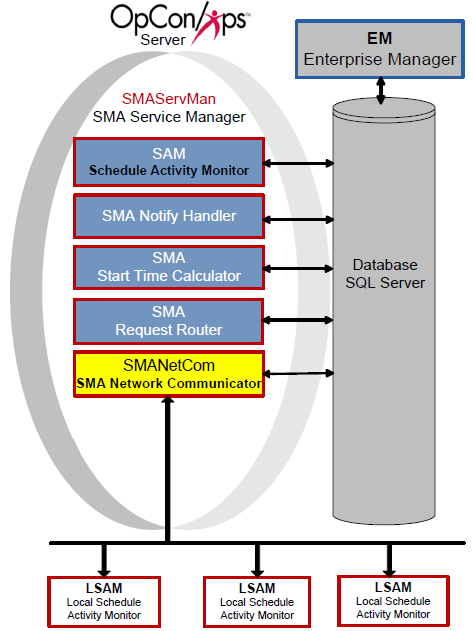
SMA Network Communications Module (SMANetCom)
The SMANetCom component is responsible for all communication between the SAM and all LSAMs. In OpCon, SMANetCom is the communication bridge between Central Components and LSAMs. SMANetCom is a multi-threaded application, allowing the dedication of one thread per LSAM.
SMANetCom sends job start information to each LSAM and then requests job status updates, writing the feedback from the LSAMs into the database. When a job completes, the LSAMs respond with the completion status. Continually reading SMANetCom messages in the database, the SAM uses this information to report statuses and resolve dependencies.
TLS Security
The OpCon server supports TLS 1.2 for securing communication between itself and any LSAMs that are upgraded and configured to use TLS. Before communication starts, the OpCon server verifies the identity of the LSAM by exchanging digital certificates with it. Certificates may be either from a Certificate Authority or they may be self-signed certificates.
There must always be a TLS Server Certificate representing the LSAM's server role in the communications connection (that is, the OpCon central application server acts as a client when requesting a connection with each LSAM). There may optionally also be a TLS Client Certificate that represents the OpCon application server (where the OpCon application server always takes the role of a Client in TCP/IP communications and in TLS certificate exchanges).
To make it possible for the OpCon application server to enable TLS security, SMANetCom needs to have either (1) a copy of a self-signed certificate from the LSAM certificate or (2) a copy of the Certificate Authority (or other root) certificate representing the agency that issued the LSAM digital certificate(s). It may be typical for a site to use a single Certificate Authority (CA) to issue certificates for all the LSAMs, so only one CA would be required within the OpCon application server machine. For self-signed certificates published by the LSAM machines themselves, there is no separate CA, so the certificate itself is required.
The certificates for authenticating each LSAM must be installed in the standard certificate store of the local Windows machine. Refer to the Microsoft documentation for instructions about installing certificates in the Windows certificate store where the OpCon server application is installed.
If TLS client authentication is used, the LSAM must similarly be able toauthenticate the SMANetCom certificate. The matching certificate or the root certificate must be stored as documented for the LSAM's host platform.
SMA Technologies documentation for each LSAM will provide guidelines for configuring the LSAM options that control TLS Security. Those documents identify the certificate store resource that is appropriate for each operating system, and they describe how the LSAM communication programs are connected to locally stored certificates.
Once the TLS server and client identities are established, the encrypted communication can begin. If there is a problem in establishing the identity, the communication fails immediately. There are settings in the OpCon machine records and also in the LSAM local configuration file that must be set on to start using TLS security. These control values can be used to assure that no communication will occur without valid certificates. The same control values can be used to disable TLS security, for example, in case some administrative problem is preventing data communication, and the site wishes to continue OpCon communication without using TLS security.
Refer to General and Communication Settings in the Concepts online help for options to configure TLS correctly.
Keep in mind that SMA Technologies is only providing a means by which its software can use TLS Security tools. SMA Technologies does not provide or support certificate publication, and it also does not attempt to duplicate the instructions for managing certificate stores in each operating system. The OpCon user is responsible for understanding and implementing those resources. Support for digital certificate publication is available from certificate publishing agencies. Instructions for generating digital certificate requests and for installing certificates in local certificate stores should be available from either the operating system vendor or from a third-party source that provided the digital certificate management tools.
Validation of the Digital Certificate Distinguished Name
TLS Security best practices indicate that the Distinguished Name (DN) that was assigned to a digital certificate should always be validated. Although the possession of the certificate's private key is supposed to verify the identity of the TLS Server (and of a TLS Client), validating the Distinguished Name helps to prevent some common forms of man-in-the-middle security attacks.
To implement this type of certificate validation, update the "TLS Certificate Distinguished Name" field in the OpCon machine record, under the Communications Settings tab of the Advanced Machine Properties. The value typed into this field must match exactly the value that was entered during the digital certificate request process.
SMANetcom will use this value, when it is not blank, to validate the digital certificates presented by each LSAM. When this field is blank or not present, the value chosen for validating the LSAM's DN will be chosen according to the following decision logic:
The FQDN (Fully Qualified Domain Name) from the machine record, if not blank.
If the FQDN is blank, the IP address will be used to request a FQDN from:
- The local Host Name table; otherwise,
- The DNS (Domain Name Services) from the TCP/IP network.
If no FQDN can be determined, the OpCon Machine name will be used.
According to these rules, it becomes critical to correctly specify the Distinguished Name whenever a digital certificate request is being generated.
There is no option at this time for the OpCon user to indicate that no DN validation should be processed. If DN validation is unsuccessful, the only remedy (until the DN validation value is fixed) would be to disable TLS Security and allow communication to run unsecured. However, using the local system's certificate store, it should be relatively easy to view the details of a certificate, record the actual Distinguished Name that was assigned to that certificate, and then register this name correctly in the OpCon machine record. A similar process may also be used by individual LSAMs when validation of the TLS Client certificate (from the OpCon application server) will be required.
User Control of TLS Security Operation
SMA Technologies has provided parallel controls over TLS Security, especially for the SMA File Transfer feature, which support turning on or off the TLS Security operations. Either the OpCon Machine Record -- Advanced Machine Options or the local LSAM configuration options can be configured to (1) always require TLS Security or (2) temporarily disable TLS Security.
TLS Security activation can be controlled separately for the SMA File Transfer feature, without directly impacting the OpCon Job Scheduling and JORS services (which share and are controlled by the OpCon Machine Record -- Advanced Machine Options -- Communications Settings). To control TLS Security for only the SMA File Transfer functions, use either the local LSAM controls, or modify the OpCon Machine record via the Advanced Machine Options, under the File Transfer tab.
Configuration
SMANetCom configuration determines basic service and communication settings, logging behavior, and the actions taken when failover occurs. The SMANetCom.exe file and SMANetCom.ini files reside in the <Configuration Directory>\SAM\ folder.
The Configuration Directory location is based on where you installed your programs. For more information, refer to File Locations in the Concepts online help.
The tables contain the definitions of each configuration parameter. If a value of "Y" is in the Dynamic column, any changes take effect immediately upon saving the file. All other configuration settings require the service to be restarted before the change takes effect.
SMANetCom.ini
All settings in the configuration file apply to the machine on which the file resides.
Service Settings
Service Settings contain basic information for SMANetCom processing.
| Service Settings | Default | Dynamic (Y/N) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ShortServiceName | SMA_NetCom | N | Defines the internal name of the service stored in the registry. The name must be unique. |
| DisplayServiceName | SMA NetCom | N | Defines the service name shown in the Services Applet. |
| SMANetComName | <Default> | N | Defines the name of this instance of SMANetCom if RunMode=Service. If RunMode=Managed, the SMA Service Manager controls the SMANetCom Name. For more information, refer to Set up Multiple SMANetCom Instances. # (hash symbol) and ' (single quotation/apostrophe sign) are NOT allowed in a SMANetComName. The reasons are the # sign is treated as a comment in SMAServMan.ini file, and the '(apostrophe) is not allowed from EM and it might cause potential database issues. |
| RunMode | Managed | N | Determines how the application is started and managed. Valid values are Managed and Service. When the value is Managed, the SMA Service Manager starts and manages this application and names NETCOM according to the SMASERVMAN.INI file. The Service setting allows the user to run SMANetCom as a Service. From a Command Prompt, '-install' or '-remove' is used to install/uninstall the SMANetCom service. The users can start/stop/restart the SMANetCom Service from Services Applet. |
| LocalIPv4Address (optional) | <Default> | N | Defines the IPv4 Address associated with the socket used in SMANetCom with a local endpoint to connect with LSAMs. Some machines may have multiple IP addresses. The user can designate one specific IP address used to talk with LSAMs. |
| LocalIPv6Address (optional) | <Default> | N | It is the same as LocalIPv4Address, except it is used on IPv6 machines. |
Service Setting Details
- The SMANetComName setting is available to set in the event that multiple instances of SMANetCom are required to support the volume of LSAMs. Each LSAM can be assigned to its own SMANetCom in the LSAM machine definition's Advanced Settings in the database.
- One SMANetCom instance (based on its name) can support maximum 2048 LSAMs; however, administrators should determine the maximum number for an environment based on performance.
- When multiple SMANetCom instances are needed due to the volume of LSAMs, only one SMANetCom.exe is needed. The SMANetCom.exe can have multiple copies in different locations, but SMA Technologies does not recommend this configuration.
- To run multiple instances of SMANetCom from the same SMA Service Manager, configure an additional application to call SMANetCom with a unique name.
- SMANetCom must have its Run Mode set to Managed.
- The SMANetCom instance will use the first argument in the CommandLineArguments from the SMAServMan.ini file to set the value for the SMANetComName.
- Each defined instance of SMANetCom must have a unique name.
- Each instance of SMANetCom will create its own SMANetCom*.log files. For example, if SMANetCom123 is the first argument in CommandLineArguments, SMANetcom123 will write its log messages to SMANetCom_SMANetCom123.log and SMANetCom_SMANetCom123Trace.log.
Set up Multiple SMANetCom Instances
- Log in as a local administrative user.
- Right-click Start and select Explore.
- Go to the Folders frame.
- Browse to the <Configuration Directory>\SAM\ directory.
- Right-click the SMAServMan.ini file and select Edit.
- Scroll down to the [Application List] section.
- Add another line at the end of the list and name the new application.
- Scroll down to the [SMANetCom] section.
- Click in front of the [SMANetCom] heading and drag the mouse to the end of the settings for the application to select all of the section.
- Press Ctrl + C to copy the settings.
- Scroll down to the bottom of the application settings.
- Make sure there is at least one blank line below the last setting and place the cursor in the blank line.
- Press Ctrl + V to paste the settings.
- Rename [SMANetCom] to the new application name (e.g., [SMANetCom2]).
- For the CommandLineArguments setting, set the value to the new application name (e.g., SMANetCom2).
- Use menu path: File > Save.
- Close ☒ the SMAServMan.ini file.
General Settings
General Settings provide InitializationScript path and TerminationScript path.
| General Settings | Default | Dynamic (Y/N) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mode | StandAlone | N | Determines SMANetCom's role in the failover process. Valid values are Primary, Secondary, or StandAlone. StandAlone indicates SMANetCom is not configured for failover. Note: When SMAServMan manages SMANetCom, the mode must be set to StandAlone. The Primary and Secondary settings are reserved for future use. |
| InitializationScript | <Blank> | N | Provides the path and filename of the script SMANetCom executes upon startup. Always enclose the path and file name in two sets of double quotes (""<Path>""). |
| TerminationScript | <Blank> | N | Provides the path and filename of the script SMANetCom executes upon shutdown. Always enclose the path and file name in two sets of double quotes (""<Path>""). |
SAM Database Communication Parameters
| SAM Database Communication Parameters | Default | Dynamic (Y/N) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAMDBLoginTimeoutInSeconds | 5 | N | Determines the length of time in seconds to allow for a login. If this time is exceeded, SMANetCom signals an error condition. |
| SAMCheckMsgsFromSAMInMilliseconds | 500 | N | Determines how often SMANetCom polls the database for SAM messages. The frequency is in milliseconds. |
| SAMCheckLSAMConfigurationInMilliseconds | 1000 | N | Determines how often SMANetCom checks each LSAM's configuration parameters for an update. The frequency is in milliseconds. |
Primary Mode Settings
The Primary Mode Settings are reserved for future use.
Secondary Mode Settings
The Secondary Mode Settings are reserved for future use.
Debug Options
The Debug Options configure the SMANetCom logging behavior.
| + | Debug Options | Default | Dynamic (Y/N) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MaximumLogFileSize | 150000 | Y | Defines the maximum size in bytes for each log file. Determines when the current log file is closed and a new file is started. When the file reaches this maximum size, it is "rolled over." This setting creates small, manageable log files. SMANetCom.log resides in the <Output Directory>\SAM\Log directory. When the log file reaches the maximum size, SMANetCom archives the log file. When SMANetCom is installed with the SAM, the SAM maintains the archive folders. Note: Each SMANetCom instance based on its SMANetComName has its SMANetCom log file as mentioned in the Details of Service Settings. |
| TraceSAMMessages | ON | Y | Enables/Disables SMANetCom to create the SMANetComTrace log file. If OFF, SMANetCom creates only the SMANetCom log file. If ON, SMANetCom creates both the SMANetCom log and SMANetComTrace log files. The SMANetComTrace log contains all records regarding TX messages. SMA Technologies strongly recommends leaving this value set to ON. Note: Each SMANetCom instance based on its SMANetComName has its own SMANetComTrace log file as mentioned in the Details of Service Settings. |
| DumpInputBuffer (optional) | OFF | Y | Determines the Enable/Disable SMANetCom to write the messages from LSAMs into the SMANetComTrace log file. This setting should not be enabled unless the user receives an indication from SMA Technologies. |
| DumpOutputBuffer (optional) | OFF | Y | Determines the Enable/Disable SMANetCom to write the messages to LSAMs into the SMANetComTrace log file. This setting should not be enabled unless the user receives an indication from SMA Technologies. |
| TraceLevel (optional) | 0 | Y | Determines the debug setting by developer ONLY. This setting should not be enabled unless the user receives an indication from SMA Technologies. The valid setting is 0 to 3. |
| DebugMachineNameWithTraceLevel2 (optional) | NONE | Y | Determines the debug setting by developer ONLY. This setting should not be enabled unless the user receives an indication from SMA Technologies. The valid setting is NONE, ALL, or the machine's name. |
Event Log Settings
The following sections provide settings to customize logging in the Application Log of the Windows Event Viewer.
| Service Start | Default | Dynamic (Y/N) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Msg | $SERVICENAME started. | Y | Defines the log message indicating SMANetCom has started. Modify the text for a different message. Set to NULL to disable this setting. $SERVICENAME is a supported token for this message type. |
| Type | 4 | Y | Defines the message type: 1 equals Error, 2 equals Warning, 4 equals Information |
| Service Stop | Default | Dynamic (Y/N) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Msg | $SERVICENAME stopped. | Y | Defines the log message indicating SMANetCom has stopped. Modify the text for a different message. Set to NULL to disable this setting. $SERVICENAME is a supported token for this message type. |
| Type | 4 | Y | Defines the message type: 1 equals Error, 2 equals Warning, 4 equals Information |