Loops
VisualCron supports several loop types to automate repetitive tasks:
Loop Types
For Loop
Executes a task a specific number of times using numeric start and end values (e.g., from 1 to 100).
While Loop
Continues execution as long as a condition is true. Useful for dynamic checks like “while file exists” or “while value < threshold.”
Do While Loop
Similar to While, but guarantees at least one execution before checking the condition.
For Each Loop
Iterates over a list of items—such as rows in a spreadsheet or lines in a string.
Flow / Label / Go To
These allow more advanced control, such as jumping to specific labeled tasks or breaking out of loops based on conditions.
End Loop / Continue Loop
- End Loop stops the loop entirely.
- Continue Loop skips the current iteration and starts the next—ideal for exception handling.
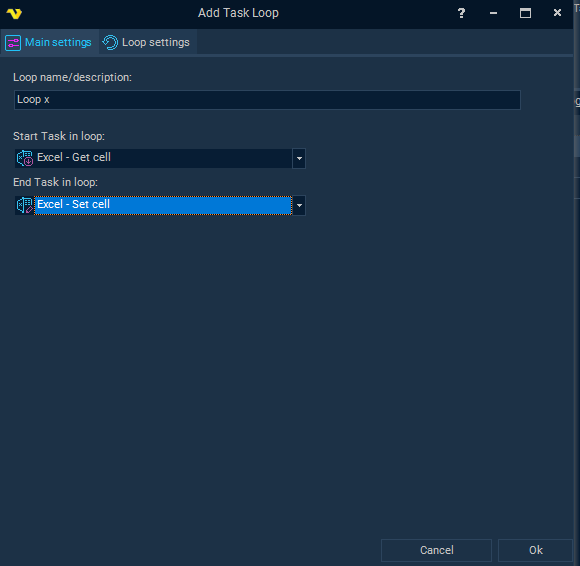
These loop types are configured within the VisualCron Job Task interface, where you define start/end tasks and loop conditions.
Configuring Loops
Defining Loop Boundaries
Set start and end tasks to encapsulate actions within a loop for clear execution boundaries.
Setting Loop Conditions
Loop conditions include numeric ranges, booleans, or list iterations to control loop execution flow.
Using Variables and Expressions
Dynamic loop configuration uses variables and expressions for adaptable and responsive automation workflows.
Loop Settings Interface
The loop settings interface allows selection of loop types and input of relevant parameters easily.
Exception Management
Error Logging
VisualCron logs errors during loop execution, aiding in troubleshooting and improving reliability.
Conditional Failure Handling
Using conditional branches allows skipping problematic data or retrying failed tasks gracefully.
Retry Logic Implementation
Retry logic in loops enables multiple task attempts before exiting, enhancing workflow resilience.
Basic Loop Logic Example
Select to Add a Loop to the Task flow
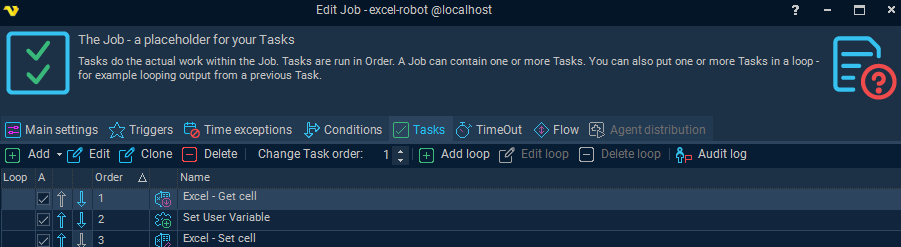
Configure the Loop logic
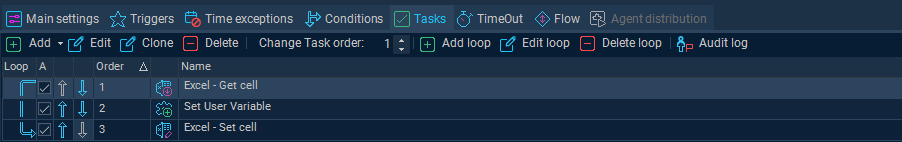
Verify the Loop exists in the Task flow and test with Trigger and Conditions if necessary.
Best Practices
Avoid Infinite Loops
Set clear exit conditions to prevent loops from running endlessly and causing system issues.
Modularize Loop Logic
Break loop logic into modules to improve readability and make maintenance easier.
Monitor Nested Loops
Keep track of performance impact as nested loops can consume significant system resources.
Use Descriptive Naming
Document loop behavior with clear variable names and comments to enhance understanding.