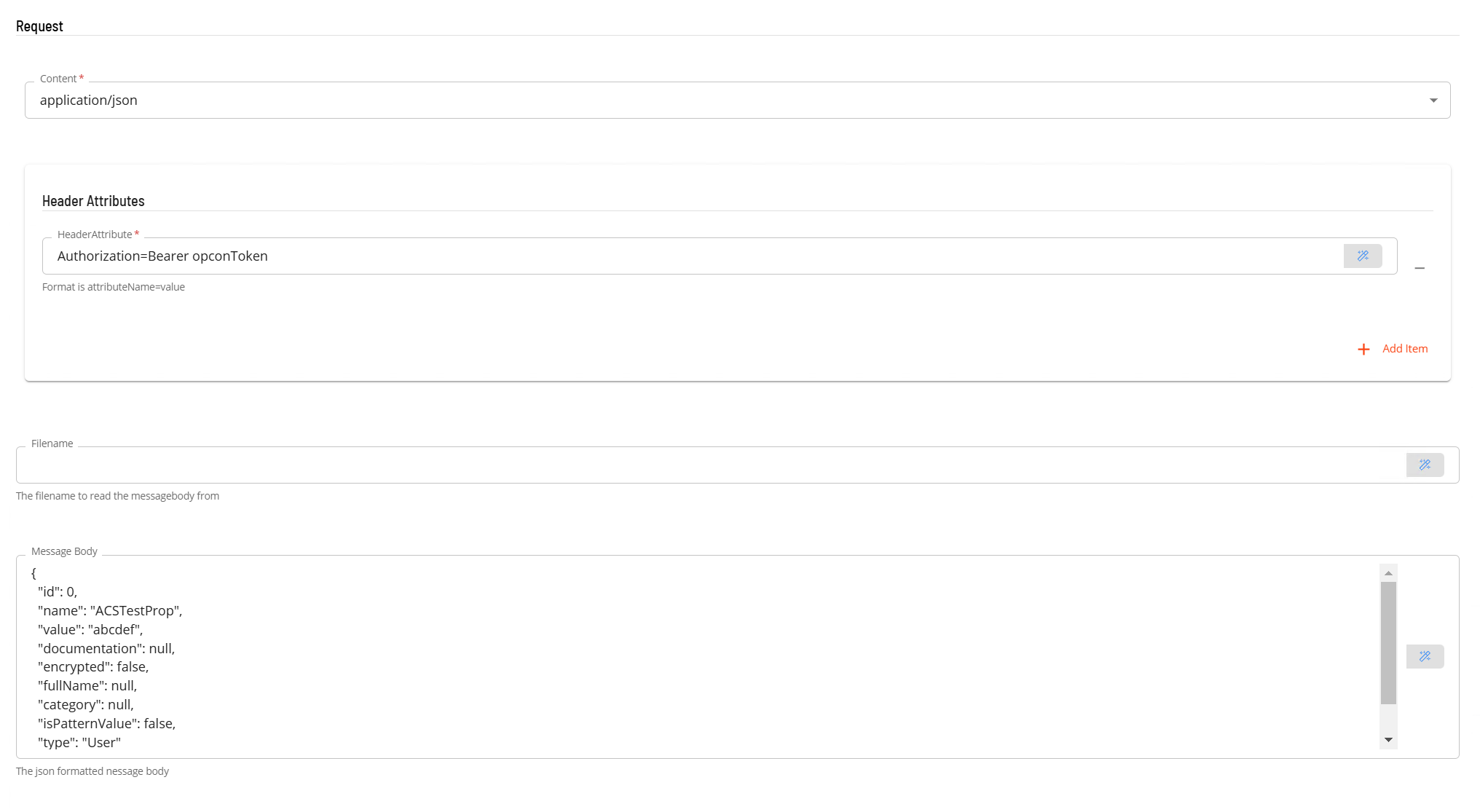
- In the Request section
- Select the Content from the drop-down list (application/json).
- In Header Attributes enter a reference to the authorization token previously created if an Authorization header is required. Enter a name value pair that contains the matching name of a schedule instance property (i.e. Authorization=Bearer schedule instance property name).
- In the Filename field enter the name of a file that contains the message body to be submitted with the POST request. Please note that the file location is relative to the system where the plugin is installed (either a Filename or a Message Body must be present).
- In the Message Body field, enter the message body to be submitted with the POST request. (either a Filename or a Message Body must be present).

- In the Response section
- Select the Content from the drop-down list (application/json).
- In the Response Variables if required, define a variable to contain data extracted from the returned JSON data. The extracted data will be stored as a schedule instance property in the schedule making the extracted information available to subsequent tasks. The format of the field definition is variable-name=jsonpath (i.e. acsPropid=$.id) where
- variable-name is the name of the variable that will be created as a schedule instance property.
- jsonpath is the attribute value to extract from the returned JSON data using JPath notation - enter $.id
- In the Completion section is an optional section that can be used to examine the value of an attribute in the returned JSON to determine if the task completed successfully.
- In the Attribute field, enter the attribute location in JPath format (i.e. $.result.message).
- In the Good Result field enter value(s) that define a good completion. Multiple values can be entered separated by a forward slash character (i.e. Success/Complete).
- In the Bad Result field enter value(s) that define a failed completion. Multiple values can be entered separated by a forward slash character (i.e. Error/Failed).
PUT Task
The PUT task is used to submit data to a remote Rest-API. Prior to executing a PUT request if authentication is required, an authentication task (BASICTOKEN, OAUTH2TOKEN or OPCONTOKEN) must be executed successfully to store the required token as a schedule instance property of the schedule. The PUT task should have a dependency set on the authentication task.
Variables can be used to define values that will be replaced in the Url and MsgBody fields. This allows 'place holders' to be defines and the values substituted during the execution of the task. Properties can also be used to provide dynamic or static values for variable substitution. An example would be to create a variable TestVar=ABC. The name of the variable TestVar which is defined in the Url or the MsgBody will be replaced with the value ABC.
- Open Solution Manager.
- From the Home page select Library
- From the Administration Menu select Master Jobs.
- Select +Add to add a new master job definition.
- Fill in the task details.
- Select the Schedule name from the drop-down list.
- In the Name field enter a unique name for the task within the schedule.
- Select ACS Webservices from the Job Type drop-down list.
- Select PUT from the Task Type drop-down list.
Enter details for Task Type PUT.
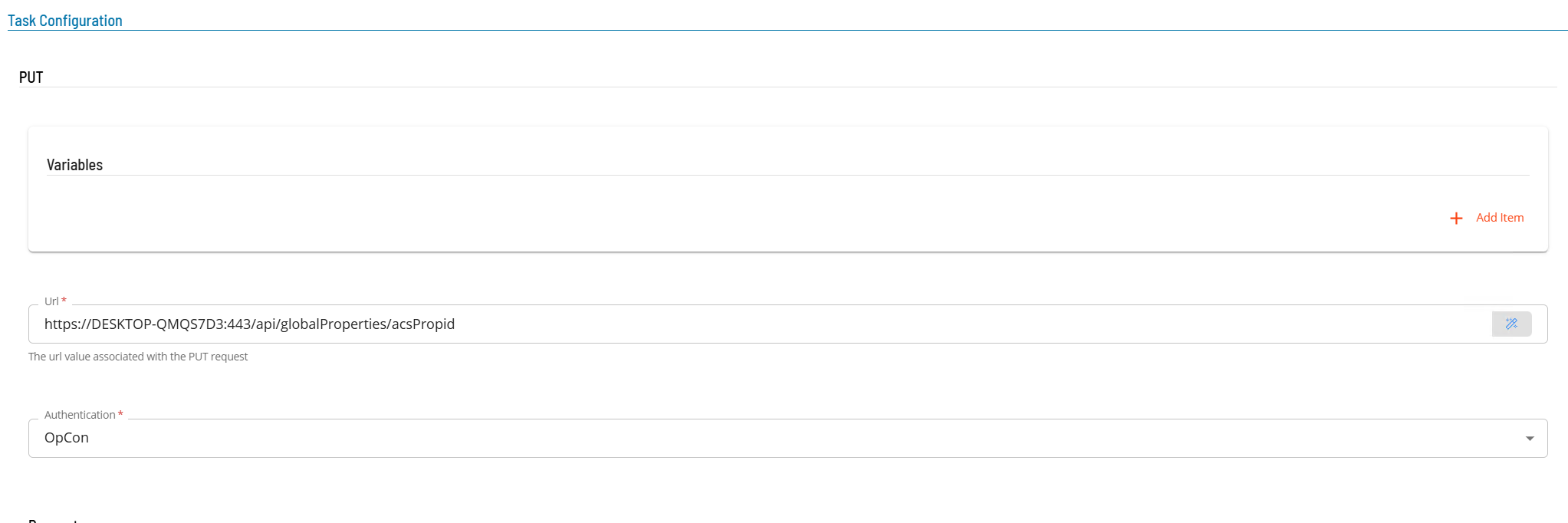
- Select the Task Details button.
- In the Integration Selection section, select the primary integration which is an ACS Webservices connection previously defined.
- In the Task Configuration section
- In Variables define name value pairs that can be used for substitution in url and message bodies.
- In the Url field enter the full address of the end point (i.e. https://server:port/api/tokens).
- From Authentication select an Authentication method for the task from the drop-down list (None, Basic, OAuth2, OpCon).
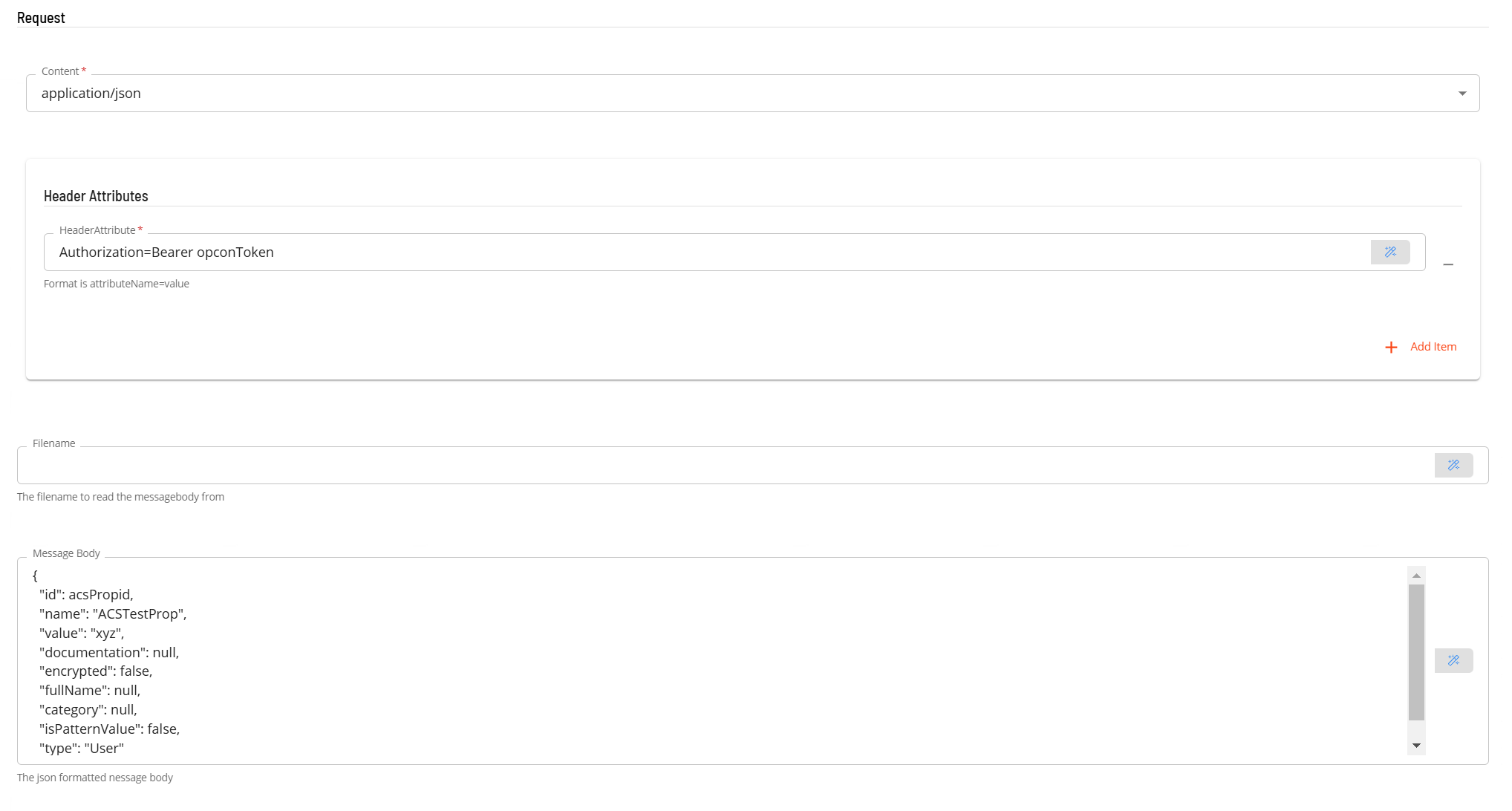
- In the Request section
- Select the Content from the drop-down list (application/json).
- In Header Attributes enter a reference to the authorization token previously created if an Authorization header is required. Enter a name value pair that contains the matching name of a schedule instance property (i.e. Authorization=Bearer schedule instance property name).
- In the Filename field enter the name of a file that contains the message body to be submitted with the PUT request. Please note that the file location is relative to the system where the plugin is installed (either a Filename or a Message Body must be present).
- In the Message Body field, enter the message body to be submitted with the PUT request. (either a Filename or a Message Body must be present).
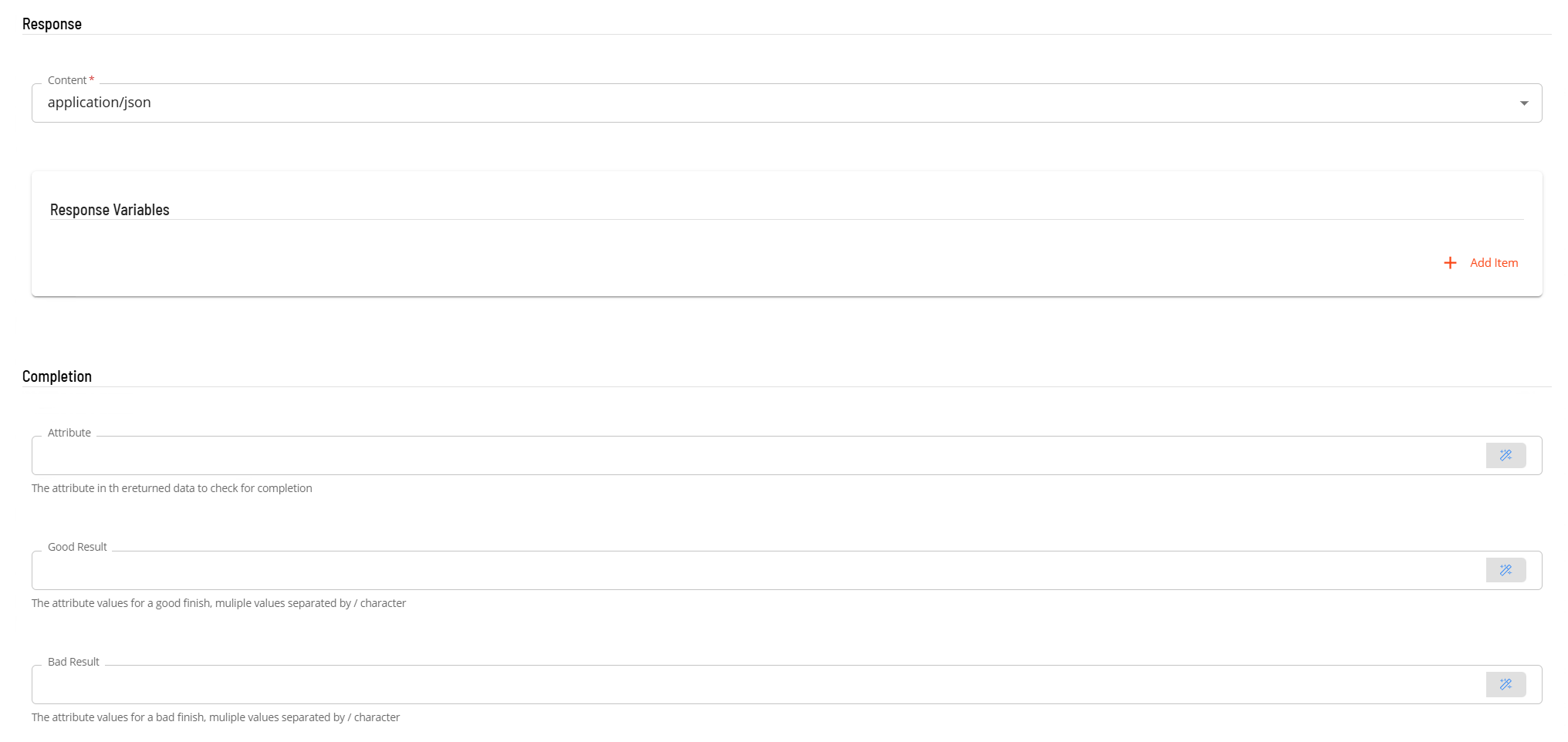
- In the Response section
- Select the Content from the drop-down list (application/json).
- In the Response Variables if required, define a variable to contain data extracted from the returned JSON data. The extracted data will be stored as a schedule instance property in the schedule making the extracted information available to subsequent tasks. The format of the field definition is variable-name=jsonpath (i.e. acsPropid=$.id) where
- variable-name is the name of the variable that will be created as a schedule instance property.
- jsonpath is the attribute value to extract from the returned JSON data using JPath notation - enter $.id
- In the Completion section is an optional section that can be used to examine the value of an attribute in the returned JSON to determine if the task completed successfully.
- In the Attribute field, enter the attribute location in JPath format (i.e. $.result.message).
- In the Good Result field enter value(s) that define a good completion. Multiple values can be entered separated by a forward slash character (i.e. Success/Complete).
- In the Bad Result field enter value(s) that define a failed completion. Multiple values can be entered separated by a forward slash character (i.e. Error/Failed).
PATCH Task
The PATCH task is used to submit data to a remote Rest-API. When using a PATCH request, only the changed data needs to be included in the message body instead of the complete data (PUT request). Prior to executing a PATCH request if authentication is required, an authentication task (BASICTOKEN, OAUTH2TOKEN or OPCONTOKEN) must be executed successfully to store the required token as a schedule instance property of the schedule. The PATCH task should have a dependency set on the authentication task.
Variables can be used to define values that will be replaced in the Url and MsgBody fields. This allows 'place holders' to be defines and the values substituted during the execution of the task. Properties can also be used to provide dynamic or static values for variable substitution. An example would be to create a variable TestVar=ABC. The name of the variable TestVar which is defined in the Url or the MsgBody will be replaced with the value ABC.
- Open Solution Manager.
- From the Home page select Library
- From the Administration Menu select Master Jobs.
- Select +Add to add a new master job definition.
- Fill in the task details.
- Select the Schedule name from the drop-down list.
- In the Name field enter a unique name for the task within the schedule.
- Select AC SWebservices from the Job Type drop-down list.
- Select PATCH from the Task Type drop-down list.
Enter details for Task Type PATCH.
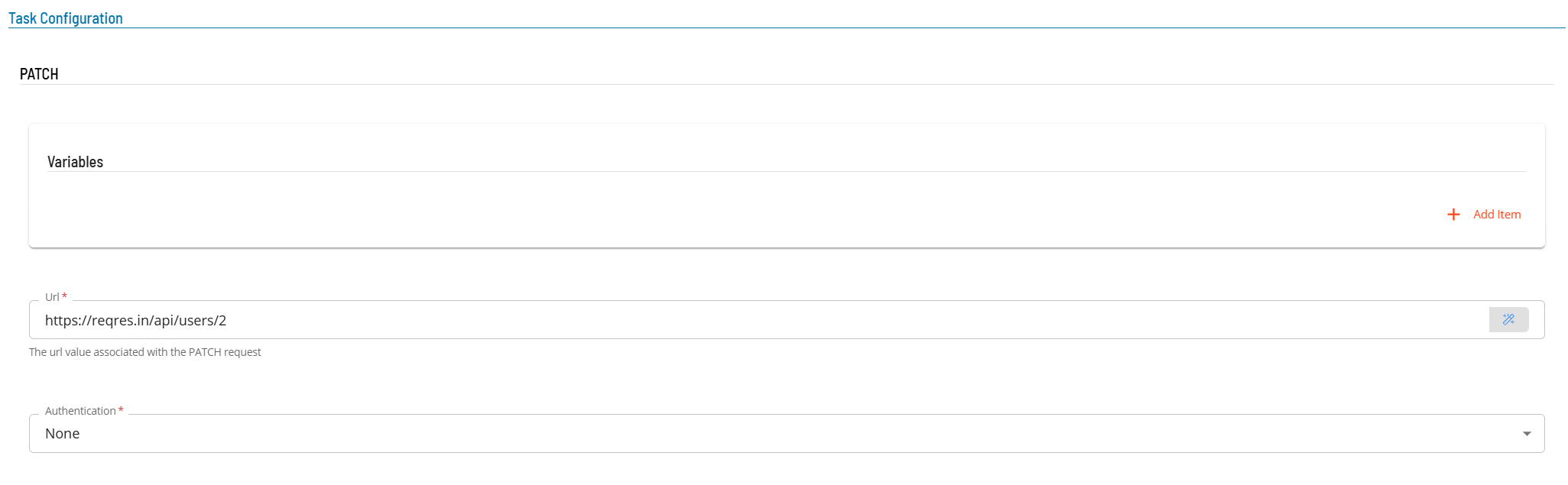
- Select the Task Details button.
- In the Integration Selection section, select the primary integration which is an ACS Webservices connection previously defined.
- In the Task Configuration section
- In Variables define name value pairs that can be used for substitution in url and message bodies.
- In the Url field enter the full address of the end point (i.e. https://server:port/api/tokens).
- From Authentication select an Authentication method for the task from the drop-down list (None, Basic, OAuth2, OpCon).
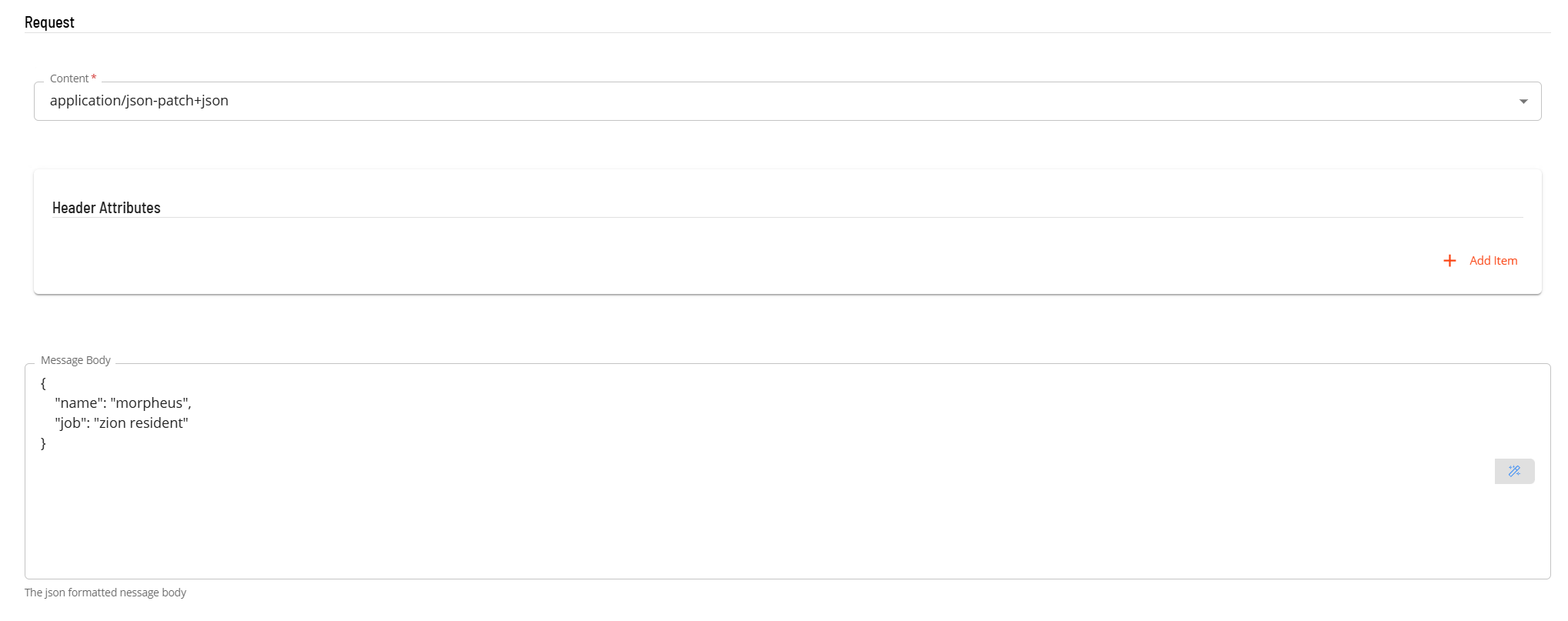
- In the Request section
- Select the Content from the drop-down list (application/json-patch+json).
- In Header Attributes enter a reference to the authorization token previously created if an Authorization header is required. Enter a name value pair that contains the matching name of a schedule instance property (i.e. Authorization=Bearer schedule instance property name).
- In the Message Body field, enter the message body to be submitted with the PATCH request.
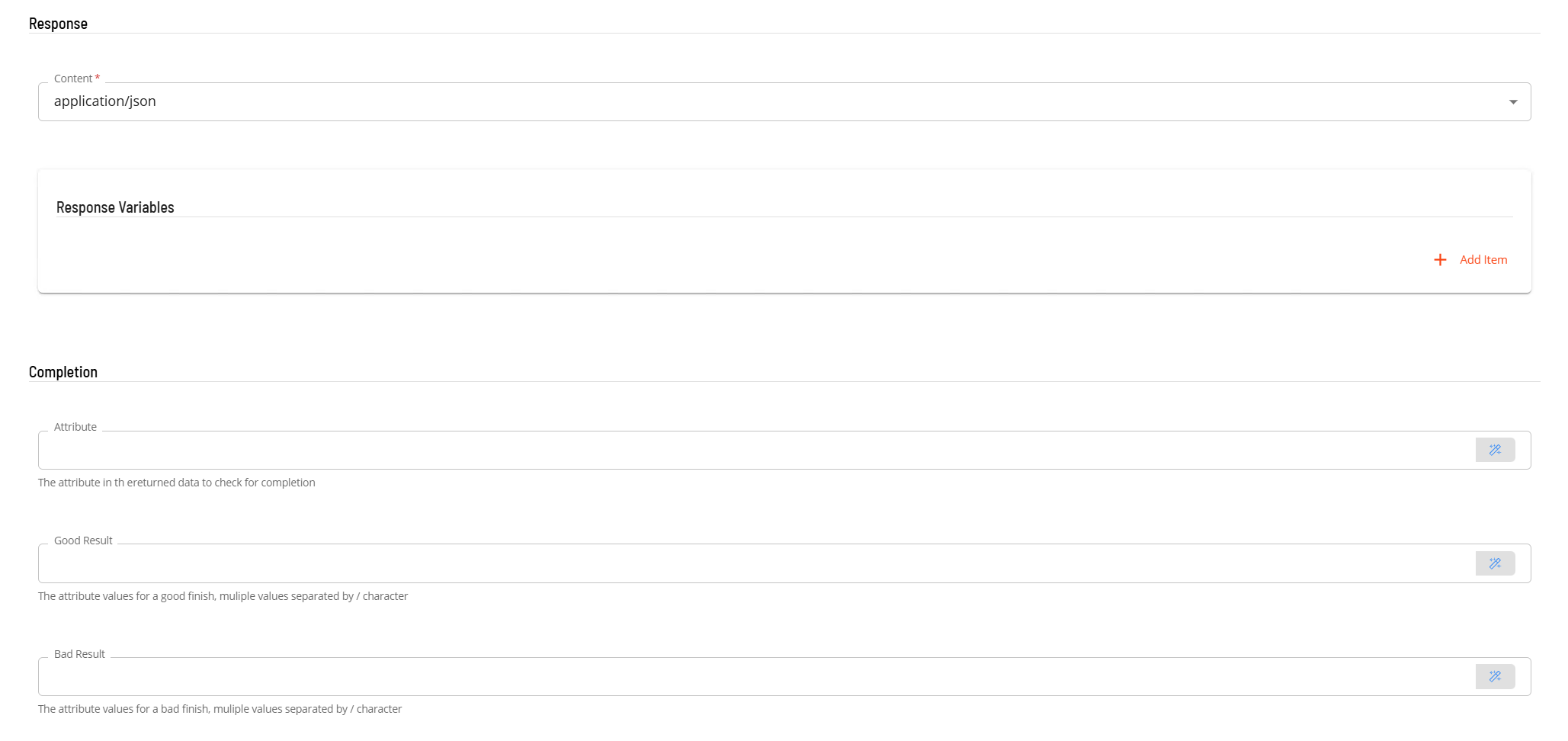
- In the Response section
- Select the Content from the drop-down list (application/json).
- In the Response Variables if required, define a variable to contain data extracted from the returned JSON data. The extracted data will be stored as a schedule instance property in the schedule making the extracted information available to subsequent tasks. The format of the field definition is variable-name=jsonpath (i.e. acsPropid=$.id) where
- variable-name is the name of the variable that will be created as a schedule instance property.
- jsonpath is the attribute value to extract from the returned JSON data using JPath notation - enter $.id
- In the Completion section is an optional section that can be used to examine the value of an attribute in the returned JSON to determine if the task completed successfully.
- In the Attribute field, enter the attribute location in JPath format (i.e. $.result.message).
- In the Good Result field enter value(s) that define a good completion. Multiple values can be entered separated by a forward slash character (i.e. Success/Complete).
- In the Bad Result field enter value(s) that define a failed completion. Multiple values can be entered separated by a forward slash character (i.e. Error/Failed).
DELETE Task
The DELETE task is used to submit delete request to a remote Rest-API. Prior to executing a DELETE request if authentication is required, an authentication task (BASICTOKEN, OAUTH2TOKEN or OPCONTOKEN) must be executed successfully to store the required token as a schedule instance property of the schedule. The DELETE task should have a dependency set on the authentication task.
- Open Solution Manager.
- From the Home page select Library
- From the Administration Menu select Master Jobs.
- Select +Add to add a new master job definition.
- Fill in the task details.
- Select the Schedule name from the drop-down list.
- In the Name field enter a unique name for the task within the schedule.
- Select ACS Webservices from the Job Type drop-down list.
- Select DELETE from the Task Type drop-down list.
Enter details for Task Type DELETE.
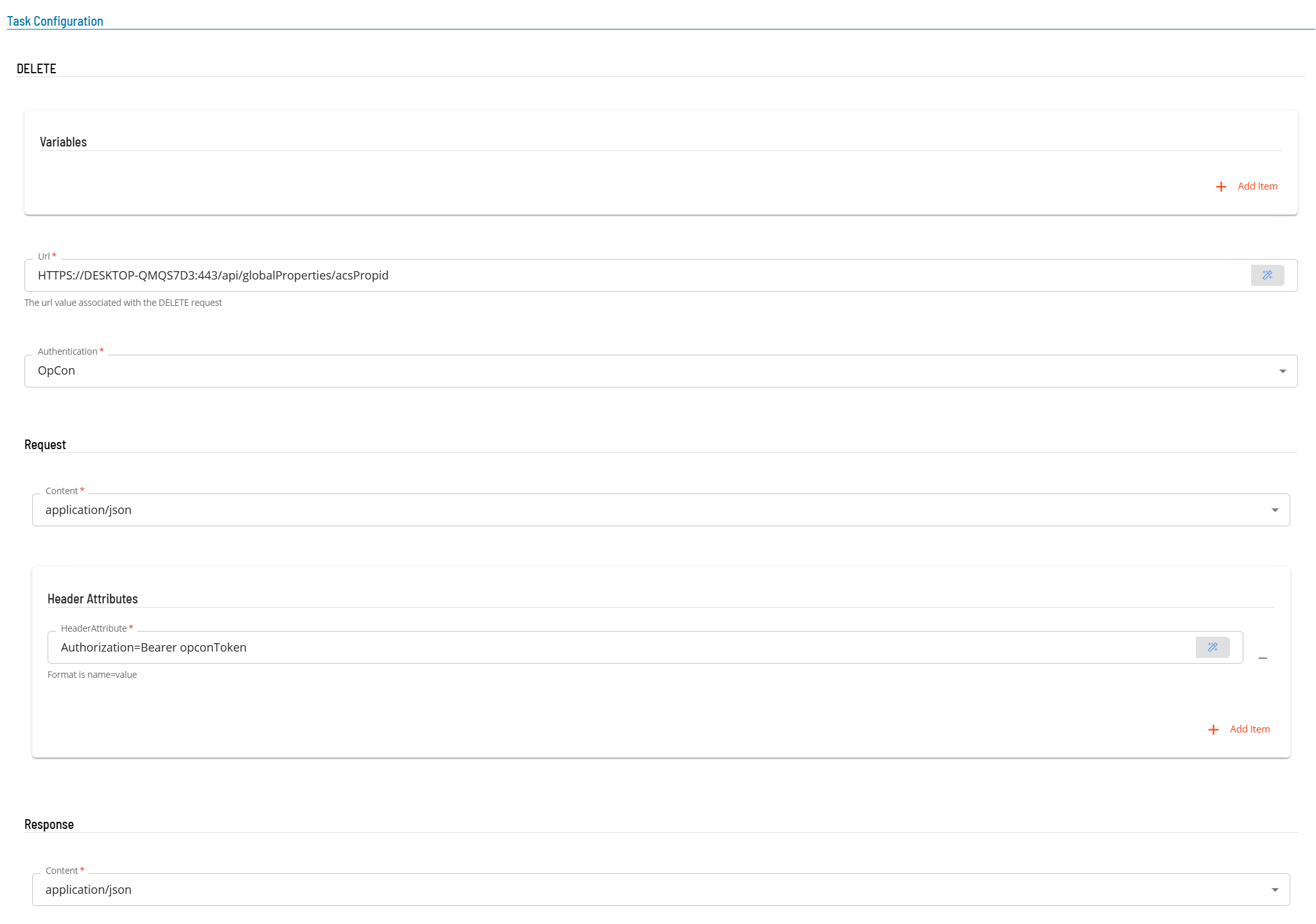
Select the Task Details button.
In the Integration Selection section, select the primary integration which is an ACS Webservices connection previously defined.
In the Task Configuration section
- In Variables define name value pairs that can be used for substitution in url and message bodies. Defining SERVER=DESKTOPA will replace the value SERVER in the url and message body with value DESKTOPA.
- In the Url field enter the full address of the end point (i.e. https://server:port/api/globalProperties/acsPropid where acsPropid was saved in a previous task as a Response Variable acsPropid=$.id.
- From Authentication select an Authentication method for the task from the drop-down list (None, Basic, OAuth2, OpCon).
In the Request section
- Select the Content from the drop-down list (application/json).
- In Header Attributes enter a reference to the authorization token previously created if an Authorization header is required. Enter a name value pair that contains the matching name of a schedule instance property (i.e. Authorization=Bearer schedule instance property name).
In the Response section
- Select the Content from the drop-down list (application/json).