LSAM Work Management Authority
This discussion assumes the reader is familiar with the other information provided in the IBM i LSAM documentation and with the principles of IBM i Work Management. The description of work management authority in this section includes a combination of principles of both the IBM i LSAM and the IBM i operating system itself. Some of the other sections of this topic may also prove helpful in understanding this discussion of LSAM work management.
An introduction to the authority assigned to SMANET is provided in the previous section of this topic. This section is focused on the work flow path that is followed as a job request defined in the OpCon job master file is submitted for execution under IBM i. The minimal authorities required in order for the LSAM server programs to successfully manage jobs as user SMANET are listed below.
If a high security environment requires that user SMANET not be allowed to have *ALLOBJ authority, the IBM i LSAM Installation Instructions warn that the site administrator must develop an authority matrix that will enable user SMANET to accomplish its assigned tasks. The following list of authorities required by SMANET and the LSAM Submit Job flow chart below may help to identify and manage the authorities required to successfully submit jobs.
Authorities Required by SMANET
Here is a summary of the minimal authorities required for the user profile SMANET to manage jobs and complete other LSAM server functions. This list of authorities includes information adapted from IBM's IBM i documentation about the SBMJOB command.
- *CHANGE authority to the LSAM environment libraries (default names are: SMAGPL, SMADTA, SMAPTF and SMAPGM) and to their contents. The LSAM software is installed with user SMANET as the owner of the LSAM libraries and all the contents of those libraries. Therefore, *CHANGE authority is assumed.
- *USE authority to IBM i libraries QSYS (the IBM i system library, where PUBLIC normally has USE authority by definition) and QGPL.
- *USE authority to most of the IBM i commands. (Confidential documentation about the IBM i commands used by LSAM software is available to SMA technical support staff.)
- *USE authority to libraries of third-party software, and their contents, that may include objects used for submitting jobs.
- *USE authority to every user profile that will be named in a submitted job.
- *USE authority to the commands specified in the Prerun and Call data entry boxes of the Call Information tab of each IBM i job master record in the OpCon User Interface.
- *USE authority to every job description that will be named in a submitted job.
- *USE authority to every job queue where submitted jobs will be placed.
- *USE authority to every subsystem description that will run submitted jobs.
- *USE and *ADD authority to the message queue specified on the Message queue (MSGQ) parameter of the submitted job (which, for the IBM i LSAM, will be the SMAMSGQ located in the SMADTA (or equivalent) library), and *EXECUTE authority to the library that contains the message queue (which, for the IBM i LSAM, will be the SMADTA library or its equivalent in an alternate LSAM environment).
- *JOBCTL special authority.
- The IBM i LSAM job scheduler server program puts jobs on hold briefly as it performs certain administration tasks, and then it uses the RLSJOB command. It may also need to perform the CHGJOB and CHGACCCDE commands before releasing a submitted job.
- *SPLCTL special authority (or an equivalent authority to the QPJOBLOG spool file and output queue where job logs will be stored).
- Spool control special authority, or the equivalent specific authorities, is required for the LSAM server programs to manage the job log spool files resulting from jobs it submits. This is required to support the OpCon View Job Output (JORS) function.
- Spool control special authority, or the equivalent specific authorities, is required when any job is accompanied by spool file management options that are available on the OpCon User Interface definition of IBM i job master records.
- Refer to IBM documentation about IBM i for more information on the specific authorities that may be used in place of the *SPLCTL special authority, if this special authority must be restricted.
IBM i LSAM Server Submit Jobs
The following flow chart shows how job definition information is communicated to the LSAM server programs. This figure is explained on the following pages.
LSAM Submit Job Flow
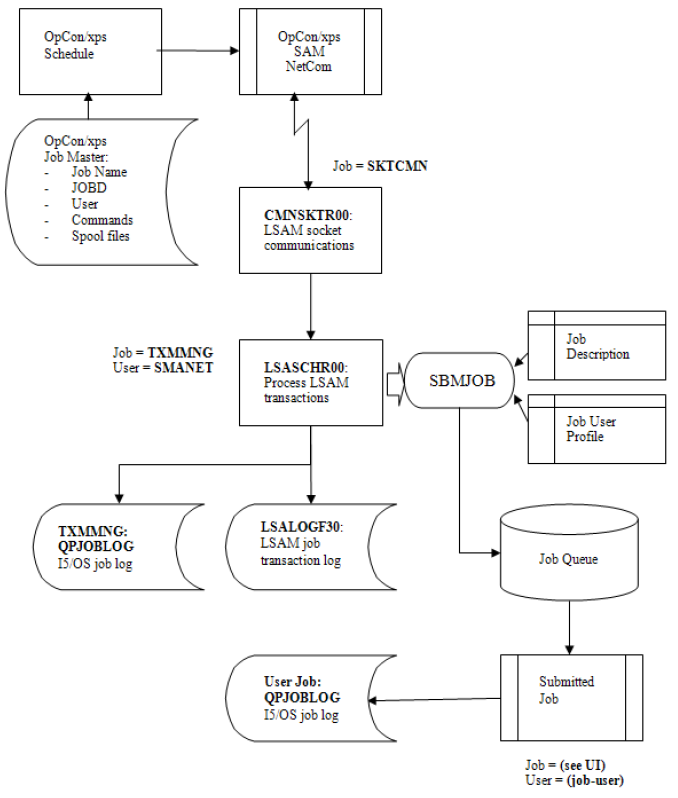
Diagnosis of LSAM Job Submission
If user SMANET does not have *ALLOBJ authority, it is likely that problems could arise in the process used by the LSAM software to submit jobs, until the client site administrator has successfully tested and debugged the object authority matrix used to manage SMANET authorities.
Detailed instructions about various tools and procedures that support diagnosis of job failures is presented in the Guide to Job Failure Diagnosis.
Following is a summary of the most helpful and specific resources that can be used to identify errors that might occur in the LSAM job submission process. This list is based on the flow chart LSAM Submit Job Flow, above.
- The LSAM server jobs should be set to perform verbose job logging. This can be accomplished by changing the LOG parameter of the job description SMADTA/SMALSAJ00. Set the LOG parameter to the values (4 00 *SECLVL). Active server jobs can each be changed while they are active, or the LSAM server subsystem can be ended from the LSAM menu system, and then restarted after the LSAM server job description has been changed.
- The LOG parameter values can be reset for quieter logging after it is clear that the OpCon schedules are all performing normally. Reducing server job logging helps improve performance and also reduces consumption of disk space.
- The job log of the LSAM server job TXMMNG will normally show details about errors that occur as it executes the IBM i SBMJOB command. This job can be quickly found by executing option 3: Check LSAM Subsystem Status, from the LSAM menu 6: LSAM Management Menu. The following display will appear. This example shows option 5 typed next to job TXMMNG. From the IBM i Work with Job menu, use option 10 to view the job log. It may be necessary to press function key F10 to show all job log details, and function key F16 moves the log view quickly to the most recent entries at the bottom of the job log.
Work with Active Jobs Screen
Work with Active Jobs SYSTEMNAME
00/00/00 00:00:00 CDT
CPU %: .0 Elapsed time: 00:00:00 Active jobs: 236
Type options, press Enter.
2=Change 3=Hold 4=End 5=Work with 6=Release 7=Display message
8=Work with spooled files 13=Disconnect ...
Current
Opt Subsystem/Job User Type CPU % Function Status
SMASBSC QSYS SBS .0 DEQW
JORCMN SMANET BCH .0 PGM-JORCMNR00 DEQA
LSAJOR SMANET BCH .0 PGM-LSAJORR00 DEQW
LSAMNG SMANET BCH .0 PGM-DLTLOGR00 DEQW
MSGMNG SMANET BCH .0 PGM-LSARCMR00 DEQA
SKTCMN SMANET BCH .0 PGM-CMNSKTR00 DEQA
TXMMNG SMANET BCH .0 PGM-LSASCHR00 DEQW
Bottom
Parameters or command
===>
F3=Exit F5=Refresh F7=Find F10=Restart statistics
F11=Display elapsed data F12=Cancel F23=More options F24=More keys
- The LSAM TXMMNG job also logs each SBMJOB command and any errors to the LSAM log file LSALOGF30. This log file can be quickly viewed using the LSAM Management Menu 6, option 5: View LSAM logs. From the View LSAM Logs menu, select option 4: Display LSAM submit job log (calls program LSALOGR31 which presents formatted displays of log entry lists and log entry details).
- Sometimes there is helpful information in the IBM i operator message queue (usually QSYSOPR). This message queue must be examined shortly after any problem occurs, so that critical information is not lost from this active message queue. When a critical LSAM error message is found, it is very helpful to SMA Support if the following information is captured and reported:
- Position the cursor over the message and press the Help key (the key sequence ALT + F1 = Help when using the standard keyboard map of the display emulator of Series Access). Print or copy and paste the full message help screen, including subsequent pages of the secondary help text.
- Press function key F9=Display message details to view a screen that often lists the name of the program that issued the message, and it may also identify the line of the program where the message event occurred.
- If an operator must respond to an error message, and there are no other instructions applying to the error, an answer of "D" = dump may produce a helpful formatted program dump report among the printed output of the job that issued the message. Attempt to locate and save the dump report. The first page of the dump report often contains helpful diagnostic information about program errors.
The LSAM software is distributed with program observation turned off, so most LSAM programs will not produce a complete program dump showing program variables. An SMA Support technician may need to offer the client a specially compiled version of a failing program if an error arises that is difficult to diagnose, so that a full formatted program dump may be obtained the next time the error occurs.