Copy Files from Test to Production
Previously published versions of this Reference Information topic described manual procedures for copying database files between LSAM environments. That method is no longer supported due to changes in the database (specifically, the introduction of automatically generated "as identity" keys for some files). Instead, this topic documents how to use LSAM menu functions to easily engage Agent programs that handle the complexities and are able to transfer data reliably.
Since LSAM version 18.1, it is important to note the two key fields of information that represent the software patch level of this Agent software, which are critical to successful Export/Import operations.
- PTF Level: This is the value that is used at the lowest level to represent the actual patch level of the LSAM software. Although the "PTF Name" (also known as the "PTF Number" field, such as PTF181006) is still a unique key that may be used to reference a patch, SMA will request the "PTF Level" value from a client to determine that client's patch level for this Agent software. For example, it would be common that the PTF Level number of a PTF Named "PTF181006" to be 006. But this is not always true, and the PTF Level number is the master control that is used to designate the software patch level of the LSAM.
- DB Level: The database level of the LSAM software indicates a cut-off point among the PTF Levels where database changes were made using the LSAM software patching tools. These enhancements to the Agent are small enough that a simple patch can install them, rather than requiring a full LSAM Upgrade to a new Version. The DB Level is the control level that is used to match LSAM environments when the LSAM Data Export/Import tool is being used. It is no longer required that two LSAM environments must match exactly at the PTF Level (although that is good practice). Only the database level MUST match. A change in the DB Level also marks a point among all the PTFs where a Rollback operation is usually not permitted. That is, the PTF Rollback capability will usually prevent rolling the software patches backwards past a DB Level boundary, although this may sometimes be permitted. But a single PTF rollback will not move the DB Level backward.
How to Export and Import Data
This is a step-by-step outline of how to perform LSAM data exporting and importing, including the optional rollback process. The reasons for these steps are explained in the next section, where there is a flow chart of the whole Export/Import process. It may also be helpful to refer to the Screens and Windows section later in this topic for more detail about each step in the procedure.
SMA has published a detailed example with instructions for automating the LSAM Data Export/Import process. SMA recommends learning about how Export/Import works, here, and then consider implementing the automated solution. This solution is posted in the SMA Innovations Lab, at the SMA GitHub repository:
https://github.com/smatechnologies/ibmi-export-import/blob/master/UserGuide-Automate-Exp-Imp.md
Automated Export/Import would be especially helpful for service bureaus who operate many IBM i partitions. But it is certainly also useful for sites who maintain a separate IBM i LSAM Test environment, where automation solutions can be exported/imported to the Production LSAM environment.
Configure Export/Import options (one time)
- In the command line, enter SMAGPL/STRSMA. For more information on STRSMA command parameters, refer to the STRSMA Command.
- Enter 3 to select the Events and Utilities sub-menu in the SMA Main Menu.
- Enter 10 to choose the Data Export/Import Utilities Menu in the Events and Utilities Menu.
- Enter 7 to choose Export/Import options configuration in the Data Export/Import Utilities menu.
- Refer to the Screens and Windows section, later in this topic, for detailed instructions about the fields in the configuration function. Note the library name where export and import save files will be stored - these can be changed, but the SMALOG library benefits from automatic LSAM procedures to purge old save files.
- When two LSAM environments exist in the same IBM i partition, it is recommended that the "Next Export Library number" should be set to start at some high range, such as 100001, in one of the environments. This will help prevent conflicting save file names in case data will be exported in both directions between two environments. Use a similar, but different high range for a third or fourth environment, such as when multiple environments are required for development and testing.
- Some sites using separate IBM i partitions or machines may need to carefully consider the Target Release value that is used for the data export save file. There is a control field where a specific IBM i version code may be specified, if necessary. But the normal default is "*OSDFT" which means to use the version code of the current system. This only needs to be changed if the destination partition for the import process is running an older version of IBM i. There is a similar TGTRLS option lower down in the control fields for the pre-import data backup save file, but it would be unusual to not accept the default of *OSDFT for this field. Please contact SMA Support if there are questions about using these Export/Import procedures between two different versions of IBM i.
Select LSAM primary master records for Export - using the LSAM menus
- Choose one of the LSAM features for data export in the SMA Main Menu. For example, enter 2 to choose the Message management menu.
- Enter 1 to choose the Message Management Parameters maintenance function in the Message management menu.
- Enter 8 (= Export) to choose one or more of the Message management parameter records for export. Press Enter to start the actual export process. The Work with Export Batches program is called directly from within the Work with function.
- If there is already an export batch that has a matching Group ID for this LSAM feature, skip the next two steps and proceed to step 8) to select an existing open batch.
- If there is no matching or open Export batch control press F6 to add a new Export batch control record. The Group ID for a new batch control record is forced to match the current LSAM feature.
- Complete the definition of the new Export batch by typing a descriptive name for the batch. Press Enter to complete registration of the new batch control record. The display returns to the list of Export batch control records.
- Type a 1 next to the desired (or new) Export batch control record to select it, then press Enter to continue with the process of exporting the (next) selected LSAM master record (and all dependent file data) to the temporary library that was automatically created for the batch control record.
- After the data is exported to the temporary library, the screen shows a definition of the Export data batch and it offers an option to immediately close out the batch and create the Export save file by pressing function key F14. Do not press F14 if more records will be selected from the same LSAM feature and they should be included in the same Export batch. (Closing out a batch is explained below under Manage Export Batches.)
- If multiple LSAM primary master records were selected for exporting, repeat steps 8) and 9) in this segment of instructions. When all record exporting has completed, the screen will return to the list of the LSAM master records in the original Work with list for this LSAM feature.
Manage Export batches
- If function key F14 was used above to immediately close an Export batch and prepare the Export save file, then skip to step 8) below.
- Enter 3 to select the Events and Utilities sub-menu in the SMA Main Menu.
- Enter 10 to choose the Data Export/Import Utilities Menu in the Events and Utilities Menu.
- Enter 1 to choose Work with Export Batches. in the Data Export/Import Utilities menu.
- Enter 8 (= Export) to choose one or more of the Message management parameter records for export. Press <Enter> to start the actual export process. The Work with Export Batches program is called directly from within the Work with function.
- Enter 1 to choose the Message Management Parameters maintenance function in the Message management menu.
- Enter 8 (= Export) to choose one batch that has a status code of "A" to begin the export process.
- The screen to Initiate Data Export Batch appears. This is the same screen that will appear if an immediate export was selected using function key F14 above. Review the parameters that define how the export process will work. Refer to the Screens and Windows section of this topic, below, for detailed information about the fields on this screen.
- [Take note of the export save file name] and the library where the export save file will be stored, then press Enter to start the export batch preparation process.
- The program edits the batch export control values, then presents the same display with a red instruction line that says to press F14 to confirm the values and start the export process.
- If the option to Submit job to batch? was set to 0, the export process will be completed by the interactive job and a completion message will appear at the bottom of the screen. If the Submit option was left at 1 the export process will be submitted to a batch job and the name of the job will be displayed in a message at the bottom of the screen.
- Review the Export batch report. This report will either be a spool file belonging to the current interactive job, or it may be found under the name of the job that was submitted to batch.
Manage Import batches
- It is the user's responsibility to copy or move a save file that is the export data batch to the correct library in the correct IBM i partition where the data will be imported. If the target IBM i LSAM database exists within the same IBM i partition, then it is not necessary to move the export batch save file(s) - they may be imported from the same library (such as SMALOG).
- It is also the user's responsibility to make a backup of the LSAM database library (default name is SMADTA) before performing any data import operation. There are rollback tools that can help if an error occurs, but the only way to guarantee protection of the database is to make a new backup before each import operation, and then to keep track of which backups are associated with which import batches.
- To start the import process, enter the LSAM menu for the target IBM i LSAM environment.
- Enter 3 to select the Events and Utilities sub-menu in the SMA Main Menu.
- Enter 10 to choose the Data Export/Import Utilities Menu in the Events and Utilities Menu.
- Enter 4 to choose Work with Import Batches in the Data Export/Import Utilities menu.
- Typically, there will be no import batches listed. Press function key F6 to start the process of searching for export batches brought to the local IBM i partition.
- The display will show a list of save files that are not already imported in the default library (named in the Export/Import options configuration). If a different library should be searched, press the Shift+Tab keys to move up to the "Search new library" field and then press Enter to display a new list.
- Type a 1 next to one save file that should be imported, then press Enter to being the Import process.
- The display shows the "Add Import Batch" control screen. If the import save file exists within the same IBM i partition as the export environment, warning messages and override options are offered. Refer to Screens and Windows later in this topic for detailed information about each field and option. In this case the default option set suggests Replace option "A" to use an existing export work library for the import process.
- When the selected save file has been accepted for import, the display shows instructions to press Enter to continue.
- The display will return to the list of save files available for importing. Either repeat steps 8) and 9) to set up additional import batches, or press Enter (with no options typed) or F12 to return to the list of batches available for import.
- Type 8 next to the batch that should be imported, then press Enter to continue.tip
If the target (import) LSAM environment does not match the LSAM version and DB (database) level of the source (export) LSAM environment, an error message is displayed and the import process is not allowed. In this case it is possible to exit the import process and complete cumulative PTF application to bring the target LSAM environment up to the same level as the source environment. Then it is possible to return to this procedure and complete importing the batch.
- When the import is performed within the same IBM i partition as the export, a warning will appear on the display for Initiate Data Import Batch. In this case, choose an option for the field label "RSTLIB (1) or Skip (0)?" Typically, option 0 is a good choice because it avoids the unnecessary step of restoring the import work library from the save file, since that library already exists on the system. Type any other processing option changes, then press Enter to continue.
- The system displays a final confirmation screen for the import batch after editing the batch control details. If the values appear acceptable, press F14 to start the actual import process.tip
The import process performs updates to the target IBM i LSAM database. During this process, a backup save file will be created to contain any data records that will be replaced by the import process. It is possible to rollback an import batch using option 9 from the Work with Import Batches display, in case the import causes any problems or appears to corrupt data.
- If the import process was submitted to batch, a message appears at the bottom of the display naming the submitted job. Use this job name to find and review the import posting report.
- If the import process was allowed to run in the interactive job, a message appears at the bottom of the display reporting the Group, Batch and SAVF that were successfully imported; or else, an error message could be displayed if the import failed. In either case, work with the current interactive job to find and review the import posting report, to assure the results are as expected.
- After the export and import processes are completed, the list of batches available in lists from the Export/Import sub-menu functions will not show the completed batches, unless function key F15 is used to change the list subset rules.
Data Export/Import Process Explanation
Under LSAM sub-menu 3 - Events and Utilities Menu, there is an option 10 that branches to a sub-sub-menu called the Data Export/Import Utilities Menu. The functions on this menu support copying LSAM master file data from one LSAM environment, such as a Test environment, to another, such as a live Production environment.
Most of the IBM i LSAM menu-configured features are supported by complex sets of data that reside in more than one database file. It is necessary to copy all of the related data from each file whenever a primary master record should be copied between LSAM environments. The term "primary master record" refers to the main database file that defines each of the LSAM's features. In general, there is a separate LSAM sub-menu for managing each of these features. Examples of the features, with corresponding menus, include Job Tracking, Message Management and Operator Replay scripting.
Ideally, every time a new definition is added to one of these LSAM features, that definition should first be configured and tested in a Test environment, so that Production jobs and files will not be at risk. After all the testing is done, then the formal LSAM Export/Import process can be used to select primary master records and to transfer that record, along with all dependent data, from the Test environment to the Production environment. The LSAM Export/Import functions each produce a printable report to document the transfer process and, when necessary, to provide details about any errors or exceptions that are encountered. (It is important to review the posting reports before relying on the imported data.)
The file Export process begins from the master Work With function in each of the LSAM sub-menus. For example, to export a Message Management definition, begin from the sub-menu option 1 - Message management parameters. The display that lists all the message management parameters shows an option 8=Export near the top. Typing option 8 next to one or more of the list entries marks each record for export, and then pressing the Enter key begins the export process for each record, one at a time.
Using this selection method, a batch of one or more primary master definitions is assembled. The batch will include any required records from sub-files that depend on the primary master record. Batches of export data are separated according to the LSAM feature. That is, a batch of Message management records will only include records from that LSAM function, whereas a batch of Operator Replay scripts will only include Operator Replay script data. The term used by the Export/Import tools for each of these different LSAM functions is "Group", and each group has a unique Group ID.
Eventually, one or more batches of export data will be created, each with its own Batch ID and the correct Group ID. After one or more batches have been created, the Data Export/Import Utilities Menu is used to manage the Export batches on the source system. When the final export action is specified for a batch, the temporary library that was used to create the batch is saved into an IBM i save file (SAVF). At this point, the batch control record on the source machine is set to a status that closes the batch.
Any user-defined process may be used to copy the export batch save file(s) to the target LSAM machine. The target LSAM environment may exist within the same IBM i partition, in which case it is not necessary to copy or move the save file(s), unless the user prefers to keep Import work in a separate library from Export work.
After the Export batch save files are confirmed to be located in the appropriate work library for the target LSAM environment, the Import process starts from the Data Export/Import menu in the LSAM menu system of the target environment. There is an option on the menu for Work with Import Batches.
Further discussion about the Import process follows the general flow diagram that follows.
Export/Import Process Flow
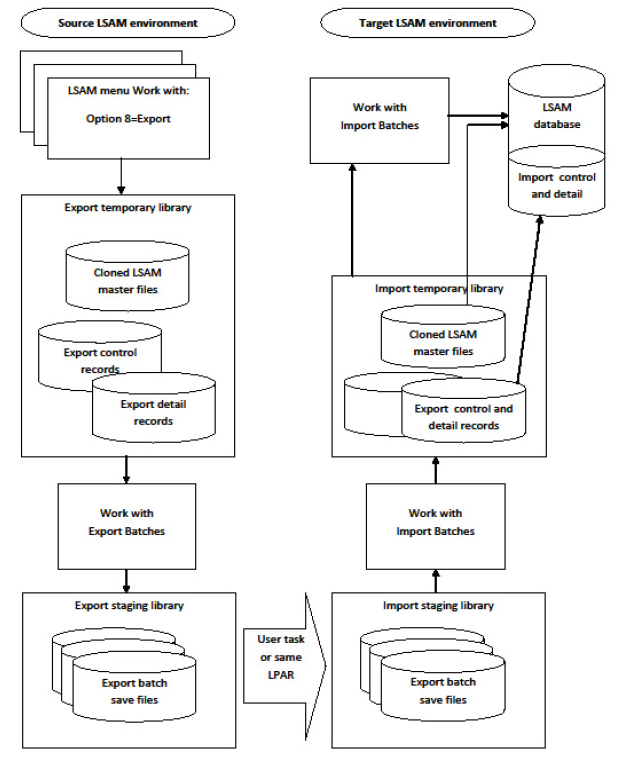
The Work with Import Batches function uses the F6=Add function key to start a search for Import save files within the target IBM i partition. The default Import library that was registered in the Export/Import options configuration function is searched first, but the user may change the name of the library to search. One at a time, Import save files may be selected to begin the data import process.
When an Import save file is selected for the actual import, the save file is used to restore a copy of the Export temporary library onto the disk of the target IBM i partition or machine. If the Import takes place in the same partition as the Export, the user is notified of an option to skip this step and just use the existing temporary library for the batch. After the data transfer work files are ready in the temporary library, their contents is use to edit the batch against the target LSAM database. A posting report is produced as the batch of data is processed. One by one, records are added to the appropriate files in the target LSAM database.
During the Import process, any records that will be replaced in the target database are first copied to a backup file in another temporary library, referred to as the Rollback library. At the end of the Import process, the Rollback temporary library is saved to an IBM i save file and the name of the Rollback save file is registered in the Import batch control record. If the results of the Import prove unacceptable, there is an option (9) on the list of Import batch control records that supports a Rollback request. When requested, the Rollback process removes all the data that was imported, and then it replaces the records (if any) that were kept in the Rollback temporary library copies of each affected LSAM database file.
Managing Export/Import Data Integrity
Great care must be exercised when managing export and import data batches. The system is unable to assure that data being imported is appropriate for the target database. However, the export/import tools are designed to preserve the integrity of individual batches of data, so that all logically dependent data is exported and imported together, and the dependency relationships are preserved. Also, during the import process, the LSAM import routines perform low-level data management that helps to update specific data fields that are expected to change when the data is imported into a different database.
Here are some possible errors that could occur when managing imported data:
- It is possible to corrupt the LSAM database if import batches are posted out of sequence.
- LSAM Dynamic Variables and Operator Replay token variables could contain current values that are specific to a system or an LSAM environment. The export/import tools cannot interpret the value contents of variable fields, therefore, it is necessary to use the batch import posting list to identify each variable table file record and then to manually inspect the value of each variable after the import to make sure that the value is appropriate for the target system.
- Message Management data comparison reference values cannot be controlled by the import tools. Therefore, it is recommended that each imported Message Management Parameters record be inspected after an import to make sure any message text comparison value still applies.
- Operator Replay script steps may contain screen content comparison rules that could include reference values that are specific to a system or to an IBM i LSAM environment. Use the import batch posting report to identify the script steps that were imported and inspect each step to be sure the step qualifier comparison data is valid in the target LSAM environment.
- Captured Data Response Rules, used for Message Management data capture, Operator Reply screen data capture and SCANSPLF report data capture can contain specific comparison reference values that might be specific to an IBM i partition or to an LSAM environment. Again, review the import posting report to identify any captured data response rules and then inspect each rule after the import to be sure any hard-coded reference values are still appropriate.
- In general, anywhere that a library name is specified, it is possible that library name could be different within a different IBM i partition or a different IBM i LSAM environment. It is necessary to become familiar with the contents of each LSAM function that might be exported and imported in order to identify data like this that is subject to change for a different LSAM environment. Obviously, soft references, such as using an LSAM Dynamic Variable or an Operator Replay token/variable, should make master files easier to adapt if the data will ever be exported to another environment.
Rolling Back An Import Batch
Despite careful attention to the guidelines suggested above, it is possible that importing a batch of data could create an unacceptable configuration of LSAM data. In this case, there is an option to remove, or roll back, any batch of imported data. To do this, use option 9 from the function Work with Import Batches (under the Export/Import Data Menu, this is function 4).
The rollback process uses the LSAM data backup save file that was automatically created during the import process in order to put back data that previously existed in the LSAM database. The import save file contents are also used to identify and delete any new data that had been added to the database during the import, data which was not replaced (and so there is no replacement data to restore from the backup save file).
Once an import batch has been rolled back, the original batch should not be used again. Instead, it is safer to start over from the export process in the source LSAM environment and to create a new batch of data.
It is possible that if an import batch is rolled back after some later batch was imported, the rollback could cause data in the LSAM database to become corrupted. It is the user's responsibility to know about the contents of each import data batch in order to prevent possible overlaps like this. If LSAM data does become corrupted after a rollback operation, manual maintenance using LSAM menu functions is the only normal recourse for application users to properly reconstruct the LSAM data. In severe cases, please contact SMA Support for assistance with analysis and data restoration.
A good way to prevent disaster is to make a backup of the LSAM database library (base name SMADTA) before performing any import batch posting or a rollback operation.
List of Exported File Names and Descriptions per Export Group
Fields name
OPRRPY Operator Replay file group
- OPRRPYF00: Operator Replay script master file
- OPRRPYF10: Operator Replay script steps
- OPRRPYF20: Operator Replay variables (tokens) table file
- LSAJORF50: Capture Application Key and Description
- OPRRPYF40: Screen data capture rules
- OPRRPYF50: Captured data response rules
- LSAVARF00: Dynamic Variables table file
OPRRPYCAPT Operator Replay Screen Capture Apps
- LSAJORF50: Capture Application Key and Description
- OPRRPYF40: Screen data capture rules
- OPRRPYF50: Captured data response rules
- OPRRPYF20: Operator Replay variables (tokens) table file
- LSAVARF00: Dynamic Variables table file
TRPMSG LSAM Global Message Management
- TRPMSGF00: Message Queue and Message ID response master file
- OPRRPYF20: Operator Replay variables (token) table file - may be loaded by response rules
- LSAJORF50: Capture Application Key and Description
- TRPMSGF30: Message Data Capture rules
- OPRRPYF50: Captured data response rules
- LSAVARF00: Dynamic Variables table file
TRPMSGCAPT Messsage Data Capture Application
- LSAJORF50: Capture Application Key and Description
- TRPMSGF30: Message Data Capture rules
- OPRRPYF50: Captured data response rules
- OPRRPYF20: Operator Replay variables (tokens) table file
- LSAVARF00: Dynamic Variables table file
SCANSPLF Scan Spool File Utility
- LSAJORF50: Capture Application Key and Description
- LSAJORF40: Scan Spool File Scan Rules master file
- OPRRPYF50: Captured data response rules
- LSAVARF00: Dynamic Variables table file
CAPJOB Capture Job Feature
- TRKJOBF00: Job Tracking Parameters master file
- JOBLDAF00: IBM i Job Local Data Area contents
- DBFCMDSRC: Command line source members
- LSAVARF00: Dynamic Variables table file
TRKJOB Job Tracking and Queuing
- TRKPARF10: Job Tracking parameters master file
- LSAVARF00: Dynamic Variables table file
RSTMOD Restricted Mode feature
- SAVRSTF20: Restricted Mode script master file
MLTJOB Multi-Step Job Scripting feature
- MLTJOBF00: Multi-Step Script master file
- MLTJOBF10: Multi-Step Script Step master file
DYNVAR LSAM Dynamic Variables (when exported individually)
- LSAVARF00: Dynamic Variables table file
- LSAVARF10: Dynamic Variables AUX Table file
Data Export/Import Screens and Windows
Data Export/Import Utilities Menu
S218CBBW DATA EXPORT/IMPORT UTILITIES MENU 00/00/00
CLEWIS 20:50:30
Select one of the following:
1. Work with Export batches
2. Export a data set (LSAEXPDTA)
3. Display Export Activity/Error Log
4. Work with Import batches
5. Import new data set (LSAIMPDTA)
6. Display Import Activity/Error Log
7. Export/Import options configuration
Selection or command (C) SMA 1995,2010
===>
F3=Exit F4=Prompt F9=Retrieve F12=Cancel
F13=Information Assistant F16=System main menu
Menu Pathways
Main Menu > Events and Utilities menu (#3) > Data Export/Import Utilities menu (# 10)
Options
The options displayed on this menu are explained in the following sections of this document. Type an option number in the Selection or command line and press <Enter> to begin using any of the options.
Export/Import Options Configuration
The configuration options for data export/import should be reviewed and set (press <Enter> to update) before using any of the export or import functions.
EXICFGD301 - LSAM Data Export/Import Configuration
Menu Pathways
Main Menu > Events and Utilities menu (#3) > Data Export/Import Utilities menu (# 10) > option 7
Usage Notes
When two LSAM environments exist in the same IBM i partition, it is recommended that the "Next Export Library number" should be set to start at some high range, such as 100001, in one of the environments. This will help prevent conflicting save file names in case data will be exported in both directions between two environments. Use a similar, but different high range for a third or fourth environment, such as when multiple environments are required for development and testing.
If two or more LSAM environments will share the library SMALOG to store export/import save files, coordinate which environment will manage SMALOG contents with the SMARGZ command to purge aged save files. For more information about managing files stored in the SMALOG library, please refer to IBM i LSAM Configuration, subject LSAM Database Maintenance. A description of how the SMARGZ command may be used for this purpose is found in Commands and Utilities.
The job description and job queue fields are optionally used whenever an export or import procedure is set to run as a batch job instead of running interactively from the export or import request screens.
On the next screen use the field "Days to retain Ex/Imp data" to indicated to the LSAM daily maintenance server job when Export/Import control data and the related working libraries should be deleted after their last use.
Fields
- Next Export Library Number: This control field is automatically updated every time a new export batch is created. Changing the starting value is only recommended for alternate LSAM environments that may reside in the same IBM i partition. In that case, it is recommended to set the starting number high range to a value such as 10001, so that there will be no library or save file name conflicts in case data is ever exported and imported in both directions between two LSAM environments.
- Export save file library: This is the library where the Export tools will put the final save file that results from preparing a batch of data for export. Using the default value of SMALOG makes it possible to take advantage of the LSAM's tools that can be used to automatically purge aged save files from this library. However, it may sometimes be convenient to specify an alternate library name when working within a test LSAM environment.
- Export save file TGTRLS: This value controls the Target Release (version of IBM i) that is assigned to the Export data save file. Specify a release version if the data will be imported on an IBM i partition that is running an earlier version of IBM i. VALUES: *OSDFT = The default is the version of the current IBM i partition. VnRnM0 = Specify the version code of the destination partition, if it is older than the urrent partition. For example, if the current partition is at V7R2M0 but the data will be imported into a partition running V7R1M0, then the value V7R1M0 must be specified in this field.
- Export job description: The job description used by default when an export process is flagged to be submitted to batch.
- (Export) Job description library: The library location of the Export job description
- Export job queue: Values: *JOBD or a specific job queue name. The job queue used when submitting an export process to a batch job.
- (Export) Job queue library: The library location of the Export job queue
- Import save file library: The library that will be searched by default after selecting F6=Add from the Work with Import Batches function. Using the default value of SMALOG makes it possible to depend on the LSAM automatic purging of aged save files from this library. Since the default value is the same for both export and import save files, it might sometimes seem more convenient to use a different library for import save files when two LSAM environments are installed within the same IBM i partition. However, the Import tools support special overrides that allow using just one library for exporting and importing data batch save files to/from the same library.
- Import job description: The job description used by default when an import process is flagged to be submitted to batch.
- (Import) Job description library: The library location of the Import job description
- Import job queue: Values: *JOBD or a specific job queue name. The job queue used when submitting an import process to a batch job.
- (Import) Job queue library: The library location of the Import job queue
- Backup save file library: The name of the library where a save file will be stored that holds the IBM i LSAM database values from before the Import process is executed. The backup save file will be used if the Rollback option is selected.
- Backup save file TGTRLS: This value controls the Target Release (version of IBM i) that is assigned to the pre-import data backup save file. Specify a release version if the backup data will ever be used to restore data to the LSAM on an IBM i partition that is running an earlier version of IBM i. This is highly unlikely. In most cases, the default value of *OSDFT should be used. VALUES: *OSDFT: The default is the version of the current IBM i partition. - VnRnM0: Specify the version code of the destination partition, if it is older than the current partition. For example, if the current partition is at V7R2M0 but the backup data will be restored into a partition running V7R1M0, then the value V7R1M0 must be specified in this field.
- Days to retain Ex/Imp data: The number of days after the last active use of Export or Import control data and any associated temporary libraries when the LSAM daily maintenance server job will automatically remove aged data.
Functions
- F3=Exit: Quits the window and returns to the menu without performing any update.
- F12=Cancel: Quits the window and returns to the menu without performing any update.
- F20=Work with existing libraries: This convenience function locates and displays a list of any export/import temporary work libraries that may exist within the current IBM i partition. Authority to the IBM command WRKOBJPDM is required to use this function key. The IBM command provides convenient access to powerful object management tools that permit viewing and working with the contents of libraries and also deleting libraries. Use caution with this function in order to avoid deleting any active export save files that are still needed to complete data batch transfers.
Work with Export Batches
This function is used to create new export batch controls and also to complete the process of collecting an export batch into a save file that can be transported to another LSAM environment. Use individual LSAM master file maintenance functions that support option 8=Export to add records into an export batch. Those functions will automatically enter this Work With function in order to support selecting an existing batch or to create a new batch control record. After the data has been exported into the temporary working library that is linked to the batch control record, the LSAM maintenance programs offer an immediate branch back to this function for the purpose of closing out a batch and making it ready for export. Otherwise, batches remain open until this function is used to close out a batch and compress it into an IBM i save file.
EXIEX0R1 - Work with Export Batches
Menu Pathways
- Main Menu > Events and Utilities menu (#3) > Data Export/Import Utilities menu (# 10) > option 1
- Direct access from LSAM master file maintenance > option 8=Export
Fields
- LSAM Env: The name of the current LSAM environment, from which data is being exported.
- Vers: The version number of the current LSAM environment. (Must match the target LSAM environment where data will be imported.)
- PTF/DB#: The PTF level of the current LSAM environment is shown first, followed by the PTF database level. The PTF level is for information only, in case of differences in the behavior of certain programs, but it is the database level that must match the target LSAM environment where data will be imported.
- Search: A value entered into this field will be compared to the entire contents of every batch control record until a match is found. Press Enter to start a new search, or use function key <F16> to continue a search to the next record.
- Subset Group: Shows the Group value that limits the current list on display. Press <F13> to change the Group Subset rule.
- Subset status: Shows the Status value that limits the current list on display. Press <F14> to change the Status Subset rule.
- Last search: Shows the search argument that was last used, where the cursor will be placed next to the first record in the list that contains a matching value. Note that the matching value may not show on this list display, in which case option 5=Display can be used to see the matching value in the control record. This Last search value may also be used to continue a search to the next record if function key <F16> is pressed while a value is displayed in this field.
- Opt: <Tab> to a row in the table and enter an option.
- Group ID: The Group label that is assigned to each batch. Group labels are controlled by the LSAM software and they cannot be changed because each batch is assigned to only one type of data records, and records from different Group IDs cannot be mixed within a single batch of export data.
- Batch ID The user-assigned name that helps to identify the data that is, or will be added to a batch. This field is both a key field used to identify a batch and a description field.
- Sts: The current status of the batch record. Use option 5=Display to see an interpretation of the status code.
- Lib/SAVF: The name of the temporary library where cloned copies of LSAM master files are used to store exported data and export control information. The save file that will be used to transport export data to another LSAM environment uses the same name as the automatically assigned library name. The numeric portion of this Lib/SAVF name is derived from the Export/Import Configuration data control field.
- Src System : Source system: The internal identifier of the IBM i partition where the LSAM environment from which data is being exported exists. This field has more significance when it is displayed in the similar list of Import Batches, since it will always be the same for all Export batch control records.
- Src LSAM : Source LSAM: The OpCon machine name for this LSAM environment. This field has more significance when it is displayed in the similar list of Import Batches, since it will always be the same as the display heading field for all Export batch control records.
Options
- 1=Select: When this list program is called directly from an LSAM master file maintenance program, use option 1 to select an open batch that can receive the data being selected with option 8=Export from the LSAM file maintenance function.
- 4=Delete: To delete an entire Export batch, including the control and detail records as well as any existing library and/or save file, type 4 next to the batch record and press <Enter> to proceed to the Delete Export Batches screen where the delete action will be confirmed (for all selected records at once).
- 5=Display: To view the complete batch control record, type 5 next to the batch record and press <Enter> to proceed to the Display Data Export Control screen.
- 7=Details: To view a list of all the LSAM master file records that belong to an export batch, type a 7 next to the batch record and press <Enter> to proceed to the Work with Export Batch Details list display.
- 8=Export: Type option 8 next to any export batch that shows a status of 'A' and press <Enter> to initiate the process of closing out that batch and compressing the temporary export staging library to an IBM i save file.
Functions
- F3=Exit: Quits the list and returns to the menu.
- F5=Refresh: Reads the export control file again and reloads the list display.
- F6=Add: Proceeds to the Add Data Export Control screen.
- F9=Print: Generates a printable report of all the records currently on display, subject to the current subset restrictions.
- F12=Cancel: Quits the list and returns to the menu, without completing any options that have not already been executed.
- F13=Subset GRP: Causes a window to be displayed where the subset rule for the Group value may be changed.
- F15=Subset STS: Causes a window to be displayed where the subset rule for the Status value may be changed.
- F17=Top: Positions the list display to the first record that qualifies to appear in the current list of control records.
- F16=Search next: Starts, or continues a search for the value that was typed in the Search argument field at the top, right of the display. When used to continue a search, the argument value used appears in the "Last search" field at the top, right of the display, and the display will be positioned with the cursor on the Opt field next to the record that matches the search argument.
- F18=Bottom: Positions the list display to the last record that qualifies to appear in the current list of control records.
- F24=More keys: Shows other function keys that may be used.
Work with Export Batches - Windows
EXIEXW01 - Subset by Group Window
Subset Export Control Records by Group
EXIEX0W1
Subset by Group
Select subset: 9
1. OPRRPY
A. OPRRPYCAPT
2. TRPMSG
B. TRPMSGCAPT
3. SCANSPLF
4. CAPJOB
5. TRKJOB
6. RSTMOD
7. DYNVAR
8. MLTJOB
9. Show all
F12=Cancel
Fields
Select subset: Type a number from the list below and press <Enter> to change the subset rule for the list of Export Batch control records.
Group values: The list of LSAM master record groups supported includes:
- OPRRPY = Operator Reply scripts, steps and related files
- OPRRPYCAPT = Operator Reply screen capture applications and rules
- TRPMSG = Message Management Parameter records and related files
- TRPMSGCAPT = Message cata capture applications and rules
- SCANSPLF = Scan Spool File rules and related records
- CAPJOB = Captured Job definitions and related files
- TRKJOB = Job Tracking and Queuing definitions and related files
- RSTMOD = Restricted Mode script records
- DYNVAR = LSAM Dynamic Variable table records (these will also appear as a related file to most of the other Groups)Show all = remove Group ID filtering of the control records list
- MLTJOB = Multi-Step Job Scripts
Functions
F12=Cancel: Quits the prompt window and returns to the list display without changing the current subset rule.
EXIEX0W2 - Subset by Status Window
Subset Export Control Records by Status
EXIEX0W2
Subset by Status
Select subset: 9
1. blank = no details
2. A active, add details
3. X selected for export
4. E export error
5. Z export finished
8. All active
9. Show all
F12=Cancel
Fields
- Select subset: Type a number from the list below and press <Enter> to change the subset rule for the list of Export Batch control records.
Functions
F12=Cancel: Quits the prompt window and returns to the list display without changing the current subset rule.
F6 = Add Data Export Control
- Screen Title: Add Data Export Control
- Screen ID: EXIEX0R2
Menu Pathways
- Main Menu > Events and Utilities menu (#3) > Data Export/Import Utilities menu (# 10) > option 1 > F6=Add
- Direct access from LSAM master file maintenance > option 8=Export > F6=Add
Fields
- Heading fields: Refer to Group values description in the previous section.
- Group ID: The Group label that is assigned to the batch. The Group label is controlled by the LSAM software when this screen is reached from direct access via option 8=Export from within a different LSAM file maintenance function, or it can selected from the controlled list of supported values when a new batch control record is being created from the Work with Export Batches list function. Group IDs cannot be changed because each batch is assigned to only one type of data records, and records from different Group IDs cannot be mixed within a single batch of export data. (Refer to the window of Group IDs above for a list of the available values.)
- Batch ID: The user-assigned name that helps to identify the data that is, or will be added to a batch. This field is both a key field used to identify a batch and a description field.
Functions
- F3=Exit: Quits the Add function and returns either to the LSAM sub-menu, or to the list display of the LSAM maintenance function where option 8=Export had been entered.
- F4=Prompt: When the cursor is positioned in the Group ID field, <F4> causes a window of supported Group ID values to appear from which a value may be selected and returned to this field. (Refer to the window for subsetting by Group ID for a representation of the prompting window that will appear.)
- F12=Cancel: Quits the Add function and returns to the list display.
Option 4 = Delete Export Batches
EXIEX0R4 - Delete Export Batches
Menu Pathways
Main Menu > Events and Utilities menu (#3) > Data Export/Import Utilities menu (# 10) > option 1 > option 4
Fields
- All fields: Refer to Work with list display, above.
Functions
- F3=Exit: Quits the Delete function and return to the LSAM sub-menu.
- F12=Cancel: Quits the Delete function and returns to the list display, with any options "4" still showing.
- F14=Confirm: Starts the delete process that actually updates the LSAM files and removes one or more batch save files and temporary batch assembly libraries.
Option 5 = Display Export Batch Control Record
EXIEX0R5 - Display Data Export Control
Menu Pathways
Main Menu > Events and Utilities menu (#3) > Data Export/Import Utilities menu (# 10) > option 1 > option 5
Fields
- Heading fields: Refer to Work with list display, above.
- Group ID: The Group label that is assigned to each batch. Group labels are controlled by the LSAM software and they cannot be changed because each batch is assigned to only one type of data records, and records from different Group IDs cannot be mixed within a single batch of export data.
- Batch ID: The user-assigned name that helps to identify the data in a batch. This field is both a key field used to identify a batch and a description field.
- Status: The current status of the batch record. Possible values for Export batches are listed on the right side of this display
- Staging Library/SAVF: The name of the temporary library where cloned copies of LSAM master files are used to store exported data and export control information. The save file that will be used to transport export data to another LSAM environment uses the same name as the automatically assigned library name. The numeric portion of this Library/SAVF name is derived from the Export/Import Configuration data control field.
- Library for export SAVF: The name of the library where the export batch save file will be, or is stored after the batch is closed and fully exported. The default name for this library is set in the Export/Import Options Configuration.
- Source partition: The system ID of the IBM i partition from which the LSAM data was exported.
- Source LSAM environment: The OpCon machine name of the LSAM environment from which data was exported.
- Source LSAM version: The LSAM software version number of the exported data. This must match the version number of the target LSAM where the data will be imported.
- Source LSAM PTF/DB level: The PTF level of the current LSAM environment is shown first, followed by the PTF database level. The PTF level is for information only, in case of differences in the behavior of certain programs, but it is the database level that must match the target LSAM environment where data will be imported.
- Target partition: The system ID of the IBM i partition to which data is imported. (This value will be updated when the batch is imported.)
- Target LSAM environment: The OpCon machine name of the LSAM environment where the data is imported. (This value will be updated when the batch is imported.)
- Import pre-post backup: The name of the temporary library and save file that are used to backup any data that will be replaced when the batch is imported. (This value will be updated when the batch is imported, if any data will be replaced.) The backup save file supports the Rollback option.
- Last update time stamp: The system date and time that any activity was performed on this batch of data. After the status reaches Z = export completed, or E = export error, this time stamp is used to calculate the purge date by the LSAM daily file maintenance server program.
- Last update user ID: The user ID of the job that performed the last activity on this batch.
- Last update IBM i job: The identifier of the IBM i job that performed the last activity on this batch.
Functions
- F3=Exit: Quits the Display function and returns to the LSAM sub-menu, or to the program that called the Work with Export Batches function.
- F7=Details: Branches to a display listing the key fields of all files and records included in the data batch. This is the same list display as shows for the option 7=Details from the Export Batch list display.
- F12=Cancel: Quits the Display function and returns to the list display, with any unexecuted options still showing.
Option 7 = Work with Export Batch Details
EXIEX0R3 - Work with Export Batch Details
Menu Pathways
- Main Menu > Events and Utilities menu (#3) > Data Export/Import Utilities menu (# 10) > option 1 > option 7
- Main Menu > Events and Utilities menu (#3) > Data Export/Import Utilities menu (# 10) > option 1 > option 5 > F7
Fields
- LSAM Env: The OpCon machine name for this LSAM environment.
- V: The software version number for this LSAM environment.
- P/D: The PTF level of the current LSAM environment is shown first, followed by the PTF database level. The PTF level is for information only, in case of differences in the behavior of certain programs, but it is the database level that must match the target LSAM environment where data will be imported.
- Group: The Group label that is assigned to each batch. Group labels are controlled by the LSAM software and they cannot be changed because each batch is assigned to only one type of data records, and records from different Group IDs cannot be mixed within a single batch of export data.
- Batch: The user-assigned name that helps to identify the data in a batch. This field is both a key field used to identify a batch and a description field.
- Search content: Type a value in this field and press <Enter> to search for a record that has this value anywhere in the record. Sometimes the found value does not appear on the list display and it is necessary to use option 5=Display to view the record details that matched. Use function key <F16> to search for the next matching record after the current search value displays underneath this field.
- File Name: The name of the LSAM database file from which a record has been exported. (Refer to the table of file and field values below for descriptions.)
- Sts: The status of the detail record. (The detail record status is only for support research purposes. Refer to the export control record for the important status of the batch.)
- Key field content...(partial): The values of the key fields are shown as a string of characters. Use option 5=Display to see the individual key fields separated and labeled.
Options
5=Display: Branches to a screen that shows a formatted display of each export detail record. This screen formats and labels the key fields according to each different file.
Functions
- F3=Exit: Quits the Work with function and returns to the LSAM sub-menu, or to the program that called the Work with Export Batches function.
- F5=Refresh: Re-reads the export details file and rebuilds the list of details.
- F9=Prt: Prints a report of this list of detail records.
- F12=Cancel: Quits the Work with function and returns to the list of export control records, with any unexecuted options still showing.
- F16=Search next: After a new content search is started (refer to the Search content field in the table above), this function key continues the search on to the next matching record, looking for the value that shows in pink under the Search content field.
- F17=Top: Repositions the list display to the first record in the list.
- F18=Bottom: Repositions the list display to the last record in the list.
Option 5 = Display Export Batch Detail Record
EXIEX0R6 - Data Export Batch Detail
Menu Pathways
Main Menu > Events and Utilities menu (#3) > Data Export/Import Utilities menu (# 10) > option 1 > option 5 > option 7 > option 5
Fields
- LSAM Env: The OpCon machine name for this LSAM environment.
- V: The software version number for this LSAM environment.
- P/D: The PTF level of the current LSAM environment is shown first, followed by the PTF database level. The PTF level is for information only, in case of differences in the behavior of certain programs, but it is the database level that must match the target LSAM environment where data will be imported.
- Group: The Group label that is assigned to each batch. Group labels are controlled by the LSAM software and they cannot be changed because each batch is assigned to only one type of data records, and records from different Group IDs cannot be mixed within a single batch of export data.
- Batch: The user-assigned name that helps to identify the data in a batch. This field is both a key field used to identify a batch and a description field.
- File Name: The name of the LSAM database file from which a record has been exported. (Refer to the table of file and field values above for a list of files per Group ID.)
- Status: The status of the detail record. (The detail record status is only for support research purposes. Refer to the export control record for the important status of the batch.)
- Primary key: The internal key that is unique within the export details master file.
- File display priority: An internally assigned sequence number that helps to control the order in which files are presented in lists or reports of export details.
- Record write time stamp: The system date and time when this detail record was added to the export batch.
- Details record link key: An internal key that keeps dependent export records from other files coordinated with the single master record of the primary file within a Group. (Refer to the list of files per Group above, where the first file named is the primary file of the group.) This link key makes it possible to replace all records associated with a single master record, in case the master record gets exported a second time into the same export batch, while the batch remains open. Thus, it is possible to make changes in the source LSAM database and re-export the master record to the export batch as long as the export batch remains open.
- Record key fields: The individual key field values for each file are listed and labeled below this prompt. The fields that will show vary depending on the file name. (The fields could change in the future, if the LSAM database is revised by a software update.)
Functions
- F3=Exit: Quits the Display function and returns to the LSAM sub-menu, or to the program that called the Work with Export Batches function.
- F12=Cancel: Quits the Display function and returns to the list of detail records, with any unexecuted options still showing.
Closing an Export Batch
While an export batch is open, multiple linked groups of detail records can be added to the batch. Before a single batch gets too big, it is probably a good idea to close the batch and make it ready for movement to another LSAM environment. A batch could include only one LSAM primary master record, which may or may not have any dependent records for other files that belong to the same Group ID. A batch is not limited in size, but it is easier to edit the import process and to recover from potential errors if there is not a large number of master records in a single batch.
Closing a batch means that the temporary library used to assemble the various files for export is saved to a single IBM i save file that has the same name as the temporary library. During this process, the control record for the export batch has its status changed to 'Z' to indicate the batch is closed and ready for transportation to another LSAM environment.
There are two ways to close a batch and make it ready for physical export. One way is to use option 8=Export from the Work with Export Batches list described below. The other way is to use option 2 from the Data Export/Import Utilities Menu, which is simply a prompt of the LSAM command LSAEXPDTA (Export a data set), also described below.
Option 8 = Initiate Data Export Batch
Option 8=Export appears in the list of master records for all Agent automation features that are supported by the Data Export/Import function.
EXIEX1R1 - Initiate Data Export Batch
This display is first presented without the F14 message showing. Type any changes to the process definition, then press <Enter> to request an edit of the process control values. After <Enter> is pressed, the F14 confirmation message will display. If the process control values appear correct, press <F14> to begin or submit the batch export closing process.
Menu Pathways
Main Menu > Events and Utilities menu (#3) > Data Export/Import Utilities menu (# 10) > option 1 > option 8
Fields
- LSAM Env: The OpCon machine name for this LSAM environment
- Vers: The software version number for this LSAM environment
- PTF/DB#: The PTF level of the current LSAM environment is shown first, followed by the PTF database level. The PTF level is for information only, in case of differences in the behavior of certain programs, but it is the database level that must match the target LSAM environment where data will be imported.
- Group ID: The Group label that is assigned to each batch. Group labels are controlled by the LSAM software and they cannot be changed because each batch is assigned to only one type of data records, and records from different Group IDs cannot be mixed within a single batch of export data.
- Batch ID: The user-assigned name that helps to identify the data in a batch. This field is both a key field used to identify a batch and a description field.
- Export save file name: The name of the temporary library where cloned copies of LSAM master files are used to store exported data and export control information. The save file that will be used to transport export data to another LSAM environment uses the same name as the automatically assigned library name. The numeric portion of this Library/SAVF name is derived from the Export/Import Configuration data control field.
- Library to store SAVF: The name of the library where the export batch save file will be, or is stored after the batch is closed and fully exported. The default name for this library is set in the Export/Import Options Configuration.
- Print posting report?: 0=No, 1=Yes. During the posting process a printable report is generated. This is recommended because it not only documents any errors, but it provides a control that can be used to monitor and verify the import process later on. Note that a similar, preliminary report can be generated from this screen using function key F9, but the F9 report only lists the data that is in the batch and it cannot report on export errors.
- Delete export library?:
- 0=No, 1=Yes (default). This option tells the Export program to delete the temporary export library after the export has completed normally. The export save file will be deleted automatically by the Agent using its periodic maintenance server job, but the temporary library must be managed by the export process itself. Change the default to 0=No only if it is necessary to retain the temporary library for diagnostic purposes. Otherwise, there is no value in keeping this library, and it could be restored manually from the export save file if it is needed again.
- Submit job to batch:
- 0=No: The export close-out process is run as part of this interactive job.
- 1=Yes: The export close-out process is submitted to a batch job using the following fields to define how and where the job will run.
- Job description: The job description used to define the optional batch job for the export process. The default value comes from the Export/Import Options Configuration.
- Job description library: The library location of the job description.
- Job queue:
- *JOBD = use the job queue specified in the job description.
- Queue name = use a specific job queue to route the batch job request.
- The default value for this field comes from the Export/Import options configuration.
- Job queue libr: The library location of the job queue; not used if *JOBD is specified for the Job Queue name.
Functions
- F3=Exit: Quits the Initiate Data Export function and returns to the LSAM sub-menu, or to the program that called the Work with Export Batches function.
- F9=Print: Generates a report spool file, listing the contents of the export batch.
- F12=Cancel: Quits the Initiate Data Export function and returns to the list display, with any unexecuted options still showing.
- F14=Confirm: Pressing <F14> when it is allowed will start or submit the actual process to close out an export batch and produce the IBM i save file that can be moved to another LSAM environment for importing.
Menu Option 2 = Export a data set (LSAEXPDTA)
The LSAM command LSAEXPDTA could be used, for example, by a job on an OpCon schedule to complete the process of preparing the IBM i save file that is used to transport exported data to another LSAM environment. Following this OpCon job, it would be possible to include two other jobs on the same OpCon schedule that would (a) perform a file transfer operation and then (b) use a corresponding LSAM command to complete the data import process in the target LSAM environment (documented below).
Selecting option 2 from the menu produces the same display as if the command LSAEXPDTA were typed on a command entry line and function key <F4> were pressed to prompt the command. This command may be less convenient, however, than using the Work with Export Batches option 8=Export because the Group ID and Batch ID must be known in advance and typed into the following command prompt screen, or included as keyword values when the command is entered into the main Run command line of an OpCon job for IBM i. Menu option 2 does not support automatically submitting the export closeout process to batch. To do this outside of the Work with Export Batches list function, the IBM i command SBMJOB must be used, specifying the command LSAEXPDTA and its parameters for the CMD() parameter of the SBMJOB command.
Prompted LSAM Command LSAEXPDTA - Format 1
Export LSAM data batch (LSAEXPDTA)
Type choices, press Enter.
Data export group ID . . . . . . OPRRPY Prompt for list
Data export batch ID . . . . . . _____________________________
Export batch save file . . . . . *BATCH Existing batch save file
Batch save file location . . . . *DEFAULT Library location of save file
Print export batch report? . . . 0 0=No, 1=Yes
The format of the command prompt screen may be varied by pressing function key <F11>.
Prompted LSAM Command LSAEXPDTA - Format 2 (after pressing F11)
Export LSAM data batch (LSAEXPDTA)
Type choices, press Enter.
Data export group ID . . . . . . GROUP OPRRPY
Data export batch ID . . . . . .
BATCH ____________________
Export batch save file . . . . . SAVFIL *BATCH
Batch save file location . . . . SVFLIB *DEFAULT
Print export batch report? . . . REPORT 0
The same result may be obtained by executing the following command syntax from a job that is supported by the source LSAM environment library list.
LSAEXPDTA GROUP(TRPMSG) BATCH(BATCH0003)
SAVFIL(*BATCH) SVFLIB(*DEFAULT) REPORT(1)
To submit this command to a batch job, use the IBM i command SBMJOB and include the command syntax as shown above in the CMD() parameter of the SBMJOB command. This same command syntax can be entered into the main Run command line of an IBM i job in an OpCon schedule.
Menu Pathways
- Main Menu > Events and Utilities menu (#3) > Data Export/Import Utilities menu (# 10) > option 1 > option 8
- Main Menu > Events and Utilities menu (#3) > Data Export/Import Utilities menu (# 2)
- Main Menu > command entry line > type LSAEXPDTA > press <F4>
Fields
| Parameter | Keyword | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Data Export group ID | GROUP | The Group label that is assigned to each batch. Group labels are controlled by the LSAM software and they cannot be changed because each batch is assigned to only one type of data records, and records from different Group IDs cannot be mixed within a single batch of export data. |
| Data Export batch ID | BATCH | The user-assigned name that helps to identify the data in a batch. This field is both a key field used to identify a batch and a description field. |
| Export batch save file | SAVLIB | *BATCH = the recommended special value for this parameter, causes the command processor program to find the save file name in the control record for this export batch. |
| Specific save file name = should be used only for exceptional circumstances, such as development testing. It is required that the export process be accurately represented by the export control record values. | ||
| Batch save file location | SVFLIB | *DEFAULT = the default library specified in the Export/Import Options Configuration is used to store the export save file. |
| Specific library name = may be used for special purposes. Any library is allowed to be used, and the import process provides an option to override the default library location of the save file when it is ready for importing. | ||
| Print export batch report? | REPORT | 0=No, 1=Yes. During the posting process a printable report is generated. This is recommended because it not only documents any errors, but it provides a control that can be used to monitor and verify the import process later on. Note that a similar, preliminary report can be generated from this screen using function key F9, but the F9 report only lists the data that is in the batch and it cannot report on export errors. |
| Delete library if successful? | DLTLIB | 0=No, 1=Yes (default). This option tells the Export program to delete the temporary export library after the export has completed normally. The export save file will be deleted automatically by the Agent using its periodic maintenance server job, but the temporary library must be managed by the export process itself. Change the default to 0=No only if it is necessary to retain the temporary library for diagnostic purposes. Otherwise, there is no value in keeping this library, and it could be restored manually from the export save file if it is needed again. |
Functions
- F3=Exit: Quits the Initiate Data Export function and returns to the LSAM sub-menu, or to the program that called the Work with Export Batches function.
- F9=Print: Generates a report spool file, listing the contents of the export batch.
- F12=Cancel: Quits the Initiate Data Export function and returns to the list display, with any unexecuted options still showing.
- F14=Confirm: Pressing <F14> when it is allowed will start or submit the actual process to close out an export batch and produce the IBM i save file that can be moved to another LSAM environment for importing.
Auditing the Export Process
After an export batch has been closed and stored in an IBM i save file, the export process can be audited to prove that results are correct using two tools. One is the display of the export activity and error log file, and the other is to find and review the export process batch report. (Information on Import batch posting report is provided below, under Auditing the Import Process.)
Menu Option 3 = Display Export Activity/Error Log
EXIL00R1 - Display Data Export Activity Log
Menu Pathways
Main Menu > Events and Utilities menu (#3) > Data Export/Import Utilities menu (# 10) > option 3
Fields
- Subset Group Subset Batch: Shows if a subset rule is in effect, limiting which log records are on display. When the log gets full, it is much easier to audit a batch by using the subset function to limit the list to just one Group or even to a single Batch ID. Use function key <F15> to change the subset rule or to remove a subset filter.
- Nbr of records: Displays the size of the log file as a total number of records in the file. This file will be purged to maintain its size by the LSAM daily maintenance server job, according to the LSAM general rules for operational log files.
- Env: The OpCon machine name for the current LSAM environment.
- Search content: Type a value in this field and press <Enter> to search for a record that has this value anywhere in the record. Sometimes the found value does not appear on the list display and it is necessary to use option 5=Display to view the record details that matched. Use function key <F16> to search for the next matching record after the current search value displays underneath this field.
- Group: The Group ID to which the log entry belongs.
- Batch: The user-assigned Batch ID for each log entry. (Use F11 to toggle the list sort sequence between the entry date and the Group + Batch (+ entry date) order.
- Type: Use option 5=Entry detail to see a description for each entry type. For example, the value "I" indicates a simple Information entry, but a type of "E" marks an error.
- MM-DD-HH.MM: From the complete time stamp of each log entry (which is used to sort the list in Date sequence), the list displays only the MM=Month, DD=Day, HH=Hour and .MM=Minute.
- Entry...: The first several characters of log entry text are displayed. Usually these first characters will suggest the log entry contents.
Options
5=Entry detail: Branches to a screen that shows a formatted display of each log entry.
Functions
- F3=Exit: Quits the Display function and returns to the LSAM sub-menu.
- F5=Refresh: Re-reads the log file and rebuilds the list of entries.
- F9=Print: Prints a report of the current list of log entries. The report will be limited by the current subset rules and governed by the current sort sequence.
- F11=Sort Grp/Sort Dte: Changes the sort order of the list. The current primary sort fields are colored pink and underlined in the column heading labels. This function key is not supported if a subset rule is in effect because the subset rule replaces the option of sorting by Group and Batch, and the limited list is displayed in date sequence within which ever Group is selected. If the Batch ID was not specified in the subset rules, the Batch ID is the primary sort sequence within the single Group ID, and records are sorted in date sequence for each batch.
- F12=Cancel: Quits the Display function and returns to the LSAM sub-menu.
- F16=Search next: After a new content search is started (refer to the Search content field in the table above), this function key continues the search on to the next matching record, looking for the value that shows in pink under the Search content field.
- F17=Top: Repositions the list display to the first record in the list.
- F18=Bottom: Repositions the list display to the last record in the list.
- F24=More keys: Changes the function key legend on line 23 to show other supported function keys. All keys that are allowed to be active still work even if they do not appear in the function key legend line.
Option 5 = Export Activity Log Detail
EXIL00R5 - Export Activity Log Detail
The entry text provides an explanation of the meaning of each log entry. Common log entries include a marker when each export process starts, showing the definition of the export batch, and also a corresponding entry that records the normal completion of the export process. If an entry is logging an error, the detected error message ID appears in red characters.
Menu Pathways
Main Menu > Events and Utilities menu (#3) > Data Export/Import Utilities menu (# 10) > option 3 > option 5
Fields
- Group: The Group label that is assigned to this batch of log entries.
- Batch: The user-assigned name identifies the batch for which the log entry was made.
- If detail, primary key: When a log entry records information about a file record, the primary key of the export details master file is shown here, in case technical research must locate that record.
- Log entry type: Various log Type codes are displayed, along with text that interprets the type value.
- IBM i job writing to the log: The IBM i job identifier for the job that produced the log entry.
- Log entry time stamp: The system date and time when the log entry was added to the log file.
- Message ID (if any): Log entries that record errors will include an IBM i message ID that displays here in red characters.
- Entry text: The log entry information which should be self-explanatory.
Functions
- F3=Exit: Quits the log entry detail display and returns to the LSAM sub-menu.
- F12=Cancel: Quits the entry details display and returns to the list display, with any unexecuted options still showing.
- F20=WRKJOB: If there is any job log report or other report remaining in the system, or if the job is still active, this function key branches to the IBM i WRKJOB menu of options for the IBM i job identifier listed on this display. The user must have authority to use the IBM i command WRKJOB, otherwise this function key will not be allowed.
Work with Import Batches
This function is used to create new import batch controls and also to manage the process of posting the imported data to the LSAM database. In case an import produces undesirable results, it is also possible to use option 9=Rollback to remove the imported data and restore any previous data that was replaced by it.
EXIEX0R1 - Work with Import Batches
Menu Pathways
Main Menu > Events and Utilities menu (#3) > Data Export/Import Utilities menu (# 10) > option 4
Fields
- LSAM Env: The name of the current LSAM environment, to which data is being imported.
- Vers: The version number of the current LSAM environment. (Must match the source LSAM environment from which the data was exported.)
- PTF/DB#: The PTF level of the current LSAM environment is shown first, followed by the PTF database level. The PTF level is for information only, in case of differences in the behavior of certain programs, but it is the database level that must match the target LSAM environment where data will be imported.
- Search: A value entered into this field will be compared to the entire contents of every batch control record until a match is found. Press Enter to start a new search, or use function key <F16> to continue a search to the next record.
- Subset Group: Shows the Group value that limits the current list on display. Press <F13> to change the Group Subset rule.
- Subset Status: Shows the Status value that limits the current list on display. Press <F14> to change the Status Subset rule.
- Last search: Shows the search argument that was last used, where the cursor will be placed next to the first record in the list that contains a matching value. Note that the matching value may not show on this list display, in which case option 5=Display can be used to see the matching value in the control record. This Last search value may also be used to continue a search to the next record if function key <F16> is pressed while a value is displayed in this field.
- Opt: <Tab> to a row in the table and enter an option.
- Group ID: The Group label that is assigned to each batch. Group labels are controlled by the LSAM software and they cannot be changed because each batch is assigned to only one type of data records, and records from different Group IDs cannot be mixed within a single batch of import data.
- Batch ID: The name assigned by the user at export that helps to identify the data that is included in a batch. This field is both a key field used to identify a batch and a description field.
- Sts: The current status of the batch record. Use option 5=Display to see an interpretation of the status code.
- Lib/SAVF: The name of the temporary library where cloned copies of LSAM master files store imported data and import control information. The save file that was used to transport import data from the export LSAM environment uses the same name as the automatically assigned library name. The numeric portion of this Lib/SAVF name is derived from the import/Import Configuration data control field.
- Src System: Source system: The internal identifier of the IBM i partition from which the data is being imported.
- Src LSAM: Source LSAM: The OpCon machine name for the export LSAM environment.
Options
- 2=Chg: This Change option is shown for future use, perhaps to support the process of resetting a batch status during recovery from an import or rollback error. However, no changes to the control records are supported at this time.
- 4=Dlt: To delete an entire import batch, including the control and detail records as well as any existing library and/or save file, type 4 next to the batch record and press <Enter> to proceed to the Delete import Batches screen where the delete action will be confirmed (for all selected records at once).
- 5=Dsp: To view the complete batch control record, type 5 next to the batch record and press <Enter> to proceed to the Display Data import Control screen.
- 7=Details: To view a list of all the LSAM master file records that belong to an import batch, type a 7 next to the batch record and press <Enter> to proceed to the Work with Import Batch Details list display.
- 8=Import: Type option 8 next to any import batch that shows a status of 'I' and press <Enter> to initiate the process of posting the data to the LSAM database. (Refer to Import Batch Posting, below.)
- 9=Rollback: Batches showing a status of 'D' are eligible for Rollback, in case the imported data produced undesirable results. Type a 9 next to the control record and press <Enter> to initiate the rollback process.
Functions
- F3=Exit: Quits the list and returns to the menu.
- F5=Refresh: Reads the import control file again and reloads the list display.
- F6=Add: Proceeds to the List Import Save Files display where new import Control data can be selected for addition to the local LSAM control file. (This function is documented below, under Import Batch Posting.)
- F9=Print: Generates a printable report of all the records currently on display, subject to the current subset restrictions.
- F12=Cancel: Quits the list and returns to the menu, without completing any options that have not already been executed.
- F13=Subset GRP: Causes a window to be displayed where the subset rule for the Group value may be changed.
- F15=Subset STS: Causes a window to be displayed where the subset rule for the Status value may be changed.
- F17=Top: Positions the list display to the first record that qualifies to appear in the current list of control records.
- F16=Search next: Starts, or continues a search for the value that was typed in the Search argument field at the top, right of the display. When used to continue a search, the argument value used appears in the "Last search" field at the top, right of the display, and the display will be positioned with the cursor on the Opt field next to the record that matches the search argument.
- F18=Bottom: Positions the list display to the last record that qualifies to appear in the current list of control records.
- F24=More keys: Shows other function keys that may be used.
Work with Import Batches - Windows
Subset by Group Window
Subset Import Control Records by Group
EXIIM0W1
Subset by Group
Select subset: 9
1. OPRRPY
A. OPRRPYCAPT
2. TRPMSG
B. TRPMSGCAPT
3. SCANSPLF
4. CAPJOB
5. TRKJOB
6. RSTMOD
7. DYNVAR
8. MLTJOB
9. Show all
F12=Cancel
Fields
- Select subset: Type a number from the list below and press <Enter> to change the subset rule for the list of import Batch control records.
- Group values: The list of LSAM master record groups supported includes:
- OPRRPY = Operator Reply scripts, steps and related files
- OPRRPYCAPT = Operator Reply screen capture applications and rules
- TRPMSG = Message Management Parameter records and related files
- TRPMSGCAPT = Message cata capture applications and rules
- SCANSPLF = Scan Spool File rules and related records
- CAPJOB = Captured Job definitions and related files
- TRKJOB = Job Tracking and Queuing definitions and related files
- RSTMOD = Restricted Mode script records
- DYNVAR = LSAM Dynamic Variable table records (these will also appear as a related file to most of the other Groups)Show all = remove Group ID filtering of the control records list
- MLTJOB = Multi-Step Job Scripts
Functions
F12=Cancel: Quits the prompt window and returns to the list display without changing the current subset rule.
Subset by Status Window
Subset Import Control Records by Status
EXIIM0W2
Subset by Status
Select subset: 9
1. I Ready for import
2. U Selected for import
3. F Failed import update
4. C Corrected IMP errors
5. D Done with import
6. R Rolled back
7. Q Rollback failed
8. All active
9. Show all
F12=Cancel
Fields
- Select subset: Type a number from the list below and press <Enter> to change the subset rule for the list of import Batch control records.
Functions
F12=Cancel: Quits the prompt window and returns to the list display without changing the current subset rule.
Option 4 = Delete Import Batches
EXIEX0R4 - Delete Import Batches
Menu Pathways
Main Menu > Events and Utilities menu (#3) > Data Export/Import Utilities menu (# 10) > option 1 > option 4
Fields
- All fields: Refer to Work with list display, above.
Functions
- F3=Exit: Quits the Delete function and return to the LSAM sub-menu.
- F12=Cancel: Quits the Delete function and returns to the list display, with any options "4" still showing.
- F14=Confirm: Starts the delete process that actually updates the LSAM files and removes one or more batch save files and temporary batch assembly libraries.
Option 5 = Display Import Batch Control Record
EXIIM0R5 - Display Data Import Control
Menu Pathways
Main Menu > Events and Utilities menu (#3) > Data Export/Import Utilities menu (# 10) > option 4 > option 5
Fields
- LSAM Env: The name of the current, local LSAM environment = OpCon machine name.
- Group ID: The Group label that was assigned to this batch.
- Batch ID: The user-assigned name that helps to identify the data in a batch.
- Status: The current status of the batch record. Possible values for import batches are listed on the right side of this display
- Import SAVF = saved LIB: The name of the temporary library where cloned copies of LSAM master files are used to store imported data and import control information. The save file that was used to transport import data to this LSAM environment uses the same name as the automatically assigned library name. The numeric portion of this Library/SAVF name is derived from the import/Import Configuration data control field.
- Location of import SAVF: The name of the library where the import batch save file was found. The default name for this library is set in the import/Import Options Configuration.
- Source partition: The system ID of the IBM i partition from which the LSAM data was imported.
- Source LSAM environment: The OpCon machine name of the LSAM environment from which data was imported.
- Source LSAM version: The LSAM software version number of the imported data. This had to match the version number of this LSAM where the data was imported.
- Source LSAM PTF/DB level: The PTF level of the current LSAM environment is shown first, followed by the PTF database level. The PTF level is for information only, in case of differences in the behavior of certain programs, but it is the database level that must match the target LSAM environment where data will be imported.
- Target partition: The system ID of this IBM i partition to which data was imported.
- Target LSAM environment: The OpCon machine name of this LSAM environment where the data was imported.
- Import pre-post backup: The name of the temporary library and save file that are used to backup any data that was/will be replaced when the batch is imported. (This value is updated when the batch is imported, if any previous data is replaced.) The backup save file supports the Rollback option.
- Last update time stamp: The system date and time that any activity was performed on this batch of data. After the status reaches Z = import completed, or E = import error, this time stamp is used to calculate the purge date by the LSAM daily file maintenance server program.
- Last update user ID: The user ID of the job that performed the last activity on this batch.
- Last update IBM i job: The identifier of the IBM i job that performed the last activity on this batch.
Functions
- F3=Exit: Quits the Display function and returns to the LSAM sub-menu, or to the program that called the Work with import Batches function.
- F7=Details: Branches to a display listing the key fields of all files and records included in the data batch. This is the same list display as shows for the option 7=Details from the Import Batch list display.
- F12=Cancel: Quits the Display function and returns to the list display, with any unexecuted options still showing.
Option 7 = Work with Import Batch Details
EXIIM0R3 - Work with Import Batch Details
Menu Pathways
- Main Menu > Events and Utilities menu (#3) > Data import/Import Utilities menu (# 10) > option 4 > option 7
- Main Menu > Events and Utilities menu (#3) > Data import/Import Utilities menu (# 10) > option 4 > option 5 > F7
Fields
- LSAM Env: The OpCon machine name for this LSAM environment
- V: The software version number for this LSAM environment
- P: The software PTF (patch) level for this LSAM environment
- Group: The Group label that was assigned to this batch.
- Batch: The user-assigned name that helps to identify the data in a batch. This field is both a key field used to identify a batch and a description field.
- Search content: Type a value in this field and press <Enter> to search for a record that has this value anywhere in the record. Sometimes the found value does not appear on the list display and it is necessary to use option 5=Display to view the record details that matched. Use function key <F16> to search for the next matching record after the current search value displays underneath this field.
- File Name: The name of the LSAM database file from which a record has been imported. (Refer to the table of file and field values above for descriptions.)
- Sts: The status of the detail record. (The detail record status is only for support research purposes. Refer to the import control record for the important status of the batch.)
- Key field content...(partial): The values of the key fields are shown as a string of characters. Use option 5=Display to see the individual key fields separated and labeled.
Options
5=Display: Branches to a screen that shows a formatted display of each import detail record. This screen formats and labels the key fields according to each different file. (Refer to the Export Batch Details display for an example of this display format.)
Functions
- F3=Exit: Quits the Work with function and returns to the LSAM sub-menu.
- F5=Refresh: Re-reads the import details file and rebuilds the list of details.
- F9=Prt: Prints a report of this list of detail records.
- F12=Cancel: Quits the Work with function and returns to the list of import control records, with any unexecuted options still showing.
- F16=Search next: After a new content search is started (refer to the Search content field in the table above), this function key continues the search on to the next matching record, looking for the value that shows in pink under the Search content field.
- F17=Top: Repositions the list display to the first record in the list.
- F18=Bottom: Repositions the list display to the last record in the list.
Import Batch Posting
The import process starts with the List Import Save Files function, documented above, which was initiated by pressing F6=Add from the Work with Import Batches list function. From the list of unposted save files found, one is selected by typing option 1 next to the name of that save file. This begins the first phase of import processing, during which the batch control data is extracted from the save file and inserted into the local LSAM Import control files.
After an import batch save file has been registered in the control files of the target LSAM environment, the second phase of posting the imported data to the LSAM database is initiated by typing option 8 next to an unposted batch in the Work with Import Batches list.
It is important to find and review the posting report that is generated during the update processing phase. As documented near the beginning of this topic, it is important to verify the contents of certain record types, looking for values that might need to be changed when data has been inserted into this different LSAM environment. Details supporting this step, and the import activity/error log, are documented below.
In case the import process produces undesirable results, it is usually possible to remove the imported data and restore the LSAM database to its previous state by using option 9=Rollback from the Work with Import Batches list display.
It is possible to automate the data import process, for example by configuring IBM i jobs in an OpCon schedule, using the LSAM command LSAGETIMP, as documented below. Combined with the LSAM command LSAEXPDTA, plus an intermediate file transfer step, the whole process of exporting and importing data could be automated, that is, after records are manually selected from master files in the source LSAM environment.
SMA may choose to utilize the data Export/Import tools for the purpose of offering pre-configured data that could be inserted into an LSAM database in order to facilitate the process of configuring the LSAM to automate certain third-party applications. SMA will notify clients about the availability of pre-configured data during the OpCon product installation process.
F6 = List Import Save Files (Add Data Import Control)
EXIIM0R7 - List Import Save Files @ SMALOG
Menu Pathways
Main Menu > Events and Utilities menu (#3) > Data Export/Import Utilities menu (# 10) > option 4 > F6=Add
Options
1=Select: Type a 1 next to any save file that shows a blank Sts field, then press <Enter> to import the control information for that import batch.
Fields
- Heading fields: Refer to list display, above.
- SAVF Name: The name of the save file that was discovered in the library named in the screen title.
- Sts: The status of an import batch would normally be blank when the save file has not yet been imported, but if a save file appears in this list (as when the subset rule has changed) and the same save file was already registered in the local LSAM import control file, then a status value will appear in this column. Use option 5=Display to see the interpretation of the status codes.
- Description: The description of the save file is taken from the *FILE object that was found in the named library.
- Subset: The current list subset rule that is in effect is shown. Use function key F11 to see all save files, including ones that have already been imported into the local LSAM import control file.
Functions
- F3=Exit: Quits the Add function and returns either to the LSAM sub-menu, or to the list display of the LSAM maintenance function where option 8=import had been entered.
- F4=Prompt: When the cursor is positioned in the Group ID field, <F4> causes a window of supported Group ID values to appear from which a value may be selected and returned to this field. (Refer to the window for subsetting by Group ID for a representation of the prompting window that will appear.)
- F12=Cancel: Quits the Add function and returns to the list display.
Option 1 = Select Save File for Import (Add Import Batch)
EXIIM0R2 - Add Import Batch
This display may be presented without the warning message at the bottom, without the instruction text in the middle and without the Replace option field; these only appear when an import save file is being processed within the same IBM i partition where the export LSAM environment exists. When the warnings appear, the most efficient response to the Replace option would be A because the existing temporary library that was prepared by the export process can now be used for the import process.
Type any changes to the process definition, then press <Enter> to complete the process of adding the batch control data to the local LSAM database.
Menu Pathways
Main Menu > Events and Utilities menu (#3) > Data import/Import Utilities menu (# 10) > option 4 > F6 > option 1
Fields
- LSAM Env: The OpCon machine name for this LSAM environment.
- Vers: The software version number for this LSAM environment.
- PTF/DB#: The PTF level of the current LSAM environment is shown first, followed by the PTF database level. The PTF level is for information only, in case of differences in the behavior of certain programs, but it is the database level that must match the target LSAM environment where data will be imported.
- Import save file name: The save file that contains the data to import.
- Save file library: The name of the library where the import batch save is stored. The default name for this library is set in the import/Import Options Configuration. The name appearing here is based on whatever liibrary was searched in the previous display.
- Group ID: The Group label that is assigned to the batch in the selected save file.
- Batch ID: The user-assigned name that helps to identify the data in the batch. This field is both a key field used to identify a batch and a description field.
- Source system: The name of the IBM i partition from which the import save file was transferred.
- Source LSAM: The OpCon machine name of the LSAM environment from which the import save file was exported.
- Import restore library: Normally the same as the save file itself, this is the name of the temporary library that will be restored from the save file in order to access the import data that it contains.
- Replace import library?: This option only appears when the system determines that the import restore library already exists in this IBM i partition. This typically happens when the target LSAM environment exists within the same IBM i partition as the source LSAM environment. Choose one of the following replace options:
- C=cancel: Do not process this import save file or batch; quit the function.
- R=replace: Use the contents of the save file to replace the library.
- A=accept: Use the existing temporary library and do not perform any extra work.
Functions
- F3=Exit: Quits the Add Import Batch function and returns to the LSAM sub-menu.
- F5=Refresh: Resets the screen to its starting values.
- F12=Cancel: Quits the Add Import Batch function and returns to the list display, with any unexecuted options still showing.
When the <Enter> key is pressed, the system completes any necessary restore operation to extract the temporary library from the save file, then it copies the batch control information from the temporary library to the target LSAM database. After the control data is registered, the screen displays the following confirmation.
EXIIM0R2 - Add Import Batch
The confirmation display says to press the <Enter> key to return to the List Import Save Files display. From there, additional save files could be selected for registration. To continue the process of posting the previously registered import batch, press <F12> to return to the Work with Import Batches list display. The newly registered import batch should show a status code of I (capital i, ready for Import).
The second phase of importing data begins by typing option 8 next to the newly registered import batch. Press <Enter> to start the data posting process and the following display will appear.
Option 8 = Post Imported Data (Initiate Data Import Batch)
EXIIM1R1 - Initiate Data Import Batch
The display will show a warning message and the RSTLIB option if the import batch temporary library already exists. This appears to be the same override that was required in the previous steps, however, the previous steps were processing only the import control information, whereas this step handles the LSAM database content. Since the stepscould be performed at different times, the request to acknowledge the existing temporary library must be presented again.
The confirmation message in the middle of the screen, and the function key legend entry for <F14> only appear after the <Enter> key is pressed first to submit the import options for editing.
Menu Pathways
Main Menu > Events and Utilities menu (#3) > Data import/Import Utilities menu (# 10) > option 4 > option 8
Fields
- Heading fields: Refer to previous displays for documentation of the same fields. Only fields unique to this display are listed in this table.
- RSTLIB (1) or Skip (0)?: If the SAVF restore-to library already exists on the system, this processing option is presented.
- 1 = Use the IBM i RSTLIB command to replace the library from the contents of the save file.
- 0 = Skip the RSTLIB step and accept the existing library. (This is the most efficient option to use when processing an import within the same IBM i partition where the export LSAM environment exists.)
- Print posting report?:
- 0=No.
- 1=Yes. Always use option 1 in order to obtain the posting report. It is necessary to review the posting report, not only for potential errors, but also to identify any files that might contain data requiring a manual update to adapt the data to the current LSAM environment.
- Delete import library?: 0=No, 1=Yes (default). This option tells the Import program to delete the temporary import library after the import has completed normally. The import save file will be deleted automatically by the Agent using its periodic maintenance server job, but the temporary library must be managed by the import process itself. Change the default to 0=No only if it is necessary to retain the temporary library for diagnostic purposes. Otherwise, there is no value in keeping this library, and it could be restored manually from the import save file if it is needed again.
- Submit job to batch?:
- 0=No.
- 1=Yes. When this option is specified, the following fields may be used to override the default values for the job description and job queue.
- Job description: The IBM i job description that governs the attributes of the batch job that will be submitted.
- Job description library: The name of the IBM i library where the job description is located.
- Job queue:
- *JOBD = use the job queue named in the job description.
- Queue name = use a different job queue to route the batch job into an IBM i subsystem.
- Job queue library: The name of the IBM i library where the job queue is located.
Functions
- F3=Exit: Quits the Initiate Data Import function and returns to the LSAM sub-menu.
- F9=Print: Generates a report spool file, listing the contents of the import batch.
- F12=Cancel: Quits the Initiate Data import function and returns to the list display, with any unexecuted options still showing.
- F14=Confirm: Pressing <F14> when it is allowed will start or submit the actual process to update the LSAM database with the import batch data.
Automating the Import Process
The LSAM menu functions support partial automation of the data import process. It is also possible to fully automate both the export process and the import process, except that selecting records for export is currently supported only by manual selection of records to export from each of the LSAM master file maintenance functions.
A method for nearly complete automation of the whole process is described below, using the LSAM command LSAIMPGET. This method might be recommended by SMA if it chooses to offer to clients sets of pre-configured LSAM master file data that would help a client more quickly automate certain third-party software applications.
Partial automation of the second phase of the Import process is supported by the LSAM command LSAIMPDTA. The Export/Import menu option 5 provides prompted access to the command LSAIMPDTA, where the menu option produces the same result as if the command were typed in a command entry line and then the function key <F4> were pressed to prompt the command.
SMA has published a detailed example with instructions for automating the LSAM Data Export/Import process. SMA recommends learning about how Export/Import works, here, and then consider implementing the automated solution. This solution is posted in the SMA Innovations Lab, at the SMA GitHub repository:
https://github.com/smatechnologies/ibmi-export-import/blob/master/UserGuide-Automate-Exp-Imp.md
Automated Export/Import would be especially helpful for service bureaus who operate many IBM i partitions. But it is certainly also useful for sites who maintain a separate IBM i LSAM Test environment, where automation solutions can be exported/imported to the Production LSAM environment.
Menu Option 5 = Import a data set (LSAIMPDTA)
Selecting option 5 from the menu produces the same display as if the command LSAIMPDTA were typed on a command entry line and function key <F4> were pressed to prompt the command. Both the menu option and this command may be less convenient, however, than using the Work with Import Batches option 8=Import because the command parameters must be known in advance and typed into the following command prompt screen, or included as keyword values when the command is entered into the main Run command line of an OpCon job for IBM i. Menu option 5 does not support automatically submitting the import posting process to batch. To do this outside of the Work with Import Batches list function, the IBM i command SBMJOB must be used, specifying the command LSAIMPDTA and its parameters for the CMD() parameter of the SBMJOB command.
Prompted LSAM Command LSAIMPDTA - Format 1
Import LSAM data batch (LSAIMPDTA)
Type choices, press Enter.
Data Import group ID . . . . . . PRRPY Prompt for list
Data Import batch ID . . . . . . ____________________
Import library name . . . . . . *DEFAULT Usually same as save file
Do RSTLIB? (No if same SYS) . . 1 0=No, 1=Yes
Print import batch report? . . . 0 0=No, 1=Yes
The format of the command prompt screen may be varied by pressing function key <F11>.
Prompted LSAM Command LSAIMPDTA - Format 2 (after pressing F11)
Import LSAM data batch (LSAIMPDTA)
Type choices, press Enter.
Data Import group ID . . . . . .
GROUP OPRRPY
Data Import batch ID . . . . . .
BATCH _____________________
Import library name . . . . . . IMPLIB *DEFAULT
Do RSTLIB? (No if same SYS) . . RSTLIB 1
Print import batch report? . . . REPORT 0
The same result may be obtained by executing the following command syntax from a job that is supported by the source LSAM environment library list. This example demonstrates different parameter values:
LSAIMPDTA GROUP(TRPMSG) BATCH(BATCH001) IMPLIB(*DEFAULT) RSTLIB(0) REPORT(1)
To submit this command to a batch job, use the IBM i command SBMJOB and include the command syntax as shown in the CMD() parameter of the SBMJOB command. This same command syntax can be entered into the main Run command line of an IBM i job in an OpCon schedule.
Menu Pathways
- Main Menu > Events and Utilities menu (#3) > Data Export/Import Utilities menu (# 10) > option 4 > option 8
- Main Menu > Events and Utilities menu (#3) > Data Export/Import Utilities menu (# 6)
- Main Menu > command entry line > type LSAIMPDTA > press <F4>
Fields
| Parameter | Keyword | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Data Import group ID | GROUP | The Group label that was assigned to the batch. |
| Data Import batch ID | BATCH | The user-assigned Batch name that was assigned to the batch. |
| Export batch save file | IMPLIB | *BATCH = the recommended special value for this parameter, causes the command processor program to find the save file name in the control record for this export batch. |
| Specific save file name = should be used only for exceptional circumstances, such as development testing. It is required that the export process be accurately represented by the export control record values. | ||
| Batch save file location | RSTLIB | *DEFAULT = the default library specified in the Export/Import Options Configuration is used to store the export save file. |
| Specific library name = may be used for special purposes. Any library is allowed to be used, and the import process provides an option to override the default library location of the save file when it is ready for importing. | ||
| Print export batch report? | REPORT | 0=No, 1=Yes. During the posting process a printable report is generated. This is recommended because it not only documents any errors, but it provides a control that can be used to monitor and verify the import process later on. |
| Delete library if successful? | DLTLIB | 0=No, 1=Yes (default). This option tells the Import program to delete the temporary import library after the import has completed normally. The import save file will be deleted automatically by the Agent using its periodic maintenance server job, but the temporary library must be managed by the import process itself. Change the default to 0=No only if it is necessary to retain the temporary library for diagnostic purposes. Otherwise, there is no value in keeping this library, and it could be restored manually from the import save file if it is needed again. |
Functions
- F3=Exit: Quits the Initiate Data Export function and returns to the LSAM sub-menu, or to the program that called the Work with Export Batches function.
- F9=Print: Generates a report spool file, listing the contents of the export batch.
- F12=Cancel: Quits the Initiate Data Export function and returns to the list display, with any unexecuted options still showing.
- F14=Confirm: Pressing <F14> when it is allowed will start or submit the actual process to close out an export batch and produce the IBM i save file that can be moved to another LSAM environment for importing.
Automated Import Process (LSAIMPGET)
The LSAM command LSAIMPGET (Get LSAM data Import SAVFs) consolidates both phase one and phase two of the Import process. When there are not exceptional circumstances, this command is able to find one or more import batch save files and then execute the whole process of restoring the temporary data libraries and posting the data to the target LSAM database. This command can be used instead of the menu functions and commands documented above in this section about the Import process.
The command LSAIMPGET could be used, for example, by a job on an OpCon schedule to complete the process of updating the IBM i LSAM database. This job might be the third task in an OpCon schedule that would (a) execute the LSAEXPDTA command to prepare an export batch save file, (b) perform a file transfer operation and then (c) use this LSAIMPGET command to complete the data import process in the target LSAM environment.
There is no menu support for the command LSAIMPGET. It is included in the LSAM software for special purposes, since the interactive Work with Import Batches typically makes it much simpler to request the posting of an import data batch.
In the following example of the command prompted with F4, notice that the Group and Batch are not required, since they will be obtained automatically from one or more import save files located in the named Import library.
Prompted LSAM Command LSAIMPGET - Format 1
Get LSAM data Import SAVFs (LSAIMPGET)
Type choices, press Enter.
Import save file . . . . . . . . *ALL *ALL = unimported SAVFs
Location of Import SAVF . . . . *DEFAULT Library holding import SAVF
Auto-exec Import update? . . . . 1 0=No, 1=Yes
Print import batch report? . . . 0 0=No, 1=Yes
The format of the command prompt screen may be varied by pressing function key <F11>.
Prompted LSAM Command LSAIMPGET - Format 2 (after pressing F11)
Get LSAM data Import SAVFs (LSAIMPGET)
Type choices, press Enter.
Import save file . . . . . . . . SAVFIL *ALL
Location of Import SAVF . . . . SAVLIB *DEFAULT
Auto-exec Import update? . . . . AUTOPOST 1
Print import batch report? . . . REPORT 0
Despite the default value of the command parameter REPORT being set to 0 = no report, it is strongly recommended that the import posting process always be audited by printing (setting the REPORT keyword value to 1) and then inspecting the batch posting report.
Following is an example of the command syntax, demonstrating how to limit the command to just one import batch instead of allowing it to find and post all previously unposted batches. The value for the SAVLIB keyword could be left at *DEFAULT, since the normal setting for the Export/Import Options Configuration (menu option 7) is to use the SMALOG library for export/import save files.
LSAIMPGET SAVFIL(SMAX000001) SAVLIB(SMALOG)
AUTOPOST(1) REPORT(1)
To submit this command to a batch job, use the IBM i command SBMJOB and include the command syntax as shown in the CMD() parameter of the SBMJOB command. This same command syntax can be entered into the main Run command line of an IBM i job in an OpCon schedule.
Fields
| Parameter | Keyword | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Import save file | SAVFIL | - *ALL = find all unposted save files in the library (SAVLIB). |
| - Save File Name = post only this named import save file. | ||
| Location of Import SAVF | SAVLIB | The library to search for the save file(s) named in the SAVFIL parameter. |
| Auto-exec Import update? | AUTOPOST | - 0=No: Perform only phase one of the import process, ending after the import batch control data is added to the target LSAM database. |
| - 1=Yes: Perform both phases of the import process, including through the step of updating the target LSAM database with all the imported data. | ||
| Print export batch report? | REPORT | 0=No, 1=Yes. During the posting process a printable report is generated. This is recommended because it not only documents any errors, but it provides a control that can be used to monitor and verify the import process later on. |
| Delete library if successful? | DLTLIB | 0=No, 1=Yes (default). This option tells the Import program to delete the temporary import library after the import has completed normally. The import save file will be deleted automatically by the Agent using its periodic maintenance server job, but the temporary library must be managed by the import process itself. Change the default to 0=No only if it is necessary to retain the temporary library for diagnostic purposes. Otherwise, there is no value in keeping this library, and it could be restored manually from the import save file if it is needed again. |
Auditing the Import Process
After an import batch has been posted to the LSAM database, the import process should be audited to prove that results are correct using two tools. One is the display of the import activity and error log file, and the other is to find and review the import process batch report.
Menu Option 6 = Display Import Activity/Error Log
EXIL00R1 - Display Data Import Activity Log
Menu Pathways
- Main Menu > Events and Utilities menu (#3) > Data import/Import Utilities menu (# 10) > option 6
- A detailed explanation about the log view is provided above, under the Export Activity Log. Note in the screen for this section how an error message is marked by a Typ value of E and the error message ID is colored red under the Entry... column.
- The Entry detail for the error screen is described below.
Option 5 = Import Activity Log Detail
EXIL00R5 - Import Activity Log Detail
A detailed description of this screen is provided above under the Export Activity Log.
This example shows how an error message will be logged. An attempt is made to retrieve the text of the error message, but more information will be found in the full error message description. If this cannot be found in the job log of the job producing the error (use F20=WRKJOB to find the job log), many of the error messages appearing in this log are described in either the LSAM main message file, SMAMSGF, or in the IBM i system main message file, QCPFMSG. Use the IBM i command DSPMSGD to Refer to the full description of the message. Often a message will include instructions in the secondary message text.
Data Import Batch Report
The posting audit report for an Import batch can be easily located by using the function key <F20> from the Import Activity Log, Entry Detail display.
The following report example demonstrates a completely failed import update process, showing the same error message as appears in the Import Activity Log, Entry Detail.
Data Import Batch Report - Error Example
*...+....1....+....2....+....3....+....4....+....5....+....6....+....7....+....
EXIIMPP10 Data Import Batch Report 00/00/00 15:49:48
PAGE: 1
LSAM Env: SMAGPL3 This Sys: B00B30XX Version: 18.1
Src Env: SMADEFAULT Src Sys: B00B30ZZ PTF/DB#: 018 001
Group: TRPMSG Batch: BATCH001 Import lib: MAX000001
File Name Key field content...(partial)
ERROR> Saved library MAX000001 not equal Import save file name SMAX000001
Total removed records: 0
Total import records : 0
* * * END OF REPORT * * *
Following is an example of a successful import batch update audit report.
Data Import Batch Report - Successful
*...+....1....+....2....+....3....+....4....+....5....+....6....+....7....+....
EXIIMPP10 Data Import Batch Report 00/00/00 15:49:48
PAGE: 1
LSAM Env: SMAGPL3 This Sys: B00B30XX Version: 18.1
Src Env: SMADEFAULT Src Sys: B00B30ZZ PTF/DB#: 018 001
Group: TRPMSG Batch: BATCH001 Import lib: MAX000001
File Name Key field content...(partial)
TRPMSGF00 RECID# MsgQueue MsgQueLib MsgId MsgFile JobName
0000002 JSMITH QUSRSYS CPF9897 *ALL *ALL
TRPMSGF30 AppID SEQ#
CAPTMSG01 010
OPRRPYF50 CaptureRuleId SQ# RS#
CAPTMSG01 010 010
LSAVARF00 TokenName SQ# T
HELPIT1 000 V
LIBLVAR01 000 V
TRPMSGF00 RECID\# MsgQueue MsgQueLib MsgId MsgFile JobName
0000003 JSMITH QUSRSYS CPF9897 *ALL *ALL
Total removed records: 0
Total import records : 6
* * * END OF REPORT * * *
Following is an example of how a successful import batch posting report looks when a second batch of data is imported for the same record keys as appear in the report above. Notice the flags next to lines where data is being replaced in the LSAM database, and also notice the different totals at the bottom of the report. In the following example, at least one new record is added to one of the files (which is why, in theory, the new import was executed). This unique record will be handled differently in the Rollback process, described in the following section of documentation.
Data Import Batch Report - With Data Replacement
*...+....1....+....2....+....3....+....4....+....5....+....6....+....7....+....
EXIIMPP10 Data Import Batch Report 00/00/00 17:02:48
PAGE: 1
LSAM Env: SMAGPL3 This Sys: B00B30XX Version: 18.1
Src Env: SMADEFAULT Src Sys: B00B30ZZ PTF/DB#: 018 001
Group: TRPMSG Batch: BATCH004 Import lib: MAX000004
File Name Key field content...(partial)
TRPMSGF00 RECID# MsgQueue MsgQueLib MsgId MsgFile JobName
* RPL 0000002 JSMITH QUSRSYS CPF9897 *ALL *ALL
TRPMSGF30 AppID SEQ\#
* RMV CAPTMSG01 010
CAPTMSG01 010
CAPTMSG01 020
OPRRPYF50 CaptureRuleId SQ# RS#
* RMV CAPTMSG01 010 010
CAPTMSG01 010 010
LSAVARF00 TokenName SQ\# T
* RPL HELPIT1 000 V
* RPL LIBLVAR01 000 V
Total removed records: 2
Total import records : 6
*RPL = Replaced records copied to backup SAVF before update.
*RMV = Group of records removed before import, copied to SAVF.
SAVF (save file) with backed up records: SMAB000004 in library: SMABAK
* * * END OF REPORT * * *
The example report above illustrates that whenever data is being replaced in the target LSAM database, there are two different methods that might be used, depending on the relationships among data records that comprise a given batch of updates. Also, when either method of data replacement has been used, the report will print a description of the abbreviations that appear to the left of replaced records.
Both types of data replacement are always supported by a backup process. A save file is automatically created in the SMABAK library (a library that is also used by the LSAM for backing up files that are replaced by the SMA File Transfer facility). This backed up data save file supports the Rollback process, documented in the next section. The last text line in the report names the backup save file and the library where it was stored. This same information is recorded in the LSAM Import control record for the batch, so that it will be available for an optional Rollback procedure.
*RPL = Replacing a record is the same as updating a record that already exists. This method is appropriate when each record stands alone and is not part of a group of records.
*RMV = Removing records is required for some files where records must work together as a group. For any one record to be updated, the whole group must first be removed before the new data can be imported (also as a group).
Rollback Process
If a data import produces undesirable results, it is possible to remove the imported data and restore the LSAM database to its prior condition using option 9=Rollback from the Work with Import Batches list display.
The Rollback function should only be used when no other Import process has updated the same records in the LSAM database after the batch selected for rollback. Used out of sequence, the Rollback can corrupt the LSAM database. It is the user's responsibility to be aware of all Import data batches, their contents and the sequence of events. In case the database becomes corrupted, manual maintenance of the LSAM master files is required to fix the problems.
It is also required that the current LSAM database PTF level be equal to the PTF level stored in the Import batch control record, otherwise the Rollback option cannot be used.
No automatic backup is performed during a rollback update, therefore it might be a good idea to backup the SMADTA library before performing this process.
To start the rollback process, begin with the Export/Import menu option 4 - Work with Import Batches. When this list is first displayed, a subset rule is in effect limiting the display to only active batches that have not yet been posted. Press <F15> to change the Status subset rule. Choose either subset rule 5 for "Done with import" or rule 9 for "Show all" in order to find the Import batch that needs to be rolled back.
When the Import batch control record has been identified, type option 9 next to that batch control record and press <Enter> to initiate the Rollback process. The following screen is displayed.
EXIIM2R1 - Initiate Data Import Rollback
Menu Pathways
Main Menu > Events and Utilities menu (#3) > Data import/Import Utilities menu (# 10) > option 4 > option 9
Fields
- Heading fields: Refer to previous displays for documentation of the same fields. Only fields unique to this display are listed in this table.
- Rollback save file name: This is the name of the save file that contains the LSAM database records backups from when the Import batch was posted.
- Rollback SAVF library: The library location of the save file that was created during the Import posting process. This library name is taken from the specific Import batch control record, so normally it should not be changed. However, the field may be updated in case the site has decided to move the database backup save files to another location, or in case the save file had to be restored from an off-system backup medium into a temporary working library.
- Print posting report?:
- 0=No.
- 1=Yes. Always use option 1 in orderto obtain the posting report. It is recommended that the rollback audit report be reviewed to assure the results are expected. This report can also be used as a guide to search for the actual records in the LSAM inquiry functions as an additional means of auditing the results.
- Submit job to batch?:
- 0=No.
- 1=Yes. When this option is specified, the following fields may be used to override the default values for the job description and job queue.
- Job description: The IBM i job description that governs the attributes of the batch job that will be submitted.
- Job description library: The name of the IBM i library where the job description is located.
- Job queue:
- **JOBD8 = use the job queue named in the job description.
- Queue name = use a different job queue to route the batch job into an IBM i subsystem.
- Job queue library: The name of the IBM i library where the job queue is located.
Functions
- F3=Exit: Quits the Rollback function and returns to the LSAM sub-menu.
- F9=Print: Generates a report of the batch details. This report resembles the posting audit report (illustrated below) but it will not show any error messages as might appear during the actual database update.
- F12=Cancel: Quits the Rollback function and returns to the list display, with any unexecuted options still showing.
- F14=Confirm: Starts or submits the actual rollback action.
When the <F14> key is pressed, the system completes any necessary restore operation to extract a temporary library from the save file, then it performs database updates as necessary to restore the LSAM database to its condition as of before the Import batch. If the task submitted to a batch job, a message appears showing the name of the batch job. If the task is completed in the same interactive job, a completion message appears when it is done. After the task is completed, view the spool files for the current job or use the IBM i command WRKJOB to view spool files for the submitted job name that appeared in the submitted job message. Review the posting audit report. An example of a rollback audit report appears below.
Data Import Batch Report - with Data Replacement
*...+....1....+....2....+....3....+....4....+....5....+....6....+....7....+....
EXIIMPP10 Data Import Batch Report 00/00/00 17:02:48
PAGE: 1
LSAM Env: SMAGPL3 This Sys: B00B30C5 Version: 18.1
Rb Svf Lib: SMABAK
Group: TRPMSG Batch: BATCH004 Rbk Svf: SMAB000004
File Name Key field content...(partial)
TRPMSGF00 RECID# MsgQueue MsgQueLib MsgId MsgFile JobName
0000002 JSMITH QUSRSYS CPF9897 *ALL *ALL
TRPMSGF30 AppID SEQ#
* DEL CAPTMSG01 010
* DEL CAPTMSG01 020
CAPTMSG01 010
OPRRPYF50 CaptureRuleId SQ# RS#
* DEL CAPTMSG01 010 010
CAPTMSG01 010 010
LSAVARF00 TokenName SQ# T
HELPIT1 000 V
LIBLVAR01 000 V
Total removed records: 3
Total restore records: 5
* * * END OF REPORT * * *
The example report above illustrates that whenever data is being replaced in the target LSAM database, there are two different methods that might be used, depending on the relationships among data records that comprise a given batch of updates. There is no backup made before this rollback update is performed.
Records that are unmarked were either updated in place, or they were put back into the database (after previously being removed by the Import posting process).
*DEL = Deleting (removing) records is required for some files where records must work together as a group. For any one record to be updated, the whole group must first be deleted before the previous record group can be restored in tact.