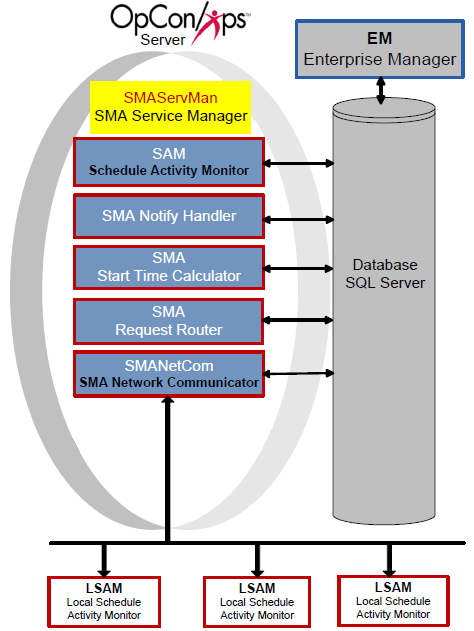
SMA Service Manager (SMAServMan)
SMAServMan is responsible for managing the application group of the SAM-SS. Responsibilities include application startup, shutdown, and failover. In failover scenarios, two SMAServMans communicate with each other and coordinate the smooth transition from the primary to the secondary machine (and from the primary to secondary database depending on configuration).
Configuration
SMAServMan configuration determines basic service settings, logging behavior, the application group, and the actions taken when an application or machine fails. The SMAServMan.ini file resides in the <Configuration Directory>\SAM\ folder. The table contains the definitions of each configuration parameter. If a value of "Yes" is in the Dynamic column, any changes take effect immediately upon saving the file. All other configuration settings require the service to be restarted before the change takes effect.
The Configuration Directory location is based on where you installed your programs. For more information, refer to File Locations in the Concepts online help.
SMAServMan.ini
All settings in the configuration file apply to the machine on which the file resides.
General Settings
General Settings contain basic information for the service registration to the Windows operating system.
| General Settings | Default | Dynamic (Y/N) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ShortServiceName | SMA_Servman | N | Defines the internal name of the service stored in the registry. The name must be unique. |
| DisplayServiceName | SMA Service Manager | N | Defines the service name shown in the Services Applet. |
| Mode | StandAlone | N | Determines the SMAServMan's role in the failover process. Valid values are Primary, Secondary, or StandAlone. StandAlone indicates SMAServMan is not configured for failover. Primary indicates SMAServMan is configured for failover and controls the primary application group. Secondary indicates SMAServMan is configured for failover and controls the secondary application group. |
| InitializationScript | <Blank> | Y | Provides the path and filename of the script SMAServMan executes upon startup. |
| TerminationScript | <Blank> | Y | Provides the path and filename of the script SMAServMan executes upon shutdown. |
Primary Mode Settings
If necessary, Primary Mode Settings determine the SMAServMan's behavior as manager of the primary application group.
| Primary Mode Settings | Default | Dynamic | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| FailOverSocketNumber | <Blank> | N | Defines the socket number for communication between the primary and secondary services. This parameter must be the same in the primary and secondary configuration files. |
| TimeOutInSecondsForSync | 60 | N | Determines the maximum allowable time for synchronization with an SMAServMan on another machine. This parameter does not apply to a StandAlone machine. |
| SyncInitFailureScript | <Blank> | Y | Provides the path and filename of the script SMAServMan executes if the initial synchronization with the Secondary SMAServMan fails after the allowable time specified by the TimeOutInSecondsForSync configuration parameter. |
| SyncLostScript | <Blank> | Y | Provides the path and filename of the script SMAServMan executes if the Secondary SMAServMan fails to contact the Primary SMAServMan after initial synchronization is successful. |
| NormalShutdownScript | <Blank> | Y | Provides the path and filename of the script SMAServMan executes when it is shutdown in an orderly manner. Examples of a normal shutdown are stopping SMAServMan by way of the Service Control Manager or the NET STOP command. |
| AbnormalShutdownScript | <Blank> | Y | Provides the path and filename of the script SMAServMan executes when there is a critical failure in the Primary application group or the SMAServMan has an unrecoverable error. |
If necessary, Secondary Mode Settings determine the SMAServMan's behavior as manager of the secondary application group.
| Secondary Mode Settings | Default | Dynamic | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| FailOverSocketNumber | <Blank> | N | Defines the socket number for communication between the primary and secondary SMAServMans. This parameter must be the same in the primary and secondary configuration files. |
| PrimaryMachine | <Blank> | N | Provides the machine name or the TCP/IP address of the primary machine. This parameter only applies to the secondary machine. |
| SecondsBetweenPings | 15 | N | Determines the frequency of pings from the secondary to the primary machine. This parameter does not apply to a StandAlone machine. |
| PingRetryCount | 0 | N | Determines the number of consecutive ping "failures" before initiating failover. This parameter does not apply to a StandAlone machine. |
| PingTimeOutInMilliseconds | 1000 | N | Determines the number of milliseconds in the timeout period. If there is no response to the ping within the timeout period, SMAServMan increments the PingRetryCount. If the PingRetryCount reaches the maximum, SMAServMan behaves according to the SyncLostFailover setting. This parameter does not apply to a StandAlone machine. |
| SyncInitFailureScript | <Blank> | Y | Provides the path and filename of the script SMAServMan executes if the initial synchronization with the Primary SMAServMan fails after the allowable time specified by the SecondsBetweenPings configuration parameter. |
| PrimaryNormalShutdownFailover | N | N | Determines if the Secondary SMAServMan starts the secondary application group when the Primary SMAServMan shuts down normally. Examples of a normal shutdown are stopping SMAServMan by way of the Service Control Manager or the NET STOP command. If N, the Secondary SMAServMan does not start the secondary application group. If Y, the Secondary SMAServMan will start the secondary application group that begins processing with the OpCon database. |
| PrimaryNormalShutdownScript | <Blank> | Y | Provides the path and filename of the script SMAServMan executes when the Primary SMAServMan is shutdown normally. Examples of a normal shutdown are stopping SMAServMan by way of the Service Control Manager or the NET STOP command. |
| PrimaryAbnormalShutdownFailover | N | N | Determines if the Secondary SMAServMan starts the secondary application group when the Primary SMAServMan shuts down abnormally (i.e., with a critical failure in the primary application group or the Primary SMAServMan has an unrecoverable error). If N, the Secondary SMAServMan will not start the secondary application group. If Y, the Secondary SMAServMan will start the secondary application group that begins processing with the OpCon database. |
| PrimaryAbnormalShutdownScript | <Blank> | Y | Provides the path and filename of the script SMAServMan executes when the Primary SMAServMan is shutdown abnormally. Examples of an abnormal shutdown are a critical failure in the primary application group or when the Primary SMAServMan has an unrecoverable error. Note: SMA Technologies provides a script called StopRepl.cmd for customers using database. For information on configuring this script, refer to Modifying the Stop Replication Command File in the Database Information online help. SMA Technologies strongly recommends defining the StopRepl.cmd file for the PrimaryAbnormalShutdownScript. |
| SyncLostFailover | N | N | Determines if the Secondary SMAServMan starts the secondary application group when it loses synchronization with the Primary SMAServMan. If N, the Secondary SMAServMan will not start the secondary application group. If Y, the Secondary SMAServMan will start the secondary application group that begins processing with the OpCon database. |
| SyncLostScript | <Blank> | Y | Provides the path and filename of the script SMAServMan executes when it loses communication with the Primary SMAServMan. Examples of communication loss are network connection failure or Primary machine crash. |
| ShutdownScript | <Blank> | Y | Provides the path and filename of the script SMAServMan executes when it is shutdown in an orderly manner. Examples of a normal shutdown are stopping SMAServMan by way of the Service Control Manager or the NET STOP command. |
| AbnormalShutdownScript | <Blank> | Y | Provides the path and filename of the script SMAServMan executes. This script executes in the following situations:When there is a critical failure in the secondary application group.When the Secondary SMAServMan has an unrecoverable error. |
Debug Options
The Debug Options configure the SMAServMan logging behavior.
| Debug Options | Default | Dynamic (Y/N) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ArchiveDaysToKeep | 100 | Y | Determines the number of days of history (i.e., archive folders) to keep. Caution: This number must be greater than the "Maximum number of days archived SAM logs should be kept" logging setting in the Global Options. For additional information, refer to Logging in the Concepts online help. |
| MaximumLogFileSize | 15000 | Y | Defines the maximum size in bytes for each log file. Determines when the current log file is closed and a new file is started. When the file reaches this maximum size, it is "rolled over." This setting creates small, manageable log files. SMAServMan.log resides in the <Output Directory>\SAM\Log directory. When the log file reaches the maximum size, SMAServMan archives the log file. The SAM then maintains the archive folders. |
| Trace | OFF | Y | Enables/Disables the SMAServMan to write more messages to the SMAServMan log file. |
Application List
The Application List contains the name of each application managed by the SMAServMan.
| Application List | Default | Dynamic (Y/N) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Application1 | SAM | N | Lists an application to be managed by SMAServMan. SMAServMan requires SAM in the Application List. |
| Application2 | SMANetCom | N | Lists an application to be managed by SMAServMan. SMAServMan requires SMANetCom in the Application List. |
| Application3 | SMANotifyHandler | N | Lists an application to be managed by SMAServMan. |
| Application4 | SMARequestRouter | N | Lists an application to be managed by SMAServMan. |
| Application5 | SMAStartTimeCalculator | N | Lists an application to be managed by SMAServMan. |
| Application9 | SMALDAPMon | N | Lists an application to be managed by SMAServMan. |
| Application10-Application50 | None | N | For SMA Technologies use only. |
| Application51+ | None | N | Available for user customization. The maximum number of applications is 100. |
Application Parameters
For each application in the Application List, there is a major heading in the configuration file. Each heading contains a list of parameters for that application.
| Parameter | Dynamic (Y/N) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ApplicationPath | N | This is the full path name to the executable. |
| StartInDirectory | N | This setting determines the current directory where the application is started. |
| CommandLineArguments | N | Defines the arguments in the application's command line. |
| InitialTimeOutInSeconds | Y | Process startup typically takes longer than the "main" loop of the process. If the application has not made the initial call to SMAServMan within this time limit, it is considered to be "hung" or "in error" and is terminated. If the application has a heavy processing load, consider extending this timeout to prevent unnecessary termination of the application. |
| ApplicationTimeOutInSeconds | Y | If the application has not called the DLL function in this number of seconds since the last call, it is considered to be "hung" or "in error" and is terminated. If the application has a heavy processing load, consider extending this timeout to prevent unnecessary termination of the application. |
| DependsOnApplication | Y | If the application specified in this parameter fails and cannot be restarted, the dependent application is terminated. |
| RestartApplicationLimit | Y | If this parameter is zero, no attempt is made to restart a "hung" application. The application restart is only attempted until the internal restart count exceeds this limit. It may be possible that the application simply cannot come back up without human intervention. Once the application has come up and communicated with SMAServMan, the internal restart count is set back to 0 because the restart was successful. |
| SecondsBetweenRestartAttempts | Y | This is the number of seconds to wait after a failed restart attempt before making another restart attempt. |
| ApplicationHungScript | Y | If SMAServMan terminated the application after determining that the application was "hung," this optional user-defined script is run (e.g., command file to pass an event to the SMA Notify Handler). |
| RestartFailedScript | Y | If SMAServMan was unable to restart the application, this optional user-defined script is run. |
| AutoRestartInMinutes | Y | If this parameter is greater than zero, the application is shut down and restarted in this number of minutes. |
| SecondsBetweenAutoRestartAttempts | Y | If the application is to be restarted, this parameter dictates how many seconds to wait from the time the application was shut down to attempting its start up. |
| CriticalApplication | Y | If the application cannot be restarted and this parameter is TRUE, all applications are shutdown and the service is stopped. If the application cannot be restarted and this parameter is FALSE, SMAServMan does not shut down any other applications and continues monitoring. The CriticalApplication setting for the SAM and SMANetCom must be TRUE. If this is the Primary machine, failover occurs. |
Application Hung Scripts
SMA Technologies supplies command files for default application hung scripts. These scripts must be configured for proper execution in the event one of the applications hangs. The scrips are installed to the <Configuration Directory>\SAM folder. By default, the SMAServMan.ini file contains the path to the SQL Authentication script names.
The Configuration Directory location is based on where you installed your programs. For more information, refer to File Locations in the Concepts online help.
The following list contains the names of the Application Hung Scripts:
| SQL Authentication Script Names | Windows Authentication Script Names |
|---|---|
| SAMHung.cmd | SAMHung_WinAuth.cmd |
| SMANetComHung.cmd | SMANetComHung_WinAuth.cmd |
| SMANotifyHandlerHung.cmd | SMANotifyHandlerHung_WinAuth.cmd |
| SMARequestRouterHung.cmd | SMARequestRouterHung_WinAuth.cmd |
| SMAStartTimeCalculatorHung.cmd | SMAStartTimeCalculatorHung_WinAuth.cmd |
Each of the Application Hung Scripts calls their own respective supplemental script (e.g., SAMHung.cmd calls SAM.cmd) to execute database queries relevant to the "hung" application, and output the results to a text file for troubleshooting. The following list contains the names for the supplemental scripts:
| SQL Authentication Script Names | Windows Authentication Script Names |
|---|---|
| SAM.cmd | SAM_WinAuth.cmd |
| SMANetCom.cmd | SMANetCom_WinAuth.cmd |
| SMANotifyHandler.cmd | SMANotifyHandler_WinAuth.cmd |
| SMARequestRouter.cmd | SMARequestRouter_WinAuth.cmd |
| SMAStartTimeCalculator.cmd | SMAStartTimeCalculator_WinAuth.cmd |
Hung Script Configuration
For each of the Application Hung Scripts and supplemental scripts, complete the following procedures to configure each file:
Configure a Hung Script
- Log in as a local administrative user.
- Right-click on Start and select Explore.
- Go to the Folders frame.
- Browse to the <Configuration Directory>\SAM\ directory.
- Right-click on the desired hung command file (e.g., SAMHung.cmd) and select Edit.
- Search for <insert SMTP server name here> and replace that text with the SMTP server name.
- Search for <insert email recipient here> and replace that text with the recipient email address.
- Search for <insert domain name here> and replace that text with the email domain name.
- Search for <insert drive letter> and replace that text with the drive letter containing the SAM installation. Also, ensure that the path to the SAM folder is correct.
- Click File > Save in the menu bar.
- Repeat Steps 6 - 10 for each hung command file.
Configure a Supplemental Hung Script
- Log in as a local administrative user.
- Right-click on Start and select Explore.
- Go to the Folders frame.
- Browse to the <Configuration Directory>\SAM\ directory.
- Right-click on the desired supplemental hung command file (e.g., SAMHung.cmd) and select Edit.
- Search for all occurrences of <DB server name> and replace that text with the OpCon database server name.
- Search for all occurrences of <path to output file> and replace that text with the path to the desired location for output files from the SQL commands.
- Search for all occurrences of <DSN> and replace that text with the DSN to the OpCon database.
- If editing a SQL Authentication command file, search for all occurrences of <sa password> and replace that text with the OpCon database sa password.
- Click File > Save in the menu bar.
- Repeat Steps 6 - 10 for each supplemental hung command file.
Operating the SMA Service Manager
To control the SMA Service Manager status, use the Windows Service Control Manager. The procedures below explain the process of starting and stopping the SMAServMan.
Start the SMA Service Manager
After properly configuring the SMA Service Manager, complete the following steps to start the service:
- Use menu path: Start > Control Panel.
- In the Control Panel window: Double-click the Administrative Tools icon.
- In the Administrative Tools window: Double-click the Services icon.
- In the Services window: Scroll down to the SMA OpCon Service Manager service.
- Change the SMAServMan's Startup Type to Automatic (Delayed Start) using the following steps:
- Double-click on SMA OpCon Service Manager.
- Select Automatic (Delayed Start) in the Startup type drop-down list and click OK.danger
SMA Technologies recommends leaving the SMA OpCon Service Manager service set to Automatic (Delayed Start) to avoid potential issues at startup time while other services and programs start up.
- In the Services List: Click on SMA OpCon Service Manager then click Start.
- View the SMAServMan, SAM, Critical, SMANetCom, and SMANetComTrace logs to verify that the SAM and SMANetCom connected successfully to the database. Use menu path: Start > Programs > OpConxps > Log Monitors > Log File Name.
Stop the SMA Service Manager
If necessary, complete the following steps to stop the SMA Service Manager:
- Use menu path: Start > Control Panel.
- Double-click the Administrative Tools icon.
- Double-click the Services icon.
- Scroll down to the SMA OpCon Service Manager service.
- Click on SMA OpCon Service Manager and click Stop.